Abstract
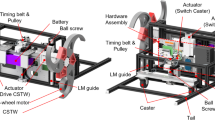
This paper introduces an efficient steering control method for the articulated body mobile robot “Koryu-II (KR-II)”. KR-II is a real robot, composed of six cylindrical segments linked in series and has a long snake-like appearance. The main issue on KR-II's steering control is, given from a remote human operator the velocity and orientation commands for the foremost segment, to automatically generate joint commands for all the following segments, such that they follow the foremost segment's trajectory. The derived method is based on a trajectory planning scheme in the inertial reference frame, and is feasible for real time computation. It also presents good energy efficiency and trajectory tracking performance characteristics, and can be extended for KR-II's “W-Shaped Configuration” steering control, which augments the lateral stability of the robot, essential for locomotion over uneven terrain. The validity of these methods are verified by experiments on the mechanical model KR-II.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Burdick,J. W., Radford J. and Chirikjian,G. S. 1993. Hyperredundant robots: kinematics and experiments, International Symposium on Robotics Research, Pennsylvania, USA, pp. 1–16 (Oct. 1993).
Commissariat A l'Energie Atomique. 1987. Rapport d'activite 1987, Unité de Génie Robotique Avancé, France.
Fukushima, E. F. and Hirose, S. 1995. How To Steer The Long Articulated Robot “KR-II”, 7th International Conference on Advanced Robotics, Sant Feliu de Guixols, Spain,pp. 729–735 (Sept. 20–22).
Hirose, S. 1993. Biologically Inspired Robots, Oxford University Press.
Hirose, S., Fukushima, E. F. and Tsukagoshi,S. 1995. Basic Steering Control Methods for The Articulated Body Mobile Robot, IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 15(1): 5–14
Hirose, S. and Morishima, A. 1988. A Articulated Body Mobile Robot, Proc. ROMANSY Symp., Udine, Italy.
Hirose, S. and Morishima, A. 1989. Basic Motion Regulation of Articulated Body Mobile Robot, Proc. 5th Int. Symp. Robotics Research, Tokyo, Japan, pp. 433–440 (Aug. 28–31).
Hirose, S. and Morishima, A. 1990. Design and Control of a Mobile Robot With an Articulated Body, International Journal of Robotics Research, 9(2):99–114.
Hirose, S., Morishima, A.,Tsukagoshi, S., Tsumaki T. and Monobe H. 1991. Design of Practical Snake Vehicle: Articulated Body Mobile Robot KR-II, Fifth International Conference on Advanced Robotics, Pisa, Italy, Vol. 1, pp. 831–838 (June 19–22).
Hirose, S., Umetani, Y. and Oda, S. 1981. An active cord mechanism with oblique swivel joints and its control, Proc. 4th ROMANSY Symp., Zaborow, Poland, pp. 395–407.
Umetani, Y. and Hirose, S. 1974. Biomechanical study of serpentine locomotion, Proc. 1st ROMANSY Symp., Udine, pp. 171–184.
Waldron, K. J., Kumar V. and Burkat,A. 1987. An actively coordinated mobility system for a planetary rover, Proc. 1987 ICAR, pp. 77–86.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukushima, E.F., Hirose, S. An efficient steering control formulation for the articulated body mobile robot “KR-II”. Auton Robot 3, 7–18 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00162464
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00162464