Abstract
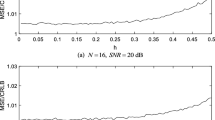
The ability of spread spectrum systems to combat interference can only be realised if the receiver is precisely synchronised with the incoming signal. The use of the sliding correlator for the acquisition of direct sequence spread spectrum signals is a popular method. Previous work considered either the single user in the fading and delay mobile environment or multi-users in the additive white Gaussian noise environment. In this paper the acquisition performance of the sliding correlator for direct sequence spread spectrum signals is investigated for the uplink case and in an environment where interference is caused both by multiple users and by multipath delays with different fading rates. The results show that a longer correlator length is required for optimum mean acquisition time in a slow fading environment. However in the multi-user, multipath environment when larger delays are present, the use of a longer correlation length is necessary in order to optimise the mean acquisition time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.F. Sage, “Serial synchronisation of pseudonoise system”, IEEE Trans. Commun., Vol. COM-13, pp. 123–127, 1964.
A. Polydoros and C.L. Weber, “A unified approach to serial search spread spectrum code acquisition — part I: General theory”, IEEE Trans. Commun., Vol. COM-32, pp. 542–560, 1984.
R.L. Pickholtz, D.L. Schilling and L.B. Millstein, “Theory of spread-spectrum communications — A tutorial”, IEEE Trans. Commun., Vol. COM-30, pp. 855–884, 1982.
J.K. Holmes and C.C. Chen, “Acquisition time performance of PN spread spectrum systems”, IEEE Trans. Commun., Vol. COM-25, pp. 778–783, 1977.
D.M. Dicarlo and C.L. Weber, “Statistical performance of single dwell serial synchronization systems”, IEEE Trans. Commun., Vol. COM-28, pp. 1382–1388, 1980.
P.M. Hopkins, “A unified analysis of pseudonoise synchronization by envelope correlator”, IEEE Trans. Commun., Vol. COM-25, pp. 770–773, 1977.
W.S.S. Jibrail and A.-R.J. Houmadi, “Acquisition of direct sequence spread spectrum signals using sliding correlators”, Int. J. Electronics, Vol. 71, pp. 733–743, 1991.
J.W. Mark and I.F. Blacke, “Rapid acquisition techniques in CDMA spread spectrum system”, Proc. F. Commun. Radar Signal Process (UK), Vol. 1131, pp. 223–232, 1984.
G.L. Turin, J.L. Clapp, T.L. Johnston, S.B. Fine and D. Lavry, “A statistical model of urban multipath propagation”, IEEE Trans. Vech. Technol., Vol. VT-21, pp. 1–9, 1972.
A.A.M. Saleh and R.A. Valenzuela, “A statistical model for indoor multipath propagation”, IEEE Journal on Sel. Areas in Commun., Vol. SAC-5, pp. 1245–1251, 1987.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, H., Burkley, C.J. Fading rate and multipath delay effects on signal acquisition using sliding correlation in a multi-user environment. Wireless Pers Commun 2, 235–244 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01099633
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01099633