Abstract
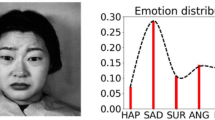
In speech emotion recognition tasks, models learn emotional representations from datasets. We find the data distribution in the IEMOCAP dataset is very imbalanced, which may harm models to learn a better representation. To address this issue, we propose a novel Pairwise-emotion Data Distribution Smoothing (PDDS) method. PDDS considers that the distribution of emotional data should be smooth in reality, then applies Gaussian smoothing to emotion-pairs for constructing a new training set with a smoother distribution. The required new data are complemented using the mixup augmentation. As PDDS is model and modality agnostic, it is evaluated with three state-of-the-art models on two benchmark datasets. The experimental results show that these models are improved by 0.2% \(\sim \) 4.8% and 0.1% \(\sim \) 5.9% in terms of weighted accuracy and unweighted accuracy. In addition, an ablation study demonstrates that the key advantage of PDDS is the reasonable data distribution rather than a simple data augmentation.
This work was supported in part by the Guangdong Provincial Key Research and Development Programme under Grant 2021B0101410002.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando, A., Kobashikawa, S., Kamiyama, H., Masumura, R., Ijima, Y., Aono, Y.: Soft-target training with ambiguous emotional utterances for DNN-based speech emotion classification. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 4964–4968 (2018)
Ando, A., Masumura, R., Kamiyama, H., Kobashikawa, S., Aono, Y.: Speech emotion recognition based on multi-label emotion existence model. In: Proc. Interspeech 2019, pp. 2818–2822 (2019)
Atmaja, B.T., Shirai, K., Akagi, M.: Speech emotion recognition using speech feature and word embedding. In: 2019 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), pp. 519–523 (2019)
Baevski, A., Hsu, W.N., Xu, Q., Babu, A., Gu, J., Auli, M.: data2vec: A general framework for self-supervised learning in speech, vision and language. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. vol. 162, pp. 1298–1312 (2022)
Batliner, A., Steidl, S., Nöth, E.: Releasing a thoroughly annotated and processed spontaneous emotional database: the FAU Aibo emotion corpus. In: Proc. Workshop Lang. Resour. Eval. Conf. vol. 28, pp. 28–31 (2008)
Busso, C., et al.: IEMOCAP: Interactive emotional dyadic motion capture database. Lang. Resour. Eval. 42(4), 335–359 (2008)
Chou, H.C., Lin, W.C., Lee, C.C., Busso, C.: Exploiting annotators’ typed description of emotion perception to maximize utilization of ratings for speech emotion recognition. In: ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 7717–7721 (2022)
Cowie, R., et al.: Emotion recognition in human-computer interaction. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 18(1), 32–80 (2001)
Delbrouck, J.B., Tits, N., Dupont, S.: Modulated fusion using transformer for linguistic-acoustic emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Natural Language Processing Beyond Text, pp. 1–10 (2020)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. vol. 1, pp. 4171–4186 (2019)
Fayek, H.M., Lech, M., Cavedon, L.: Modeling subjectiveness in emotion recognition with deep neural networks: Ensembles vs soft labels. In: 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 566–570 (2016)
Fujioka, T., Homma, T., Nagamatsu, K.: Meta-learning for speech emotion recognition considering ambiguity of emotion labels. In: Proc. Interspeech 2020, pp. 2332–2336 (2020)
Gao, X., Zhao, Y., Zhang, J., Cai, L.: Pairwise emotional relationship recognition in drama videos: Dataset and benchmark. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 3380–3389 (2021)
Gupta, P., Rajput, N.: Two-stream emotion recognition for call center monitoring. In: Proc. Interspeech 2007, pp. 2241–2244 (2007)
Hazarika, D., Poria, S., Mihalcea, R., Cambria, E., Zimmermann, R.: ICON: Interactive conversational memory network for multimodal emotion detection. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 2594–2604 (2018)
Huahu, X., Jue, G., Jian, Y.: Application of speech emotion recognition in intelligent household robot. In: 2010 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence. vol. 1, pp. 537–541 (2010)
Lian, Z., Chen, L., Sun, L., Liu, B., Tao, J.: GCNet: Graph completion network for incomplete multimodal learning in conversation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(7), 8419–8432 (2023)
Lian, Z., Liu, B., Tao, J.: CTNet: Conversational transformer network for emotion recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio, Speech, Lang. Process. 29, 985–1000 (2021)
Lotfian, R., Busso, C.: Predicting categorical emotions by jointly learning primary and secondary emotions through multitask learning. In: Proc. Interspeech 2018, pp. 951–955 (2018)
Parry, J., Palaz, D., et al: Analysis of Deep Learning Architectures for Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition. In: Proc. Interspeech 2019, pp. 1656–1660 (2019)
Poria, S., Cambria, E., Hazarika, D., Majumder, N., Zadeh, A., Morency, L.P.: Context-dependent sentiment analysis in user-generated videos. In: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. vol. 1, pp. 873–883 (2017)
Seppi, D., et al: Patterns, prototypes, performance: classifying emotional user states. In: Proc. Interspeech 2008, pp. 601–604 (2008)
Sun, L., Liu, B., Tao, J., Lian, Z.: Multimodal cross-and self-attention network for speech emotion recognition. In: ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 4275–4279 (2021)
Yin, Y., Gu, Y., Yao, L., Zhou, Y., Liang, X., Zhang, H.: Progressive co-teaching for ambiguous speech emotion recognition. In: ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 6264–6268 (2021)
Zhang, H., Cisse, M., Dauphin, Y.N., Lopez-Paz, D.: mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2018)
Zhou, Y., Liang, X., Gu, Y., Yin, Y., Yao, L.: Multi-classifier interactive learning for ambiguous speech emotion recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio, Speech, Lang. Process. 30, 695–705 (2022)
Zou, H., Si, Y., Chen, C., Rajan, D., Chng, E.S.: Speech emotion recognition with co-attention based multi-level acoustic information. In: ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 7367–7371 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jiang, H., Liang, X., Xu, W., Zhou, Y. (2024). Pairwise-Emotion Data Distribution Smoothing for Emotion Recognition. In: Liu, Q., et al. Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision. PRCV 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14427. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8435-0_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8435-0_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-8434-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-8435-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)