Abstract
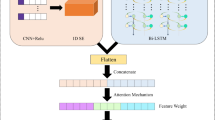
Epileptic seizure is a complex neurological disorder and is difficult to detect. Observing and analyzing the waveform changes of EEG signals is the main way to monitor epilepsy activity. However, due to the complexity and instability of EEG signals, the effectiveness of identifying epileptic region by previous methods using EEG signals is not very satisfactory. On the one hand, these methods use the initial time series directly, which reflect limited epilepsy related features; On the other hand, they do not fully consider the spatiotemporal dependence of EEG signals. This study proposes a novel epileptic seizure classification method using EEG based on a hybrid time-frequency attention deep network, namely, a time-frequency attention CNN-BiLSTM network (TFACBNet). TFACBNet firstly uses a time-frequency representation attention module to decompose the input EEG signals to obtain multiscale time-frequency features which provides seizure relevant information within the EEG signals. Then, a hybrid deep network combining convolutional neural network (CNN) and bidirectional LSTM (BiLSTM) architecture extracts spatiotemporal dependencies of EEG signals. Experimental studies have been performed on the benchmark database of the Bonn EEG dataset, achieving 98.84% accuracy on the three-category classification task and 92.35% accuracy on the five-category classification task. Our experimental results prove that the proposed TFACBNet achieves a state-of-the-art classification effect on epilepsy EEG signals.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisher, R.S., et al.: Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: definitions proposed by the international league against epilepsy (ILAE) and the international bureau for epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia 46(4), 470–472 (2005)
MacAllister, W.S., Schaffer, S.G.: Neuropsychological deficits in childhood epilepsy syndromes. Neuropsychol. Rev. 17, 427–444 (2007)
Acharya, U.R., Fujita, H., Sudarshan, V.K., Bhat, S., Koh, J.E.: Application of entropies for automated diagnosis of epilepsy using EEG signals: a review. Knowl. Based Syst. 88, 85–96 (2015)
Zhou, M., et al.: Epileptic seizure detection based on EEG signals and CNN. Front. Neuroinform. 12, 95 (2018)
Sahu, R., Dash, S.R., Cacha, L.A., Poznanski, R.R., Parida, S.: Epileptic seizure detection: a comparative study between deep and traditional machine learning techniques. J. Integr. Neurosci. 19(1), 1–9 (2020)
Vijayalakshmi, K., Abhishek, A.M.: Spike detection in epileptic patients EEG data using template matching technique. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2(6), 5–8 (2010)
Wulandari, D.P., Suprapto, Y.K., Juniani, A.I., Elyantono, T.F., Purnami, S.W., Islamiyah, W.R.: Visualization of epilepsy patient’s brain condition based on spectral analysis of EEG signals using topographic mapping. In: 2018 International Conference on Computer Engineering, Network and Intelligent Multimedia (CENIM), pp. 7–13. IEEE (2018)
Tang, L., Zhao, M., Wu, X.: Accurate classification of epilepsy seizure types using wavelet packet decomposition and local detrended fluctuation analysis. Electron. Lett. 56(17), 861–863 (2020)
Elakkiya, R.: Machine learning based intelligent automated neonatal epileptic seizure detection. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 40(5), 8847–8855 (2021)
Antoniades, A., et al.: Detection of interictal discharges with convolutional neural networks using discrete ordered multichannel intracranial EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 25(12), 2285–2294 (2017)
Shoji, T., Yoshida, N., Tanaka, T.: Automated detection of abnormalities from an EEG recording of epilepsy patients with a compact convolutional neural network. Biomed. Sig. Process. Control 70, 103013 (2021)
Tuncer, E., Bolat, E.D.: Classification of epileptic seizures from electroencephalogram (EEG) data using bidirectional short-term memory (bi-LSTM) network architecture. Biomed. Sig. Process. Control 73, 103462 (2022)
Beeraka, S.M., Kumar, A., Sameer, M., Ghosh, S., Gupta, B.: Accuracy enhancement of epileptic seizure detection: a deep learning approach with hardware realization of STFT. Circ. Syst. Sig. Process. 41, 461–484 (2022)
Xu, G., Ren, T., Chen, Y., Che, W.: A one-dimensional CNN-LSTM model for epileptic seizure recognition using EEG signal analysis. Front. Neurosci. 14, 578126 (2020)
Qiu, X., Yan, F., Liu, H.: A difference attention ResNet-LSTM network for epileptic seizure detection using EEG signal. Biomed. Sig. Process. Control 83, 104652 (2023)
Craley, J., Johnson, E., Venkataraman, A.: A spatio-temporal model of seizure propagation in focal epilepsy. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(5), 1404–1418 (2019)
Daubechies, I.: Orthonormal bases of compactly supported wavelets. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 41(7), 909–996 (1988)
Greff, K., Srivastava, R.K., Koutník, J., Steunebrink, B.R., Schmidhuber, J.: LSTM: a search space odyssey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(10), 2222–2232 (2016)
Andrzejak, R.G., Lehnertz, K., Mormann, F., Rieke, C., David, P., Elger, C.E.: Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys. Rev. E 64(6), 061907 (2001)
Acharya, U.R., Oh, S.L., Hagiwara, Y., Tan, J.H., Adeli, H.: Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 100, 270–278 (2018)
Chen, X., Ji, J., Ji, T., Li, P.: Cost-sensitive deep active learning for epileptic seizure detection. In: Proceedings of the 2018 ACM International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology, and Health Informatics, pp. 226–235 (2018)
Tajmirriahi, M., Amini, Z.: Modeling of seizure and seizure-free EEG signals based on stochastic differential equations. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 150, 111104 (2021)
Ramos-Aguilar, R., Olvera-López, J.A., Olmos-Pineda, I., Sánchez-Urrieta, S.: Feature extraction from EEG spectrograms for epileptic seizure detection. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 133, 202–209 (2020)
Siuly, S., Alcin, O.F., Bajaj, V., Sengur, A., Zhang, Y.: Exploring Hermite transformation in brain signal analysis for the detection of epileptic seizure. IET Sci. Measur. Technol. 13(1), 35–41 (2019)
Deng, Z., Xu, P., Xie, L., Choi, K.S., Wang, S.: Transductive joint-knowledge-transfer TSK FS for recognition of epileptic EEG signals. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 26(8), 1481–1494 (2018)
Acknowledgment
The authors express gratitude to the anonymous referee for his/her helpful suggestions and the partial supports of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62206005/62236002/62206001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
No author associated with this paper has disclosed any potential or pertinent conflicts which may be perceived to have impending conflict with this work.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tian, Y., Tan, C., Wu, Q., Zhou, Y. (2024). EEG Epileptic Seizure Classification Using Hybrid Time-Frequency Attention Deep Network. In: Luo, B., Cheng, L., Wu, ZG., Li, H., Li, C. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1964. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8141-0_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8141-0_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-8140-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-8141-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)