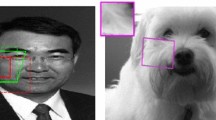
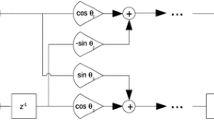
Abstract
In this paper we present a novel approach for template matching. The basic principle is expansion matching and it entails signal expansion into a set of nonorthogonal templatesimilar basis functions. The coefficients of this expansion signify the presence of the template in the corresponding locations in the image. We demonstrate that this matching technique is robust in conditions of noise, superposition, and severe occlusion. A new and more practical discriminative signal-to-noise ratio (DSNR) for matching is proposed that considers even the filter's off-center response to the template as “noise”. We show that expansion yields the optimal linear operator that maximizes the DSNR and results in a sharp response to the matched template. Theoretical and experimental comparisons of expansion matching and the widely used correlation matching demonstrate the superiority of our approach. Correlation matching (also known as matched filtering) yields broad peaks and spurious responses, both of which hamper good detection. We also show that the special case of expansion with a dense set of self-similar basis functions is equivalent to signal restoration. Expansion matching can be implemented by restoration techniques and also by our recently developed lattice architecture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrus JF, Campbell CW, Jayro RR (1975) Digital image registration using boundary maps. IEEE Trans Comput C-24, pp. 935–940
Ben-Arie J (1991) Linear lattice architectures that utilize the central limit for image analysis, Gaussian operators, sine, cosine, Fourier and Gabor transforms. Proc IEEE SPIE Conf Visual Commun Image Processing '91, Boston, pp. 823–838
Ben-Arie J (1992) Multi-dimensional linear lattice for Fourier and Gabor transforms, multiple-scale Gaussian filtering, and edge detection. In: H. Wechsler (ed) Neural Networks for Human and Machine Perception, Academic Press, pp. 231–252
Ben-Arie J, Rao KR (1991a) A lattice network for signal representation using Gaussian basis functions and max-energy paradigm. Proc IEEE 34th Midwest Symp Circuits Syst, Monterey, pp. 76–79
Ben-Arie J, Rao, KR (1991b) Parallel generation of Fourier and Gabor transforms and other shape descriptors by Gaussian wavelet groups using a set of multi-dimensional lattices. Proc IEEE 7th Workshop Multidimens Signal Processing Lake Placid, NY
Ben-Arie J, Rao KR (1991c) Signal representation by generalized non-orthogonal Gaussian wavelet groups using lattice networks. Proc IEEE Int Joint Conf Neural Networks, Singapore, pp. 968–973
Ben-Arie J, Rao KR (1992a) Lattice architectures for non-orthogonal representation of signals and generation of transforms using Gaussian sets. Technical Report IIT ECE-TR-005-92
Ben-Arie J, Rao KR (1992b) Lattice architectures for signal expansion by Gaussian set wavelets with application to recognition. Proc IEEE Int Symp Circuits Syst, San Diego, pp. 955–959
Ben-Arie J, Rao KR (1992c) On the use of non-orthogonal signal expansions for recognition. Proc Am Control Conf, Chicago, pp. 2996–3000
Ben-Arie J, Rao KR (1992d) Optimal operators for template and shape recognition by nonorthogonal image expansion, Proc 1992 SPIE Conf Intell Robots Comput Vision XI, Boston, pp. 226–237
Ben-Arie J, Rao KR (1993) A novel approach for template matching by nonorthogonal image expansion. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 3:71–84
Casasent D (1984) Unified synthetic discriminant function computational formulation. Appl Opt 23:1620–1627
Daugman JG (1988) Complete discrete 2-D Gabor transform by neural networks for image analysis and compression. IEEE Trans ASSP 36:1169–1179
Ebrahimi T, Kunt M (1991) Image compression by Gabor expansion. Opt Eng 30:873–880
Frei W, Chen CC (1977) Fast boundary detection: a generalization and a new algorithm. IEEE Trans Comput 26:988–998
Frieden BR (1967) Bandlimited reconstruction of optical objects and spectra, J Opt Soc Am 57:1013–1019
Frieden BR (1972) Restoring with maximum likelihood and maximum entropy. J Opt Soc Am 62:511–518
Haralick R, Shapiro L (1992) Computer and Robotic Vision, Addison Wesley
Harris JL (1964) Resolving power and decision theory. J Opt Soc Am 54:606–611
Helstrom CW (1967) Image restoration by the method of least squares. J Opt Soc Am 57:297–303
Higgins JR (1977) Completeness and basis properties of sets of special functions. Cambridge University Press, London
Horowitz M (1957) Efficient use of a picture correlator. J Opt Soc Am 47:327
Hueckel NH (1971) An operator which locates edges in digital pictures. J ACM 18:113–125
Hummel RA (1979) Feature detection using basis functions. Comput Graph Image Processing 9:40–55
Jain A (1989) Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall
Kumar BVKV (1986) Minimum variance synthetic discriminant functions. J Opt Soc Am 3:1579
Levine MD (1985) Vision in Man and Machine, McGraw-Hill
Mahalanobis A, Kumar BVKV, Casasent D (1987) Minimum average correlation energy filters. Appl Opt 26:3633–3640
Mostafavi H, Smith FW (1978) Image correlation with geometric distortion part I: acquisition performance. IEEE Trans A.E.S. AES-14:487–493
Papoulis A (1989) Probability, random variables, and stochastic processes. McGraw-Hill
Rabbani M, Jones PW (1991) Digital image compression techniques. SPIE Optical Engineering Press
Rao KR, Ben-Arie J (1993a) Generic face recognition, feature extraction and edge detection using optimal DSNR expansion matching. Proc IEEE Symp Circuits Syst, Chicago
Rao KR, Ben-Arie J (1993b) Image expansion by non-orthogonal basis functions extended for optimal multiple template matching. Proc IEEE Int Conf Acoustics, Speech Signal Processing, Minneapolis
Rosenfeld A, Kak A (1982) Digital Picture Processing, Academic Press
Schalkoff RJ (1989) Digital Image Processing and Computer Vision, John Wiley
Stockham G, Cannon TM, Ingebretsen RB (1975) Blind deconvolution through digital signal processing. Proc IEEE 63:678–692
Turin GL (1976) An introduction to digital matched filters. Proc IEEE 64:1092–1112
Turk MA, Pentland AP (1991) Face recognition using eigenfaces. Proc IEEE CVPR Conf, Hawaii, pp. 586–591
Wechsler H (1990) Computational Vision, Academic Press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Arie, J., Rao, K.R. Optimal template matching by nonorthogonal image expansion using restoration. Machine Vis. Apps. 7, 69–81 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01215803
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01215803