Abstract
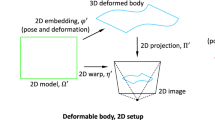
The aim of this paper is to investigate whether it is possible to construct invariants for articulated objects—these are objects that are composed of different rigid parts which are allowed to perform a restricted motion with respect to each other—which use only partial information from each component. To this end, the transformation group describing the deformations of the image of an articulated object due to relative motions of the components, and/or changes in the position of the camera, is identified. It turns out that for a planar articulated object with two rigid components that are allowed to move within the object plane, this transformation group is (anti-isomorphic to) the semi-direct product of the group one would obtain if the object was rigid, and its smallest normal subgroup containing the transformations due to the relative motions of the components. Depending on the projection model, different answers to the question above evoke. For instance, when using perspective projection no other invariants exist than those obtained by considering each part separately as a rigid object, whereas in the pseudo-orthographic case simpler invariants (using only partial information from each component) do exist. Examples of such invariants are given.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Bourbaki, Groupes et Algèbres de Lie, Chapitre I, Éléments de Mathématique, Fasc. XXVI, Hermann: Paris, 1971.
J. Dixmier, Algèbres Enveloppantes, Cahiers Scientifiques, Fasc. XXXVII, Gauthiers-Villars: Paris/Bruxelles/Montréal, 1974.
T. Moons, E.J. Pauwels L.J. Van Gool, and A. Oosterlinck, “Foundations of semi-differential invariants,” International Journal of Computer Vision, Vol. 14 (1995), pp. 25–47.
T. Moons, E. Pauwels, L. Van Gool, and A. Oosterlinck, “View-point invariant characterization of objects composed of different rigid parts: a mathematical framework,” in F. Dillen, L. Vrancken, L. Verstraelen, and F. Van de Woestijne (Eds.), Geometry and Topology of Submanifolds V, World Scientific: Singapore/New Jersey/London/Hong Kong, 1994.
J.L. Mundy and A. Zisserman (Eds.), Geometric Invariance in Computer Vision, MIT Press: Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1992.
J.L. Mundy, A. Zisserman, and D. Forsyth (Eds.), Applications of Invariance in Computer Vision, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 825, Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg/New York, 1994.
P.J. Olver, Applications of Lie Groups to Differential Equations, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Vol. 107, Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg/New York/Tokyo, 1986.
A.A. Sagle and R.E. Walde, “Introduction to Lie groups and Lie algebras,” Pure and Applied Mathematics Vol. 51, Academic Press: New York, 1973.
L.J. Van Gool, T. Moons, E.J. Pauwels, and A. Oosterlinck, Semi-differential invariants, Chapter 8, pp. 157–192, in J.L. Mundy and A. Zisserman (Eds.), Geometric Invariance in Computer Vision, MIT Press: Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1992.
L. Van Gool, T. Moons, E. Pauwels, and A. Oosterlinck, “Vision and Lie's approach to invariance” to appear in Image and Vision Computing, Vol. 13 (1995), pp. 259–277.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Postdoctoral Research Fellow of the Belgian National Fund for Scientific Research (N.F.W.O.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moons, T., Van Gool, L., Pauwels, E. et al. Viewpoint invariant characteristics of articulated objects. J Math Imaging Vis 6, 37–57 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00127374
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00127374