Abstract
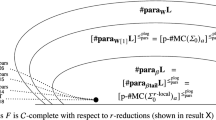
There exist many different formalisms to model the notion of resource bounded ‘truth-table’ reduction. Most papers in which truthtable reductions appear refer to the seminal paper of Ladner, Lynch and Selman for a definition. The definition of truth-table reductions given there however, pertains to only one of the possible incarnations of the notion. For larger resource bounds, this definition often coincides with other-often implicitly used-definitions of the notion. In this paper we focus our attention on resource bounds for which the various definitions probably donot pertain to the same notion. In particular, we show that coincidence of different notions implies coincidence of complexity classes likeNC 1,LOG, andP, which are widely believed to be different.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Balcázar, J. Díaz, and J. Gabarró,Structural Complexity I. Springer-Verlag, 1988.
J. Balcázar, J. Díaz, and J. Gabarró,Structural Complexity II. Springer-Verlag, 1990.
L. Berman, On the structure of complete sets: Almost everywhere complexity and infinitely often speedup.Proc. 17th IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computing (1976), 76–80.
L. Berman andH. Hartmanis, On isomorphisms and density of NP and other complete sets.SIAM J. Comput. 6 (1977), 305–322.
R.B. Boppana andM. Sipser, The complexity of finite functions. InHandbook of theoretical computer science, ed.J. van Leeuwen, vol. A Algorithms and Complexity, 757–804. Elsevier, Amsterdam. New York. Oxford. Tokyo, 1990.
H. Buhrman, S. Homer, andL. Torenvliet, On complete sets for nondeterministic classes.Math. Systems Theory 24 (1991), 179–200.
S. Cook, The complexity of theorem-proving procedures. InProc. 3rd ACM Symposium Theory of Computing, Shaker Heights, Ohio, 1971, 151–158.
J. Hartmanis, On the logtape isomorphism of complete sets.Theoretical Computer Science 7 (1978), 273–286.
N. Jones, Space bounded reducibilities among combinatorial problems.J. Comput. System Sci. 11 (1975), 68–85.
R. Karp, Reducibility among combinatorial problems. InComplexity of Computer Computations, ed.R. Miller andJ. Thatcher, 85–103. Plenum Press, New York, 1972.
R.E. Ladner andN. Lynch, Relativization of questions about logspace computability.Math. Systems Theory 10 (1976), 19–32.
R. Ladner, N. Lynch, andA. Selman, A comparison of polynomial time reducibilities.Theoret. Comput. Sci. 1 (1975), 103–123.
E. Post, Recursively enumerable sets of integers and their decision problems.Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 50 (1944), 284–316.
W.J. Savitch, Relationships between nondeterministic and deterministic tape complexities.J. Comput. System Sci. 4(2) (1970), 177–192.
P.M. Spira, On time-hardware complexity tradeoffs for boolean functions. InProc. 4th Hawai Symp. on System Sciences, North Hollywood, 1971, Western Periodicals Company, 525–527.
O. Watanabe, A comparison of polynomial time completeness notions.Theoret. Comput. Sci. 54 (1987), 249–265.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buhrman, H., Spaan, E. & Torenvliet, L. The relative power of logspace and polynomial time reductions. Comput Complexity 3, 231–244 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271369
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271369