Abstract
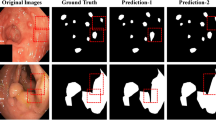
In clinical practice, colonoscopy serves as an efficacious approach to detect colonic polyps and aids in the early diagnosis of colon cancer. However, the precise segmentation of polyps poses a challenge due to variability in size and shape, indistinct boundaries, and similar feature representations with healthy tissue. To address these issues, we propose a concise yet very effective progressive region focusing network (PRFNet) that leverages progressive training to iteratively refine segmentation results. Specifically, PRFNet shares encoder parameters and partitions the feature learning process of decoder into various stages, enabling the aggregation of features at different granularities through cross-stage skip connections and progressively mining the detailed features of lesion regions at different granularities. In addition, we introduce a lightweight adaptive region focusing (ARF) module, empowering the network to mask the non-lesion region and focus on mining lesion region features. Extensive experiments have been conducted on several public polyp segmentation datasets, where PRFNet demonstrated competitive segmentation results compared to state-of-the-art polyp segmentation methods. Furthermore, we set up multiple cross-dataset training and testing experiments, substantiating the superior generalization performance of PRFNet.
J. Chen and J. Cheng—Contributed equally and should be considered co-first authors.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernal, J., Sánchez, F.J., Fernández-Esparrach, G., Gil, D., Rodríguez, C., Vilariño, F.: WM-DOVA maps for accurate polyp highlighting in colonoscopy: validation vs. saliency maps from physicians. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 43, 99–111 (2015)
Bo, D., Wenhai, W., Deng-Ping, F., Jinpeng, L., Huazhu, F., Ling, S.: Polyp-PVT: polyp segmentation with pyramid vision transformers. In: CAAI AIR (2023)
Chao, P., Kao, C.Y., Ruan, Y.S., Huang, C.H., Lin, Y.L.: HarDNet: a low memory traffic network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3552–3561 (2019)
Chen, J., et al.: TransUNet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation (2021)
Cheng, J., et al.: ResGANet: residual group attention network for medical image classification and segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 76, 102313 (2022)
Cheng, J., et al.: DDU-Net: a dual dense U-structure network for medical image segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 126, 109297 (2022)
Cheng, J., Tian, S., Yu, L., Lu, H., Lv, X.: Fully convolutional attention network for biomedical image segmentation. Artif. Intell. Med. 107, 101899 (2020)
Fan, D.P., et al.: PraNet: parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12266, pp. 263–273. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_26
Jha, D., et al.: Kvasir-SEG: a segmented polyp dataset. arXiv arXiv:1911.07069 (2019)
Lai, H., Luo, Y., Zhang, G., Shen, X., Li, B., Lu, J.: Toward accurate polyp segmentation with cascade boundary-guided attention. Vis. Comput. 39(4), 1453–1469 (2022)
Lou, A., Guan, S., Loew, M.: CaraNet: context axial reverse attention network for segmentation of small medical objects. J. Med. Imaging 10(1), 014005 (2023)
Lou, M., Meng, J., Qi, Y., Li, X., Ma, Y.: MCRNet: multi-level context refinement network for semantic segmentation in breast ultrasound imaging. Neurocomputing 470, 154–169 (2022)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Salmo, E., Haboubi, N.: Adenoma and malignant colorectal polyp: pathological considerations and clinical applications. EMJ Gastroenterol. 7, 92–102 (2018)
Srivastava, A., Chanda, S., Jha, D., Pal, U., Ali, S.: GMSRF-Net: an improved generalizability with global multi-scale residual fusion network for polyp segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.10614 (2021)
Tajbakhsh, N., Gurudu, S.R., Liang, J.: Automated polyp detection in colonoscopy videos using shape and context information. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(2), 630–644 (2016)
Tomar, N.K., Shergill, A., Rieders, B., Bagci, U., Jha, D.: TransResU-Net: transformer based ResU-Net for real-time colonoscopy polyp segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.08985 (2022)
Vázquez, D., et al.: A benchmark for endoluminal scene segmentation of colonoscopy images. J. Healthc. Eng. 2017, 4037190 (2016)
Wang, J., Huang, Q., Tang, F., Meng, J., Su, J., Song, S.: Stepwise feature fusion: local guides global. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, MICCAI 2022. LNCS, vol. 13433, pp. 110–120. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16437-8_11
Wang, W., et al.: Pyramid vision transformer: a versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 568–578 (2021)
Zhang, R., et al.: Lesion-aware dynamic kernel for polyp segmentation. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, MICCAI 2022. LNCS, vol. 13433, pp. 99–109. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16437-8_10
Zhou, Z., Siddiquee, M.M.R., Tajbakhsh, N., Liang, J.: UNet++: redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39, 1856–1867 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, J., Cheng, J., Jiang, L., Yin, P., Wang, G., Zhu, M. (2024). PRFNet: Progressive Region Focusing Network for Polyp Segmentation. In: Liu, Q., et al. Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision. PRCV 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14429. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8469-5_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8469-5_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-8468-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-8469-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)