Abstract
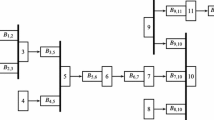
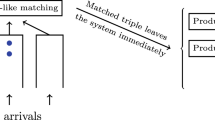
Assembly-like queues model assembly operations where separate input processes deliver different types of component (customer) and the service station assembles (serves) these input requests only when the correct mix of components (customers) is present at the input. In this work, we develop an effective approximate analytical solution for an assembly-like queueing system withN(N ⩾ 2) classes of customers formingN independent Poisson arrival streams with rates {λi=1,...,N} The arrival of a class of customers is “turned off” whenever the number of customers of that class in the system exceeds the number for any of the other classes by a certain amount. The approximation is based on the decomposition of the originalN input stream stage into a cascade ofN-1 two-input stream stages. This allows one to refer to the theory of paired customer systems as a foundation of the analysis, and makes the problem computationally tractable. Performance measures such as server utilization, throughput, average delays, etc., can then be easily computed. For illustrative purposes, the theory and techniques presented are applied to the approximate analysis of a system withN = 3. Numerical examples show that the approximation is very accurate over a wide range of parameters of interest.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.D. Harrison, Assembly-like queues, J. Appl. Prob. 10(1973)354.
G. Latouche, Queues with paired customers, J. Appl. Prob. 18(1981)684.
M.F. Neuts,Matrix-Geometric Solutions in Stochastic Models (Johns Hopkins, 1981).
V. Ramaswami, The N/G/1 queue and its detailed analysis, Adv. Appl. Prob. 12(1980)222.
H.M. Srivastava and B.R.K. Kashyap,Special Functions in Queueing Theory (Academic Press, 1982) pp. 69–75.
V. Ramaswami, A note on Neuts' versatile Markovian point process, Tech. Rep. No. 7-79, Dept. of Mathematics, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA (1979).
U.N. Bhat, Finite capacity assembly-like queues, Queueing Systems: Theory and Applications 1(1986)85.
E.H. Lipper and B. Sengupta, Assembly-like queues with finite buffer, Queueing Systems: Theory and Applications 1(1986)67.
F. Baccelli and W.A. Massey, Series-parallel, fork-join queueing networks and their stochastic ordering, to appear.
H. Heffes, A class of data traffic processes — covariance function characterization and related queueing results, BSTJ 59(1980)897.
U. Herzog, L. Woo and K.M. Chandy, Solution of queueing problems by a recursive technique, IBM J. Res. Develop. (May, 1975) 295.
D. Lucantoni, private communication.
J.J. Hunter,Mathematical Techniques of Applied Mathematics, Vol. 1–2 (Academic Press, 1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonomi, F. An approximate analysis for a class of assembly-like queues. Queueing Syst 1, 289–309 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01149540
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01149540