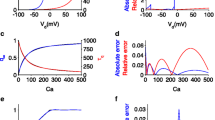
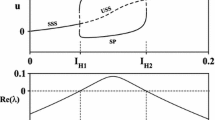
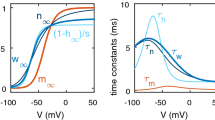
Abstract
Various nonlinear regenerative responses, including plateau potentials and bistable repetitive firing modes, have been observed in motoneurons under certain conditions. Our simulation results support the hypothesis that these responses are due to plateau-generating currents in the dendrites, consistent with a major role for a noninactivating calcium L-type current as suggested by experiments. Bistability as observed in the soma of low- and higher-frequency spiking or, under TTX, of near resting and depolarized plateau potentials, occurs because the dendrites can be in a near resting or depolarized stable steady state. We formulate and study a two-compartment minimal model of a motoneuron that segregates currents for fast spiking into a soma-like compartment and currents responsible for plateau potentials into a dendrite-like compartment. Current flows between compartments through a coupling conductance, mimicking electrotonic spread. We use bifurcation techniques to illuminate how the coupling strength affects somatic behavior. We look closely at the case of weak coupling strength to gain insight into the development of bistable patterns. Robust somatic bistability depends on the electrical separation since it occurs only for weak to moderate coupling conductance. We also illustrate that hysteresis of the two spiking states is a natural consequence of the plateau behavior in the dendrite compartment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amitai Y, Friedman A, Connors BW, Gutnick MJ (1993) Regenerative activity in apical dendrites of pyramidal cells in neocortex.Cerebral Cortex 3:26–38.
Brownstone RM, Gossard J-P, Hultborn H (1994) Voltage-dependent excitation of motoneurones from spinal locomotor centres in the cat.Exp. Brain Res. 102:34–44.
Conway BA, Hultborn H, Kiehn O, Mintz I (1988) Plateau potentials in α-motoneurones induced by intravenous injection of L-DOPA and clonidine in the spinal cat.J. Physiol. 405:369–384.
Edelstein-Keshet L (1988) Mathematical Models in Biology. Random House, New York. pp. 311–360.
Eken T, Kiehn O (1989) Bistable firing properties of soleus motor units in unrestrained rats.Acta Physiol. Scand. 136:383–394.
Fujita Y (1989) Dendritic spikes in normal spinal motoneurons of cats.Neuroscience Res. 6:299–308.
Gutman AM (1971) Further remarks on the effectiveness of the dendrite synapses.Biofizika 16:131–138.
Gutman AM (1991) Bistability of dendrites.Intl. J. Neural Sys. 1:291–304.
Hounsgaard J, Hultborn H, Jesperson B, Kiehn O (1988a) Bistability of α-motoneurones in the decerebrate cat and in the acute spinal cat after intravenous 5-hydroxytryptophan.J. Physiol. 405:345–367.
Hounsgaard J, Kiehn O (1989) Serotonin-induced bistability of turtle motoneurones caused by a nifedipine-sensitive calcium plateau potential.J. Physiol. 414:265–282.
Hounsgaard J, Kiehn O (1993) Calcium spikes and calcium plateaux evoked by differential polarization in dendrites of turtle motoneuronesin vitro, J. Physiol. 468:245–259.
Hounsgaard J, Kiehn O, Mintz I (1988b) Response properties of motoneurones in a slice preparation of the turtle spinal cord.J. Physiol. 398:575–589.
Hounsgaard J, Mintz 1 (1988) Calcium conductance and firing properties of spinal motoneurones in the turtle.J. Physiol. 398:591–603.
Huguenard JR, Hamill OP, Prince DA (1989) Sodium channels in dendrites of rat cortical pyramidal neurons.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 86:2473–2477.
Kiehn O (1991) Plateau potentials and active integration in the “final common pathway” for motor behavior.TINS 14:68–73.
Kiehn O, Eken T (1992) Discontinuous changes in discharge pattern of human motor units. (Abstract)J. Physiol. 452:277P.
Llinas R, Sugimori M (1980) Electrophysiological properties ofin vitro Purkinje cell dendrites in mammalian cerebellar slices.J. Physiol. 305:197–213.
Morris C, Lecar H (1981) Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber.Biophys. J. 35:193–213.
Pinsky PF, Rinzel J (1994) Intrinsic and network rhythmogenesis in a reduced Traub model for CA3 neurons.J. Comput. Neuro. 1:39–60.
Powers RK (1993) A variable-threshold motoneuron model that incorporates time- and voltage-dependent potassium and calcium conductances.J. Neurophysiol. 70:246–262.
Rall W (1962) Theory of physiological properties of dendrites.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 96:1071–1092.
Reuveni I, Friedman A, Amitai Y, Gutnick MJ (1993) Stepwise repolarization from Ca2+ plateaus in neocortical pyramidal cells: Evidence for nonhomogeneous distribution of HVA Ca2+ channels in dendrites.J. Neurosci. 13:4609–4621.
Rhodes PA, Gray CM (1994) Simulations of intrinsically bursting neocortical pyramidal neurons.Neural Computation 6:1086–1110.
Rinzel J, Baer SM (1988) Threshold for repetitive activity for a slow stimulus ramp: A memory effect and its dependence on fluctuations.Biophys. J. 54:551–555.
Rinzel J, Ermentrout GB (1989) Analysis of neural excitability and oscillations. In: Koch C, Segev I, eds. Methods in Neuronal Modeling: From Synapses to Networks. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. pp. 135–169.
Schwindt PC, Crill WE (1984) Membrane properites of cat spinal motoneurons. In: Davidoff R, ed. Handbook of the Spinal Cord. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY. pp. 199–242.
Stuart GJ, Sakmann B (1994) Active propagation of somatic action potentials into neocortical pyramidal cell dendrites.Nature 367:69–72.
Traub R, Wong R, Miles R, Michelson H (1991) A model of a CA3 hippocampal pyramidal neuron incorporating voltage-clamp data on intrinsic conductances.J. Neurophysiol. 66:635–649.
Walton K, Fulton BP (1986) Ionic mechanisms underlying the firing properties of rat neonatal motoneurons studiedin vitro. Neuroscience 19:669–683.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Booth, V., Rinzel, J. A minimal, compartmental model for a dendritic origin of bistability of motoneuron firing patterns. J Comput Neurosci 2, 299–312 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00961442
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00961442