Abstract
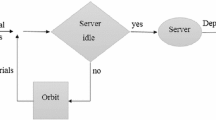
In this paper extensions to the numerical solution method of deterministic and stochastic Petri nets (DSPNs) are introduced in order to cope with deterministic transitions with marking-dependent firing delays. The basic idea lies in scaling each row of the generator matrix of the Markov chain subordinated to a deterministic transition with marking-dependent firing delay by the delay value corresponding to this marking. Computational formulas of this solution method are implemented in the software package DSPNexpress which completely automates the solution process of DSPNs. The extended modeling power of DSPNs is illustrated by a single-server queuing system with Poisson arrivals, degradable deterministic service requirements, and finite capacity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmone Marsan, M., Balbo, G., Bobbio, A., Chiola, G., Conte, G., and Cumani A. 1989. The effect of execution policies on the semantics and analysis of stochastic Petri nets.IEEE Trans. Software Eng. 15, pp. 832–846.
Ajmone Marsan, M., and Chiola, G. 1987. On Petri nets with deterministic and exponentially distributed firing times.Advances in Petri Nets 1987 (G. Rozenberg, ed.). Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 266, New York: Springer, pp. 132–145.
Bacelli, F., and Trivedi, K.S. 1983. Analysis of a M/G/2 standby redundant system.Proc. 9th Int. Symp. Computer Performance Modeling (A.K. Agarwala and S.K. Tripathi, eds.. Amsterdam: North-Holland, pp. 457–476.
Chiola, G. 1991. GreatSPN 1.5 software architecture.Proc. 5th Int. Conf. Modeling Techniques and Tools for Performance analysis, Torino Italy, pp. 117–132.
Chlamtac, I., Franta, W.R., and Levin, K.D. 1979. BRAM: the broadcast recognition access method.IEEE Trans. Comm., 27, pp. 1183–1189.
Choi, H., Mainkar, V., and Trivedi, K.S. 1993. Sensitivity analysis of deterministic and stochastic Petri nets.Proc. Int. Conf. Modeling Analysis and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems, San Diego, CA, pp. 271–276.
Ciardo, G., Blakemore, A., Chimento P.F., Muppala, J.K., and Trivedi, K.S. 1992. Automated generation of Markov reward models using stochastic reward nets.Linear Algebra, Markov Chains, and Queuing Models (C. Meyer and R.J. Plemmons, eds.), Vol. 48 of IMA Volumes in Mathematics and its Applications New York: Springer-Verlag.
Ciardo, G., Muppala, J., and Trivedi, K.S. 1989. SPNP: stochastic Petri net package.Proc. 3rd Int. Workshop Petri Nets and Performance Models, Kyoto, Japan, pp. 142–151.
Couvillion, J., Freire, R., Johnson, R., Obal, W.D., Qureshi, M.A., Rai, M., Sanders, W.H., and Twedt, J.E. 1991. Performability modeling with UltraSAN.IEEE Software, 8, pp. 69–80
Gross, D., and Miller, D.R., 1984. The randomization technique as a modeling tool and solution procedure for transient Markov processes.Oper. Res., 32, pp. 345–361.
Kulkarni, V.G., Nicola, V.F., and Trivedi, K.S. 1987. The completion time of a job on multimode systems.Adv. Appl. Probab., 19, pp. 932–954.
Leffler, S.J., McKusick, M.K., Karels, M.J., and Quarterman, J.S. 1989.The Design and Implementation of the 4.3BSD UNIX Operation System. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
Lindemann, C. 1993. An improved numerical algorithm for calculating steady-state solutions of deterministic and stochastic Petri net models.Perf. Eval. 18, (in print).
Lindemann, C. 1992a. A stochastic performance modeling technique for deterministic medium access schemes.Proc. 3rd IEEE Workshop Future Trends in Distributed Computing Systems, Taipei, Republic of China, pp. 346–353.
Lindemann, C. 1992b. DSPNexpress: a software package for the efficient solution of deterministic and stochastic Petri nets.Proc. 6th Int. Conf. Modeling Techniques and Tools for Computer Performance Evaluations. Edinburgh, GB, pp. 15–29.
Lindemann, C., Ciardo, G., German, R., and Hommel, G., 1993. Performability modeling of an automated manufacturing system with deterministic and stochastic Petri nets.Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robotics and Automation. Atlanta, GA, pp. 576–581.
Meyer, J.F. 1980. On evaluating the performability of degradable computing systems.IEEE Trans. Comput., 29, pp. 720–731.
Meyer, J.F., Movaghar, A., and Sanders, W.H. 1985. Stochastic activity networks: structure, behavior and application.Proc. 1st Int. Workshop Timed Petri Nets Torino, Italy, pp. 106–115.
Murata, T. 1989. Petri nets: properties, analysis and applications.proc. IEEE, 77, pp. 541–580.
O'Reilly and Associates Inc. 1990.The Definition Guides to the X Window System, Vol. 5, X Toolkit Intrinsics Reference Manual.
Sanders, W.H. and Meyer, J.F. 1991. A unified approach for specifying measures of performance, dependability, and performability. InDependable Computing for Critical Applications (A. Avizienis and J. Laprie, eds.). New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 216–237.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Christoph Lindemann was supported by the Federal Ministry for Research and Technology of Germany (BMFT) and by the German Research Council (DFG) under grants ITR9003 and Ho 1257/2-1, respectively.
Reinhard German was supported by Siemens Corporate Research and Development and by a doctoral fellowship from the German Research Council (DFG) under grant Ho 1257/1-2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindemann, C., German, R. Modeling discrete event systems with state-dependent deterministic service times. Discrete Event Dyn Syst 3, 249–270 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01439851
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01439851