Abstract
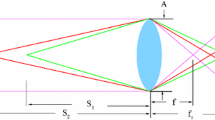
Images taken of 3D objects are generally defocused. Depth-from-focus techniques use the defocus information to determine range. However, quantitative measurement of focus is difficult and requires accurate modeling of the point-spread function (PSF). We describe a new method that determines depth using the symmetry and smoothness of focus gradient with respect to the focus position. The technique is passive and uses a monocular imaging system. The performance for estimating range is experimentally demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cardillo J, Sid-Ahmed MA (1991) 3-D position sensing using a passive monocular vision system. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Machine Intell 13:809–813
Darrell T, Wohn K (1988) Pyramid based depth from focus. Proceedings IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition '88, pp 504–509
Das S, Ahuja N (1989) Integrating multiresolution image acquisition and coarse-to-fine surface reconstruction. Proceedings of the Workshop on Interpretation of 3D Scenes, IEEE, 9–15
Engelhardt K (1988) Acquisition of 3-D data by focus sensing. Applied Optics 27:4684–4689
Ens J, Lawrence P (1993) An investigation of methods for determining depth from focus. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Machine Intell 15:97–108
Grossman P (1987) Depth from focus. Patt Recogn Lett 5:63–69
Horn BKP (1968) Focusing. MIT Project Mac. AI Memo No. 160, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Hwang T, Clark JJ, Yuille AL (1989) A depth recovery algorithm using defocus information. Proceedings IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition '89, 476–481
Jarvis RA (1976) Focus optimization criteria for computer image processing. Microscope 24:163–180
Kingslake R (1983) Optical system design. Academic Press, New York
Krotkov E (1987) Focusing. Int J Comput Vision 1:223–237
Lai S, Fu C, Chang S (1992) A generalized depth estimation algorithm with a single image. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Machine Intell 14:405–411
Nayar SK (1992) Shape from focus system for rough surfaces. Proceedings of the Image Understanding Workshop, pp 593–606
Pentland AP (1987) A new sense for depth of field. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Machine Intell 9:523–531
Pentland AP, Darrell T, Turk M, Huang W (1989) A simple, real-time range camera. Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition '89, pp 256–261
Rioux M, Biais F (1986) Compact three-dimensional camera for robotic applications. J Opt Soc Am A, 3:1518–1521
Subbarao M (1987) Direct recovery of depth-map. Proceedings of the IEEE Comput Soc Workshop Comput Vision pp 58–65
Subbarao M (1988) Parallel depth recovery by changing camera parameters. Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 149–155
Subbarao M (1989) Efficient depth recovery through inverse optics. In: H. Freeman (ed) Machine vision for inspection and measurement. Academic Press, New York, pp 101–126
Subbarao M, Natarajan G (1988) Depth recovery from blurred edges. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition'88, pp 498–503
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, S., Capson, D.W. & Caelli, T.M. Range measurement from defocus gradient. Machine Vis. Apps. 8, 179–186 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01215813
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01215813