Abstract
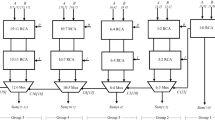
The Carry Select Adder (CSLA) is commonly used in VLSI design applications like data-processing processors, ALUs, and microprocessors to perform fast arithmetic operations. Compared to primitive designs like Ripple Carry Adder and Carry Look Ahead Adder, the regular CSLA offers optimized results in terms of area. However, it is still possible to reduce the area and power consumption of CSLA by implementing a simpler and more efficient gate-level modification. In this work, all the CSLA structures were designed using Verilog HDL while pre-layout simulation and synthesis were done using Quartus Prime, ModelSim and Synopsys EDA tools. The final results analysis obtained have proven that the BEC-based SQRT CSLA is better than regular square root CSLA (SQRT CSLA) as it has reduced total cell area by 19.54 (16-bit) and 19.44% (32-bit) as well as reduced total dynamic power by 8.52 (16-bit) and 8.75% (32-bit). Ultimately, the modified SQRT CSLA structure using BEC method showed significant lower dynamic power consumption and smaller cell area than the regular SQRT CSLA.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sireesha P, Kumar GR, Bhargavi CP, Sowjanya A (1916) Manga Rao P (2021) Retraction: design and analysis of 32 bit high speed carry select adder. J Phys Confer Ser 1:12006
Sreekanth G, Singh KJ, Sruthi NS (2016) Design of low power and area efficient carry select adder (CSLA) using verilog language. Int J Adv Eng Res Sci 3(12):78–82
Nayak VSP, Ramchander N, Reddy RS, Redy THSP, Reddy MS (2016) Analysis and design of low-power reversible carry select adder using D-latch. In: IEEE international conference on recent trends in electronics, information and communication technology (RTEICT) pp 1917–1920
Nagulapati Giri MD (2019) A survey on various VLSI architectures of carry select adder. Int J Innov Technol Explor Eng 8(5):470–474
Arunakumari S, Rajasekahr K, Sunithamani S, Suresh Kumar D (2023) Carry select adder using binary excess-1 converter and ripple carry adder. In: Lenka TR, Misra D, Fu L (eds) Micro and nanoelectronics devices, circuits and systems. Springer, Singapore, pp 289–294
Ramkumar B, Kittur HM (2012) Low-power and area-efficient carry select adder. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr Syst 20(2):371–375
Prasad G, Nayak VSP, Sachin S, Kumar KL, Saikumar S (2016) Area and power efficient carry-select adder. In: IEEE international conference on recent trends in electronics, information and communication technology (RTEICT), pp 1897–1901
Hebbar AR, Srivastava P, Joshi VK (2018) Design of high speed carry select adder using modified parallel prefix adder. Proced Comput Sci 12:317–324
Gayathri P, Mohan Kumar R (2019) RTL design of efficient high-speed adders using quantum-dot cellular automatation. Int J Recent Technol Eng 8(2):2853–2857
Abhiram T, Ashwin T, Sivaprasad B, Aakash S, Anita JP (2017) Modified carry select adder for power and area reduction. In: International conference on circuit, power and computing technologies (ICCPCT), pp 1–8
You H, Yuan J, Tang W, Qiao S (2019) An energy and area efficient carry select adder with dual carry adder cell. Electronics 8(10):1254
Anagha UP, Pramod P (2015) Power and area efficient carry select adder. In: IEEE recent advances in intelligent computational systems (RAICS), pp 17–20
Srinivasareddy B, Anjularani MD (2014) Area-efficient 128-bit carry select adder architecture
Syed Mustafaa M, Sathish M, Nivedha S, Mohammed Magribatul Noora AK, Safrin Sifana T (2022) Design of carry select adder using BEC and common boolean logic. Indian J VLSI Des 2(1):5–9
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by “Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia for Fundamental Research Grant Scheme” with project code FRGS/1/2020/TKO/USM/02/2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lyn, P.Y., Ghazali, N.A., Mohamed, M.F.P., Akbar, M.F. (2024). Design of Low-Power and Area-Efficient Square Root Carry Select Adder Using Binary to Excess-1 Converter (BEC). In: Ahmad, N.S., Mohamad-Saleh, J., Teh, J. (eds) Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Robotics, Vision, Signal Processing and Power Applications. RoViSP 2021. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1123. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9005-4_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9005-4_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-9004-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-9005-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)