Abstract
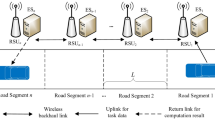
Vehicular Edge Computing (VEC) emerges as a promising paradigm by deploying computation and storage resources on edge servers located in close proximity to vehicles, such as roadside units or base stations. This proximity enables VEC to provide abundant resources and low-latency services, catering to the computational needs of vehicles. However, the dynamic nature of traffic flow presents new challenges in terms of task offloading decisions and resource allocation within VEC environments. This paper addresses the task offloading problem in VEC systems, considering the impact of dynamic traffic flow. To address this problem, we formulate an integer programming model that captures the essence of the studied scenario. To devise an efficient solution, we propose a novel traffic flow prediction-based heuristic algorithm (TFPVTO). TFPVTO incorporates different rules and strategies to generate an optimal offloading task sequence, make informed offloading decisions, and allocate resources effectively. To assess the performance of the proposed algorithm, we utilize a real-world traffic flow dataset. In order to fine-tune and optimize the algorithm’s components, we employ a multi-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) technique. The proposed TFPVTO algorithm is then rigorously compared against other state-of-the-art algorithms, namely TAVF, MONSA, and RANDOM. Through extensive experiments and statistical analysis, we demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed algorithm in terms of task offloading performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gers, F.A., Schmidhuber, J., Cummins, F.: Learning to forget: continual prediction with LSTM. In: Ninth International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks ICANN, vol. 2, pp. 850–855 (1999)
Korula, N.: Maximum weight matching in bipartite graphs (2010)
Munkres, J.R.: Algorithms for the assignment and transportation problems. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 10, 196–210 (1957)
Corey Snyder and Minh Do. STREETS: a novel camera network dataset for traffic flow. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 10242–10253 (2019)
Song, X., Guo, Y., Li, N., Zhang, L.: Online traffic flow prediction for edge computing-enhanced autonomous and connected vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 70(3), 2101–2111 (2021)
Tang, C., Wei, X., Zhu, C., Wang, Y., Jia, W.: Mobile vehicles as fog nodes for latency optimization in smart cities. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(9), 9364–9375 (2020)
Wen, Y., Zhang, W., Luo, H.: Energy-optimal mobile application execution: taming resource-poor mobile devices with cloud clones. In: Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM, pp. 2716–2720. IEEE (2012)
Xu, X., Fang, Z., Qi, L., Zhang, X., He, Q., Zhou, X.: TripRes: traffic flow prediction driven resource reservation for multimedia IoV with edge computing. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 17(2), 41:1-41:21 (2021)
Yang, B., Sun, S., Li, J., Lin, X., Tian, Y.: Traffic flow prediction using LSTM with feature enhancement. Neurocomputing 332, 320–327 (2019)
Yong, Yu., Si, X., Changhua, H., Zhang, J.: A review of recurrent neural networks: LSTM cells and network architectures. Neural Comput. 31(7), 1235–1270 (2019)
Zhang, R., et al.: Task offloading with task classification and offloading nodes selection for MEC-enabled IoV. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. (TOIT) 22(2), 51:1-51:24 (2022)
Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Chen, Y., Li, Z., Huang, J.: Cost efficient scheduling for delay-sensitive tasks in edge computing system. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Services Computing (SCC), pp. 73–80. IEEE (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xie, L., Chen, L., Li, X., Wang, S. (2024). A Traffic Flow Prediction Based Task Offloading Method in Vehicular Edge Computing. In: Sun, Y., Lu, T., Wang, T., Fan, H., Liu, D., Du, B. (eds) Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing. ChineseCSCW 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 2013. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9640-7_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9640-7_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-9639-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-9640-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)