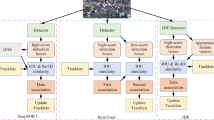
Abstract
Multi-object tracking (MOT) becomes a challenging task as non-linear motion and occlusion cause problems such as contaminated appearance, inaccurate positions and disturbed tracks. Despite great progress made by current trackers, their performance still needs improvement due to their inability to adapt their components to these challenges. In this work, we propose a new method, StrongOC-SORT, which exploits the observation-centric nature and four new modules to tackle these challenges more effectively. Specifically, we design an IoU-ReID Fusion module to minimize disruptions from rapid changes in direction. Moreover, we develop Dynamic Embedding and Observation Expansion modules that correspond to prevent track embedding from being contaminated by detection noise and to address the issue of slight overlap between observations under long-term lack of observations. Lastly, we propose an Active State module to provide discriminative tracks for association in DanceTrack. Our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on DanceTrack and MOT20 with 63.4 HOTA and 64.1 HOTA, while providing competitive performance on MOT17 with the best IDF1 and AssA. The experimental results demonstrate the robustness and effectiveness of StrongOC-SORT under occlusion and non-linear motion.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharon, N., Orfaig, R., Bobrovsky, B.Z.: Bot-sort: robust associations multi-pedestrian tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.14651 (2022)
Bae, S.H., Yoon, K.J.: Confidence-based data association and discriminative deep appearance learning for robust online multi-object tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(3), 595–610 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2691769
Bernardin, K., Stiefelhagen, R.: Evaluating multiple object tracking performance: the clear mot metrics. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2008, 1–10 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/246309
Bewley, A., Ge, Z., Ott, L., Ramos, F., Upcroft, B.: Simple online and realtime tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3464–3468 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2016.7533003
Cao, J., Weng, X., Khirodkar, R., Pang, J., Kitani, K.: Observation-centric sort: rethinking sort for robust multi-object tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.14360 (2022)
Chen, L., Ai, H., Zhuang, Z., Shang, C.: Real-time multiple people tracking with deeply learned candidate selection and person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 1–6 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME.2018.8486597
Dendorfer, P., et al.: Mot20: a benchmark for multi object tracking in crowded scenes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.09003 (2020)
Ge, Z., Liu, S., Wang, F., Li, Z., Sun, J.: YOLOX: exceeding YOLO series in 2021. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.08430 (2021)
Haynes, D., Corns, S., Venayagamoorthy, G.K.: An exponential moving average algorithm. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pp. 1–8 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2012.6252962
Jonathon, J.L., et al.: Hota: a higher order metric for evaluating multi-object tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 129(2), 548–578 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-020-01375-2
Kalman, R.E.: A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J. Basic Eng. 82(1), 35–45 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3662552
Kuhn, H.W.: The Hungarian method for the assignment problem. Naval Res. Logist. Q. 2(1–2), 83–97 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1002/nav.3800020109
Maggiolino, G., Ahmad, A., Cao, J., Kitani, K.: Deep oc-sort: multi-pedestrian tracking by adaptive re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.11813 (2023)
Meinhardt, T., Kirillov, A., Leal-Taixe, L., Feichtenhofer, C.: Trackformer: multi-object tracking with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 8834–8844 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00864
Milan, A., Leal-Taixe, L., Reid, I., Roth, S., Schindler, K.: Mot16: a benchmark for multi-object tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.00831 (2016)
Qin, Z., Zhou, S., Wang, L., Duan, J., Hua, G., Tang, W.: Motiontrack: learning robust short-term and long-term motions for multi-object tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.10404 (2023)
Ren, H., Han, S., Ding, H., Zhang, Z., Wang, H., Wang, F.: Focus on details: online multi-object tracking with diverse fine-grained representation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.14589 (2023)
Ristani, E., Solera, F., Zou, R., Cucchiara, R., Tomasi, C.: Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, vol. 9914, pp. 17–35 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48881-3_2
Sun, P., Cao, J., Jiang, Y., Yuan, Z., Bai, S., Kitani, K., Luo, P.: Dancetrack: multi-object tracking in uniform appearance and diverse motion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 20961–20970 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.02032
Sun, P., et al.: Transtrack: multiple object tracking with transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.15460 (2021)
Wojke, N., Bewley, A., Paulus, D.: Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3645–3649 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2017.8296962
Yang, F., Odashima, S., Masui, S., Jiang, S.: Hard to track objects with irregular motions and similar appearances? Make it easier by buffering the matching space. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 4788–4797 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00478
Zeng, F., Dong, B., Zhang, Y., Wang, T., Zhang, X., Wei, Y.: MOTR: end-to-end multiple-object tracking with transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 13687, pp. 659–675 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19812-0_38
Zhang, Y., et al.: Bytetrack: multi-object tracking by associating every detection box. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cisse, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13682, pp. 1–21. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20047-2_1
Zhang, Y., Wang, C., Wang, X., Zeng, W., Liu, W.: FairMOT: on the fairness of detection and re-identification in multiple object tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 129(11), 3069–3087 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-021-01513-4
Zhang, Y., et al.: Rt-track: robust tricks for multi-pedestrian tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.09668 (2023)
Zhou, X., Koltun, V., Krähenbühl, P.: Tracking objects as points. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12349, pp. 474–490. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58548-8_28
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Anhui Provincial Major Science and Technology Project (No. 202203a05020016), the National Key R &D Program of China (Nos. 2022YFB3303400 and 2021YFF0500900), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71991464 and 61877056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sun, Y., Huang, Z. (2024). StrongOC-SORT: Make Observation-Centric SORT More Robust. In: Hu, SM., Cai, Y., Rosin, P. (eds) Computer-Aided Design and Computer Graphics. CADGraphics 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14250. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9666-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9666-7_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-9665-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-9666-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)