Abstract
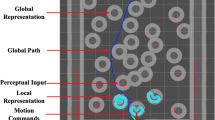
The importance of path planning is very significant in the field of robotics. This paper presents the application of multilayer perceptrons to the robot path planning problem, and in particular to the task of maze navigation. Previous published results implied that the training of feedforward multilayered networks failed, because of the non- smoothness of data. Here the path planning problem is reconsidered, and it is shown that multilayer perceptrons are able to learn the task successfully.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Latombe J-C. Robot Motion Planning. Kluwer Academic, 1991
Cameron S. Obstacle avoidance and path planning. Industrial Robot 1994; 21 (5)
Werbos PJ, Pang X. Generalized maze navigation: SRN critics solve what feedforward or hebbian nets cannot. World Congress on Neural Networks, San Diego, CA, 1996; 88–93. Lawrence Erlbaum INNS Press
Houillon P, Caron A. Planar robot control in cluttered space by artificial neural network. J Math Modeling and Computing 1993; 498–502
Pang X, Werbos P.J. Neural network design for J function approximation in dynamic programming. Neural Networks (to appear)
Bertsekas DP, Tsitsiklis JN. Neuro-Dynamic Programming. Athena Scientific, 1996
Dracopoulos DC. Evolutionary Learning Algorithms for Neural Adaptive Control. Springer-Verlag, 1997
White DA, Sofge DA (eds). Handbook of Intelligent Control. Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dracopoulos, D.C. Neural robot path planning: The maze problem. Neural Comput & Applic 7, 115–120 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01414163
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01414163