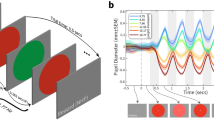
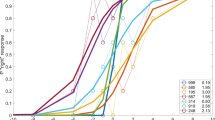
Abstract
Pupillary responses to sinusoidal light stimuli were measured over a range of light levels and frequencies. The phase lag and equivalent time delay of these responses were reduced in an approximately loglinear fashion with increasing mean light level (slope=-60ms/log unit). The magnitude of this level dependence is reduced at higher frequencies, and at higher light levels. This nonlinear level dependent signal flow (LDSF) effect is shown to be essentially independent of target distance (accommodative stimulus) which influences pupil size, and of pupil size itself. Thus most of the level dependence probably resides in the afferent path of the light-pupil reflex arc, before the accommodation signal joins the light signal in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus. A systems model is presented to the LDSF effect described here and in the companion papers (Myers and Stark 1993a, b). When parameters of the model are adjusted to fit pupillary responses to transient light stimuli over a range of light levels, the model simulates reduced phase lag in response to increased mean light level, and the reduction in this LDSF effect with increased mean light level or increasing stimulus frequency without further changes in parameters. This latter reduction explains the relatively small level dependence seen in latency data (-34ms/ log unit). These data will be shown (Myers and Stark 1990b) to be commensurate with reduction in pupil cycle time (increased frequency of oscillation) observed in high gain oscillation experiments as mean brightness increases. The model simulates directional asymmetry of pupillary response, with constriction faster than dilation, and tonic pupillary constriction in response to sinusoidal modulation of a light stimulus of fixed average brightness, the Varju-Troelstra effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell FW, Whiteside TCD (1950) Induced pupillary oscillations. Br J Ophthalmol 92:685–690
Miller SD, Thompson HS (1978) Edge-light pupil cycle time. Br J Opthalmol 62:495–500
Myers GA, Stark L (1990a) Light and target distance interact to control pupil size. Am J Physiol 258:R813-R819
Myers GA, Stark L (1990b) Topology of the near response triad. Opthalmol Physiol Opt 10:175–181
Myers GA, Stark L (1993a) Level dependent signal flow in the light pupil reflex: I. Latency of time domain responses to transient stimuli. Biol Cybern 66:229–234
Myers GA, Stark L (1993b) Level dependent signal flow in the light pupil reflex: III Phase velocity of high gain instability oscillations. Biol Cybern 68:241–246
Sandberg A, Stark L (1968) Weiner G-function analysis as an approach to non-linear characteristics of human pupil light reflex. Brain Res 11:194–211
Stark L, Cornsweet TN (1958) Testing a servoanalytic hypothesis for pupil oscillations. Science 127:588
Stark L (1959) Stability, oscillations and noise in the human pupil ervomechanism. Proc IRE 47: 1925–1935
Troelstra, A (1968) Detection of time-varying light signals as measured by the pupillary response Opt Soc Am 58 5:685–690
Varju, D (1964) Pupillenreaktionen auf sinusfurmige Leuchtdicheanderungen. Kybernetics 2:124
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Myers, G.A., Gannon, J.A. & Stark, L.W. Level dependent signal flow in the light pupil reflex. Biol. Cybern. 68, 235–240 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224857
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224857