Summary
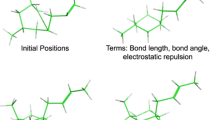
In the absence of a 3D structure of the target biomolecule, to propose the 3D requirements for a small molecule to exhibit a particular bioactivity, one must supply both a bioactive conformation and a superposition rule for every active compound. Our strategy identifies both simultaneously. We first generate and optimize all low-energy conformations by any suitable method. For each conformation we then use ALAD-DIN to calculate the location of points to be considered as part of the superposition. These points include atoms in the molecule and projections from the molecule to hydrogen-bond donors and acceptors or charged groups in the binding site. These positions and the relative energy of each conformation are the input to our new program DISCO. It uses a clique-detection method to find superpositions that contain a least one conformation of each molecule and user-specified numbers of point types and chirality. DISCO is fast; for example, it takes about 1 min CPU to propose pharmacophores from 21 conformations of seven molecules. We typically run DISCO several times to compare alternative pharmacophore maps. For D2 dopamine agonists DISCO shows that the newer 2-aminothiazoles fit the traditional pharmacophore. Using site points correctly identifies the bioactive enantiomers of indoles to compare with catechols whereas using only ligand points leads to selecting the inactive enantiomer for the pharmacophore map. In addition, DISCO reproduces pharmacophore maps of benzodiazepines in the literature and proposes subtle improvements. Our experience suggests that clique-detection methods will find many applications in computational chemistry and computer-assisted molecular design.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marshall, G.R., Barry, C.D., Bosshard, H.E., Dammkoehler, R.A. and Dunn, D.A., In Olson, E.C. and Christoffersen, R.E. (Eds.) Computer-Assisted Drug Design, American Chemical Society Symposium, No. 112, ACS, Washington 1979, pp. 205–226.
Martin, Y.C., J Methods Enzymol., 203 (1991) 587.
Martin, Y.C., J. Med. Chem., 35 (1992) 2145.
Martin, Y.C., Bures, M.G. and Willett, P., In Lipkowitz, K.B. and Boyd, D.B. (Eds.) Reviews in Computational Chemistry, VCH Publishers, New York, 1990, pp. 213–263.
Murray-Rust, P. and Glusker, J.P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 106 (1984) 1018.
Kelly, J.A. and Knox, J.R., In Jensen, B., Jorgensen, F.S. and Kofod, H. (Eds.) Frontiers in Drug Research — Crystallographic and Computational Methods, Alfred Benzon Foundation, Copenhagen, 1990, p. 252.
Ippolito, J.A., Alexander, R.S. and Christianson, D.W., J. Mol. Biol., 215 (1990) 457.
Taylor, R. and Kennard, O., Acc. Chem. Res. 17 (1984) 320.
Crippen, G.M. and Havel, T.F., In Bawden, D. (Ed.) Chemometrics Research Studies Series, Research Studies Press, Wiley, New York, 1988. We use DGEOM by Blaney, J., Crippen, G.M., Dearing, A. and Dixon, J.S. from QCPE, program number 590.
Brint, A.T. and Willett, P., J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 27 (1987) 152.
Crippen, G., J. Med. Chem., 22 (1979) 988; 23 (1980) 599; 24 (1981) 198.
Crandell, C.W. and Smith, D.H., J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 23 (1983) 186.
Danzinger, D.J. and Dean, P.M., J. Theor. Biol., 116 (1985) 215.
Namasivayam, S. and Dean, P.M., J. Mol. Graphics, 4 (1986) 46.
Kato, Y., Itai, A. and Iitaka, Y., Tetrahedron, 43 (1987) 5229.
Chau, P.-L. and Dean, P.M., J. Mol. Graphics, 5 (1987) 88, 97.
Dean, P.M. and Chau, P.-L., J. Mol. Graphics, 5 (1987) 152.
Dean, P.M., Callow, P. and Chau, P.-L., J. Mol. Graphics, 6 (1988) 28, 38.
Hermann, R.B. and Herron, D.K., J. Comput-Aided Mol. Design 5 (1991) 511.
