Abstract
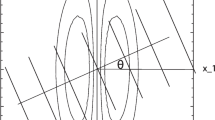
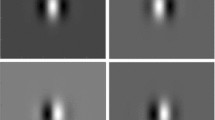
In a previously reported study (Berger et al. 1990) we analyzed distributions of interspike intervals recorded extracellularly from cat visual cortex under four stimulus conditions. Stimuli were gratings differing in orientation and spatial frequency. The probability density function of first passage time for a random walk with drift process, which is defined by its barrier height and drift coefficient, was used to characterize the generating process of axonal discharge under resting and stimulus conditions. Drift coefficient and barrier height were derived from the sample mean and standard deviation of the measured inter-spike intervals. For cells with simple receptive fields, variations in spatial frequency produced changes only in drift coefficient. Variations in barrier height were produced only by changes in orientation of the stimulus. Currently, the method used to analyze these data was implemented in a simulation which displayed the relationship between the interval distribution of impulses, the random walk which represents the time series characteristic of the spike train model and the Gabor filter function which represents the geometry of the receptive field process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker JL, Owens DG (1986) Electrophysiological pharmacology of GABA and diazepam in cultured CNS neurons. In: Olsen CW, Venter IC (eds) Benzoidiazepine/GABA receptors and chlorides channels: structural and functional properties. Liss, New York, pp 135–165
Berger D, Pribram KH, Wild H, Bridges C (1990) An analysis of neural spike-train distributions: determinants of the response of visual cortex neurons to changes in orientation and spatial frequency. Exp Brain Res 80:129–134
Campbell FW, Blakemore C (1969) On the existence of neurons in the human visual system selectively sensitive to the orientation and size of retinal images. J Physiol 203:237–260
Cull-Candy SG, Usowicz MM (1989) Whole-cell current noise produced by excitatory and inhibitory amino acids in large cerebellar neurones of the rat. J Physiol 415:533–553
Daugman JG (1980) Two-dimensional spectral analysis of cortical receptive field profiles. Vision Res 20:847–856
Daugman JG (1985) Uncertainty relation for resolution in space, spatial frequency, and orientation optimized by two-dimensional visual cortical filters. J Optom Soc Am A/2:1160–1169
Daugman JG (1989) Complete discrete 2-d Gabor transforms by neural networks for image analysis and compression. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 36:1169–1179
DeValois RL, Albrecht DG, Thorell LG, (1982) Spatial frequency selectivity of cells in the macaque visual cortex. Vision Res 22:545–559
DeValois RL, Thorell LG, Albrecht DG (1985) Periodicity of striatecortex-cell receptive fields. J Optom Soc Am A/2:1115–1123
Gerstein GL, Mandelbrot B (1964) Random walk models for the spike activity of a single neuron. Biophys J 4:41–68
Kirilov AB, Borisyuk GN, Borisyuk RM, Kovalenko Yel, Makarenko VI, Chulaevsky VA, Kryukov Vi (1989) A model oscillator for a unified submodule. In: Touretzky DS (ed) Advances in neural information processing systems. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo Calif pp 560–567
Kryukov VI (1978) Markov interaction processes and neuronal activity, In: Dold A, Eckmann B (ed) Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Vol 653: Locally interacting systems and their applications in biology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 122–139
Kulikowski JJ, Marcelja S, Bishop P (1982) Theory of spatial position and spatial frequency relation in the receptive fields of simple cells in the visual cortex. Biol Cybern 43:187–198
Lassonde MC, Ptito M, Pribram Kh (1981) Intracerebral influences on the microstructure of visual cortex. Exp Brain Res 43:131–144
Marcelja S (1980) Mathematical description of the responses of simple cortical cells. J Optom Soc Am 70:1297–1300
Pribam KH (1991) Brain and perception: holonomy and structure in figurai processing. Erlbaum, Hillsdale NJ
Pribram KH, Carlton EH (1986) Holonomic brain theory in imaging and object perception. Act Psychol 63:174–210
Romoa AS, Shalden M, Skottun BC, Freeman RD (1986) A comparison of inhibtion in orientation and spatial frequency of cat visual cortex. Nature 321:237–239
Shapley R, Lennie P (1985) Spatial frequency analysis in the visual system. Ann Rev Neurosci 8:547–583
Sillito AM, Kemp JA, Milson JA, Berardi N (1980) A re-evaluation of the mechanisms underlying simple cell orientation selectivity. Brain Res 194:517–520
Tuckwell HC (1976) On the first-exit time problem for temporally homogeneous Markov processes. J Appl Prob 13:39–48
Webster MA & DeValois RL (1985) Relationship between spatial-frequency and orientation tuning of striate-cortex cells. J Optom Soc Am A/2:1124–1132
Williams PJ, MacVicar BA, Pittman QJ (1989) Identification of a GABA-activated chloride-mediated synaptic potential in rat pars intermedia. Brain Res 483:130–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berger, D.H., Pribram, K.H. The relationship between the Gabor elementary function and a stochastic model of the inter-spike interval distribution in the responses of visual cortex neurons. Biol. Cybern. 67, 191–194 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201026
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201026