Summary
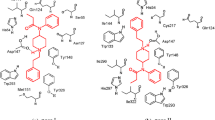
Thirteen 4,5-epoxymorphinan μ agonists with established analgesic action were docked into an Asp-Lys-His-Phe pseudoreceptor complex under a range of distance-dependent dielectric conditions. The number of compounds with potential energies of the docked complexes that agreed in rank order with corresponding analgesic potencies was determined for each condition. Two dielectric conditions, n-decane (1.991) and ethanol (24.3), enabled the greatest number of compounds to relate to their pseudoreceptors with each having 9 and 8 successes respectively. Both of these conditions demonstrated unique influences on the types of structures that were successfully docked. For example, the morphine stereoisomer α-isomorphine, the geometric isomer B/C trans-morphine, and the 8-position-substituted γ-isomorphine were successes in the n-decane condition, whereas the ethanol condition produced the substituted codeine derivatives dihydroco-deinone and dihydroxycodeinone. These findings emphasize the importance of dielectric influence when developing force-field modeled quantitative structure-activity relationships for a closely related homologous series.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dammkoehler, R.A., Karasek, S.F., Berkley Shands, E.F. and Marshall, G.R., J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Design, 3 (1989) 3.
Havel, T.F., Kuntz, I.D. and Crippen, G.M., Bull. Math. Biol., 45 (1983) 665.
Ghose, A.K., Crippen, G.M., Revankar, G.R., McKernan, P.A., Smee, D.F. and Robins, R.K., J. Med. Chem., 32 (1989) 746.
Pattabiram, N., Levitt, M., Ferrin, T.E. and Langridge, R., J. Comput. Chem., 6 (1985) 432.
Henry, E.R., Levitt, M. and Eaton, W.A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 82 (1985) 2034.
Ross, W.S., Hardin, C.C., Tinoco, I., Jr., Rao, S.N., Pearlman, D.A. and Kollman, P.A. Biopolymers, 28 (1989) 1939.
Balaji, V.N., Mobasser, A. and Rao, S.N., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 160 (1989) 109.
Rao, S.N., Lybrand, T., Michaud, D., Jerina, D.M. and Kollman, P.A., Carcinogenesis, 10 (1989) 27.
Belleau, B., Conway, T., Ahmed, F.R. and Hardy, A.D., J. Med. Chem., 17 (1974) 907.
Dimaio, J., Ahmed, F.R., Shiller, P. and Belleau, B., In Gualtieri, F., Gianella, M. and Melchiorre, C. (Eds.), Recent Advances in Receptor Chemistry, Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, 1979, pp. 221–234.
Belleau, B. and Morgan, P., J. Med. Chem., 17 (1974) 908.
Kolb, V.M. and Sheiner, S., J. Pharmaceut. Sci., 73 (1984) 719.
Bennett, L.K. and Beamer, R.L., J. Pharmaceut. Sci., 75 (1986) 769.
Bennett, L.K. and Beamer, R.L., J. Pharmaceut. Sci., 77 (1988) 986.
Cheney, B.V., J. Med. Chem., 31 (1988) 521.
Casy, A.F. and Parfitt, R.T., In Opioid Analgesics Chemistry and Receptors, Plenum Press, New York, 1986, p. 27.
Foye, W.O., In Principles of Medicinal Chemistry, Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, 1974, p. 256.
Carr III, P., In Wolff, M.E. (Ed.), Burger's Medicinal Chemistry (Fourth Edition), John Wiley & Sons, 1981, p. 729.
Pert, C.B. and Snyder, S.H., Mol. Pharmacol., 10 (1974) 868.
Reden, J., Reich, F., Rice, K.C., Jacobson, A.E., Brossi, A., Sreaty, R.A. and Klee, W.A., J. Med. Chem., 22 (1979) 256.
Merz, H.A., Langbein, A., Stockhaus, K., Walther, G. and Wick, H., Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmacol., 8 (1974) 91.
Tseng, L.-F., Loh, H.H. and Li, C.H., Nature, 263 (1976) 239.
Belluzi, J.D., Grant, N., Garsky, V., Sarantakis, D., Wise, C.D. and Stein, L., Nature, 260 (1976) 625.
Cheney, B.V., Lathi, A., Barshun, C. and Gay, D.D., Mol. Pharmacol., 22 (1982) 349.
Gussio, R., Syi, J., Pou, S., Chen, J. and Smythers, G.W., Proc. Am. Chem. Soc., 200 (August, MEDI, 53) 493.
Gussio, R., Syi, J., Pou, S., Chen, J. and Smythers, G.W., Quant. Struct.-Act. Relationsh., in press.
Gylbert, L., Acta Crystallogr., B 29 (1973) 1630.
Hagler, A.T., Lifson, S. and Dauber, P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 101 (1979) 5122.
INSIGHT II and DISCOVER: Biosym Technologies, Inc., San Diego, CA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gussio, R., Pou, S., Chen, JH. et al. A pseudoreceptor docking study of 4,5-α-epoxymorphinans with a range of dielectric constants. J Computer-Aided Mol Des 6, 149–158 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00129425
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00129425