Kuhl, F.S., Crippen, G.M. and Friesen, D.K., J. Comput. Chem., 5 (1984) 24.
Pearlman, R.S., Rusinko III, A., Skell, J.M., Balducci, R. and McGarity, C.M., CONCORD, Distributed by Tripos Associates, Inc., 1969 S. Hanley Road, Suite 303, St Louis, MO 63944, U.S.A.
Allen, F.H., Davies, J.E., Galloy, J.J., Johnson, O., Kennard, O., Macrea, C.F., Mitchell, E.M., Mitchell, G.F., Smith, J.M. and Watson, D.G., J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 31 (1991) 187.
Martin, Y.C. and Rys, J., unpublished program.
Van Drie, J.H., Weininger, D. and Martin, Y.C., J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Design, 3 (1989) 225.
Thanki, N., Thornton, J.M. and Goodfellow, J.M., J. Mol. Biol., 202 (1988) 637.
Boobbyer, D.N.A., Goodford, P.J., McWhinnie, P.M. and Wade, R.C., J. Med. Chem., 32 (1989) 1083.
Vedani, A. and Dunitz, J.D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 107 (1985) 7653.
Jeffrey, G.A. and Saenger, W., Hydrogen Bonding in Biological Structures, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1991.
Daylight Chemical Information Systems, Inc., 1991, 3951 Claremont St. Irvine, CA 92714.
Weininger, D. and Weininger, A., J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 28 (1988) 31.
Martin, Y.C., Kim, K.-H. and Bures, M.G., In Wermuth, C.G. (Ed.) Medicinal Chemistry in the 21st Century, Blackwell Scientific Publ., Oxford, 1992, pp. 295–317.
Martin, Y.C. and Danaher, E.B., In Williams, M., Glennon, R. and Timmermans, P. (Eds.) Receptor Pharmacology and Function, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1988, pp. 137–171.
Seeman, P., Watanabe, M., Grigoriadis, D., Tedesco, J.L., George, S.R., Svensson, U., Lars, J., Nilsson, G. and Neumeyer, J.L., Mol. Pharmacol., 28 (1985) 391.
Caprathe, B.W., Jaen, J.C., Wise, L.D., Heffner, T.G., Pugsley, T.A., Meltzer, L.T. and Parvez, M., J. Med. Chem., 34 (1991) 2736.
Borea, P.A., Gilli, G., Bertolasi, V. and Ferretti, V., Mol. Pharmacol., 31 (1987) 334
Codding, P.W. and Muir, A.K.S., Mol. Pharmacol., 28 (1985) 178.
Crippen, G.M., Mol. Pharmacol., 22 (1982) 11.
Loew, G.H., Villar, H.O., Jung, W. and Daview, M.F., In Rapaka, R.S., Makriyannis, A., Kuhar, M.J. (Eds.) National Institute on Drug Abuse Research Monograph Series, 112, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1991, pp. 43–61.
Tebib, S., Bourguignon, J.-J. and Wermuth, C.-G., J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Design, 1 (1987) 153.
Trifiletti, R.R. and Snyder, S.H., Mol. Pharmacol., 26 (1984) 458.
AMPAC, version 2.1 (QCPE No. 506), available from Quantum Chemical Program Exchange, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN, U.S.A.
Sheridan, R.P., Nilakantan, R., Dixon, J.S. and Venkataraghavan, R., J. Med. Chem., 29 (1986) 899.
Weiner, P.K., Langridge, R., Blaney, J.M., Schaefer, R. and Kollman, P.A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 79 (1982) 3754.
Kuntz, I.D., Blaney, J.M., Oatley, S.J., Langridge, R. and Ferrin, T., J. Mol. Biol., 161 (1982) 269.
Smellie, A.S., Crippen, G.M. and Richards, W.G., J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 31 (1991) 386.
Moon, J.B. and Howe, W.J., Tetrahedron Comput. Methodol., 3 (1990) 697.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, Y.C., Bures, M.G., Danaher, E.A. et al. A fast new approach to pharmacophore mapping and its application to dopaminergic and benzodiazepine agonists. J Computer-Aided Mol Des 7, 83–102 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00141577
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00141577