Abstract
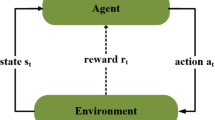
The structure of the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) has demonstrated good performance in various tasks, mainly comprising two competing sub-networks. The GAN has the potential to effectively generate artificial samples that closely resemble the actual sample distribution. The field of steganography utilizing the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) structure has witnessed a wealth of research with highly successful outcomes. This paper proposes a steganography framework that integrates reinforcement learning and introduces a new reward function to analyze the embedding cost of images in the steganography problem. In this framework, the reward function assigns distortion values to each pixel of the image and relates the security performance of steganography. Based on the conducted experiments, an enhanced steganographic embedding scheme can ultimately be achieved.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Filler, T., Judas, J., Fridrich, J.J.: Minimizing additive distortion in steganography using syndrome-trellis codes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 6(3–2), 920–935 (2011)
Pevný, T., Filler, T., Bas, P.: Using high-dimensional image models to perform highly undetectable steganography. In: Böhme, R., Fong, P.W.L., Safavi-Naini, R. (eds.) IH 2010. LNCS, vol. 6387, pp. 161–177. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16435-4_13
Holub, V., Fridrich, J.J.: Designing steganographic distortion using directional filters. In: 2012 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, WIFS 2012, Costa Adeje, Tenerife, Spain, 2–5 December 2012, pp. 234–239. IEEE (2012)
Li, B., Wang, M., Huang, J., Li, X.: A new cost function for spatial image steganography. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, ICIP 2014, Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014, pp. 4206–4210. IEEE (2014)
Li, B., Wang, M., Huang, J., Li, X.: A new cost function for spatial image steganography, pp. 4206–4210 (2014)
Sedighi, V., Cogranne, R., Fridrich, J.J.: Content-adaptive steganography by minimizing statistical detectability. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 11(2), 221–234 (2016)
Tang, W., Tan, S., Li, B., Huang, J.: Automatic steganographic distortion learning using a generative adversarial network. IEEE Sig. Process. Lett. 24(10), 1547–1551 (2017)
Xu, G., Wu, H., Shi, Y.: Structural design of convolutional neural networks for steganalysis. IEEE Sig. Process. Lett. 23(5), 708–712 (2016)
Tang, W., Li, B., Barni, M., Li, J., Huang, J.: An automatic cost learning framework for image steganography using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 16, 952–967 (2021)
Mo, X., Tan, S., Li, B., Huang, J.: MCTSteg: a Monte Carlo tree search-based reinforcement learning framework for universal non-additive steganography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 16, 4306–4320 (2021)
Mo, X., Tan, S., Tang, W., Li, B., Huang, J.: ReLOAD: using reinforcement learning to optimize asymmetric distortion for additive steganography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 18, 1524–1538 (2023)
Shi, H., Dong, J., Wang, W., Qian, Y., Zhang, X.: SSGAN: secure steganography based on generative adversarial networks. In: Zeng, B., Huang, Q., El Saddik, A., Li, H., Jiang, S., Fan, X. (eds.) PCM 2017, Revised Selected Papers, Part I. LNCS, vol. 10735, pp. 534–544. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77380-3_51
Volkhonskiy, D., Nazarov, I., Burnaev, E.: Steganographic generative adversarial networks. In: Osten, W., Nikolaev, D.P. (eds.) Twelfth International Conference on Machine Vision, ICMV 2019, SPIE Proceedings, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 16–18 November 2019, vol. 11433, p. 114333M. SPIE (2019)
Yedroudj, M., Comby, F., Chaumont, M.: Steganography using a 3-player game. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 72, 102910 (2020)
Zhang, R., Dong, S., Liu, J.: Invisible steganography via generative adversarial networks. Multim. Tools Appl. 78(7), 8559–8575 (2019)
Hayes, J., Danezis, G.: Generating steganographic images via adversarial training, pp. 1954–1963 (2017)
Zhang, K.A., Cuesta-Infante, A., Xu, L., Veeramachaneni, K.: SteganoGAN: high capacity image steganography with GANs. CoRR abs/1901.03892 (2019)
Zhu, J., Kaplan, R., Johnson, J., Fei-Fei, L.: HiDDeN: hiding data with deep networks. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018, Part XV. LNCS, vol. 11219, pp. 682–697. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01267-0_40
Baluja, S.: Hiding images in plain sight: deep steganography. In: Guyon, I., et al. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, 4–9 December 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, pp. 2069–2079 (2017)
Fridrich, J.J., Kodovský, J.: Rich models for steganalysis of digital images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 7(3), 868–882 (2012)
Silver, D., Lever, G., Heess, N., Degris, T., Wierstra, D., Riedmiller, M.A.: Deterministic policy gradient algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 31th International Conference on Machine Learning, JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, ICML 2014, Beijing, China, 21–26 June 2014, vol. 32, pp. 387–395. JMLR.org (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NSFC (Grant 62002075), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant 2023A1515011428), the Science and Technology Foundation of Guangzhou (Grant 2023A04J1723).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tang, W., Xie, Y. (2024). An Embedded Cost Learning Framework Based on Cumulative Gradient Rewards. In: Vaidya, J., Gabbouj, M., Li, J. (eds) Artificial Intelligence Security and Privacy. AIS&P 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14509. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9785-5_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9785-5_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-9784-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-9785-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)