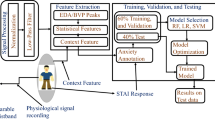
Abstract
This study aims to investigate the influence of object recognition based on intelligent algorithms on staff’s anxiety levels in professional settings. Anxiety was measured through self-report questionnaires and physiological indicators, while object recognition performance was evaluated based on the accuracy and speed of intelligent algorithm-based systems. The study provides insight into the potential impact of technology on mental health and offers suggestions for optimizing the implementation of intelligent algorithms in the workplace.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kwon, M., et al.: When humans aren’t optimal: robots that collaborate with risk-aware humans. In: 2020 15th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), pp. 43–52 (2020)
Pavlichenko, A.: Clinical staging in panic disorder and agoraphobia. Eur. Psychiatry 33(S1), S326–S326 (2016)
Raju, N.N., Naga Pavan Kumar, K.S.V.R., Nihal, G.: Clinical practice guidelines for assessment and management of anxiety and panic disorders in emergency setting. Indian J. Psychiatry 65(2), 181–185 (2023)
Gehrt, T.B., et al.: Encoding and retrieval biases for health-related scenes in patients with severe health anxiety*. Memory 27(7–8), 1–12 (2019)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 25, no. 2 (2012)
West, J.C.: The second machine age: work, progress, and prosperity in a time of brilliant technologies. Psychiatry 78(4), 380–383 (2015)
Majzlíková, E., Vitáloš, M.: Potential risk of automation for jobs in slovakia: a district- and industry-level analysis. East. Eur. Econ. 60(5), 452–478 (2022)
Autor, D.H.: Why are there still so many jobs? The history and future of workplace automation. J. Econ. Perspect. 29(3), 3–30 (2015)
Bambra, C.L.: Clear winners and losers are created by age only NHS resource allocation. BMJ Br. Med. J. 344, e3593 (2012)
Edmondson, A.C., Lei, Z.: Psychological safety: the history, renaissance, and future of an interpersonal construct. Annu. Rev. Organ. Psych. Organ. Behav. 1(1), 23–43 (2014)
Ayalp, G.G., Özdemir, N.: Relationship between test anxiety and learning styles of architecture undergraduates. Creat. Educ. 364–375 (2016)
Schlese, M., Schramm, F.: Tracing the relationship between job insecurity, individual expectations and the satisfaction of German workers (1994)
Ridley, M., et al.: Poverty, depression, and anxiety: causal evidence and mechanisms. Science 370(6522), eaay0214 (2020)
Nawrocka, S., et al.: A person-centered approach to job insecurity: is there a reciprocal relationship between the quantitative and qualitative dimensions of job insecurity? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 20(7), 5280 (2023)
Probst, T.M.: Countering the negative effects of job insecurity through participative decision making: lessons from the demand-control model. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 10(4), 320–329 (2005)
Foubert, J.: Book review: Jukka Vuori, Roland Blonk and Richard H Price (eds), sustainable working lives: managing work transitions and health throughout the life course. Work Employ. Soc. 31(4), 715–717 (2017)
Demartini, J., Patel, G., Fancher, T.: Generalized anxiety disorder. Ann. Internal Med. 170(7), ITC49–ITC64 (2019)
Holmes, E.G., et al.: Taking care of our own: a multispecialty study of resident and program director perspectives on contributors to burnout and potential interventions. Acad. Psychiatry 41(2), 159–166 (2017)
Qamar, Y., et al.: When technology meets people: the interplay of artificial intelligence and human resource management. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 34(5), 1339–1370 (2021)
Choi, S.B., Lim, M.S.: Effects of social and technology overload on psychological well-being in young South Korean adults: the mediatory role of social network service addiction. Comput. Hum. Behav. 61, 245–254 (2016)
Loureiro, S.M.C., Guerreiro, J., Tussyadiah, I.: Artificial intelligence in business: State of the art and future research agenda. J. Bus. Res. 129, 911–926 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 226-2023-00086), Research Center of Computer Aided Product Innovation Design, Ministry of Education, National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52075478), and National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21AZD056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, L., Yao, C., Huang, L., Ying, W., Ying, F. (2023). Research on the Influence of Object Recognition Based on Intelligent Algorithm on Staff’s Anxiety. In: Ciancarini, P., Di Iorio, A., Hlavacs, H., Poggi, F. (eds) Entertainment Computing – ICEC 2023. ICEC 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14455. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8248-6_40
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8248-6_40
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-8247-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-8248-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)