Abstract
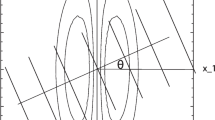
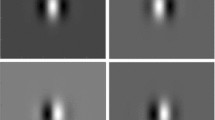
The responses of “complex” simple cells, which are an abstraction of pairs of simple cells having real receptive fields with phases in quadrature, to ideal line and edge patterns (events) are studied. These responses are generalized for events which are convolved with a Gaussian blur function. Normal and abnormal scalings lead to a unified description of the responses of cells with scaled receptive fields to ideal and blurred events. Scale tuning requirements and orientation estimation accuracy are derived. The responses in ambiguous neighbourhoods, where there are two events in the cells' receptive fields, are analyzed, considering both parallel and crossing event combinations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlow HB (1972) Single units and sensation: a neuron doctrine for perceptual psychology. Perception 1:371–394
Bigün J (1988) Local symmetry features in image processing. Doctoral thesis, Linköping University, Sweden
Buf JMH du (1992a) Modelling spatial vision at the threshold level. Spatial Vision 6:25–60
Buf JMH du (1992b) Brightness versus apparent contrast 3: Blurred disks and concentric cosine gratings. Spatial Vision 6:265–284
Buf JMH du (1992c) Abstract processes in texture discrimination. Spatial Vision 6:221–242
Buf JMH du (1993) Ambiguities in Gabor space. In: Gale AG (ed) Visual search III. Taylor and Francis Ltd, London
Caelli T, Oguztoreli MN (1987) Some task and signal dependent rules for spatial vision. Spatial Vision 2:295–315
Canny J (1986) A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell PAMI-8:679–698
De Valois RL, Yund EW, Hepler N (1982) The orientation and direction selectivity of cells in macaque visual cortex. Vision Res 22:531–544
Field DJ (1987) Relations between the statistics of natural images and the response properties of cortical cells. J Opt Soc Am A4:2379–2394
Granlund GH (1978) In search of a general picture processing operator. Comput Graph Image Proc 8:155–178
Grossberg S, Mingolla E, Todorović D (1989) A neural network architecture for preattentive vision. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng BME-36:65–84
Heitger F, Rosenthaler L, Heydt R von der, Peterhans E, Kübler O (1992) Simulation of neural contour mechanisms: from simple to end-stopped cells. Vision Res 32:963–981
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1974) Sequence regularity and geometry of orientation columns in the monkey striate cortex. J Comp Neurol 158:267–294
Koenderink JJ, Doorn AJ van (1990) Receptive field families. Biol Cybern 63:291–297
Marčelja S (1980) Mathematical description of the responses of simple cortical cells. J Opt Soc Am 70:1297–1300
Marr D, Hildreth E (1980) Theory of edge detection. Proc R Soc London Ser B-207:187–217
Morrone C, Owens R (1987) Feature detection from local energy. Pattern Recogn Lett 6:303–313
Mostafavi H, Sakrison DJ (1976) Structure and properties of a single channel in the human visual system. Vision Res 16:957–968
Olzak LA, Thomas JP (1986) Seeing spatial patterns. In: Boff KR, Kaufman L, Thomas JP (eds) Handbood of perception and human performance, vol I., Wiley, New York, pp 7-1 to 7-56
Owens R, Venkatesh S, Ross J (1989) Edge detection is a projection. Pattern Recogn Lett 9:233–244
Ross J, Morrone MC, Burr DC (1989) The conditions under which Mach bands are visible. Vision Res 29:699–715
Stork DG, Wilson HR (1990) Do Gabor functions provide appropriate descriptions of visual cortical receptive fields? J Opt Soc Am A7:1362–1373
Venkatesh S, Owens R (1990) On the classification of image features. Pattern Recogn Lett 11:339–349
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
du Buf, J.M.H. Responses of simple cells: events, interferences, and ambiguities. Biol. Cybern. 68, 321–333 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201857
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201857