Abstract
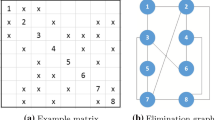
A dynamic factorization algorithm is developed which algebraically partitions the basis inverse in such a manner so that the simplex method can be executed from a series of small inverses and the basis itself. This partition is maintained dynamically so that the additional memory required to represent the basis inverse reduces to this series of small inverses for in-core implementations.
The algorithm is intended for use in solving general large-scale linear programming problems. This new method of basis representation should permit rather large problems to be solved completely in-core.
Preliminary computational experience is presented and comparisons are made with Reid's sparsity-exploiting variant of the Bartels—Golub decomposition for linear programming bases. The computational experience indicated that a significant reduction in memory requirements can usually be obtained using the dynamic factorization approach with only a slight (up to about 20%) degradation of execution time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.H. Bartels and G.H. Golub, “The simplex method of linear programming using LU decomposition”,Communications of the ACM 12 (1969) 266–268.
J. Bisschop and A. Meeraus, “Matrix augmentation and partitioning in the updating of the basis inverse”,Mathematical Programming 13 (1977) 241–254.
George B. Dantzig,Linear programming and extensions (Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, 1963).
J.J.H. Forrest and J.A. Tomlin, “Updating triangular factors of the basis to maintain sparsity in the product form simplex method”,Mathematical Programming 2 (1972) 263–278.
G.W. Graves, “A complete constructive algorithm for the general mixed linear programming problem”,Naval Research Logistics Quarterly 12 (1965) 1–34.
G.W. Graves and R.D. McBride, “The factorization approach to large-scale linear programming”,Mathematical Programming 10 (1976) 91–110.
P. Harris, “Pivot selection methods of the Devex LP code”,Mathematical Programming 5 (1973) 1–28.
E. Hellerman and D. Rarick, “Reinversion and the preassigned pivot procedure”,Mathematical Programming 1 (1971) 195–216.
E. Hellerman and D. Rarick, “The Partitioned Preassigned pivot procedure (P4)”, in: D.J. Rose and P.A. Willoughby, eds.,Sparse matrices and their applications (Plenum Press, New York, 1972) pp. 67–76.
R.D. McBride, “Factorization in large-scale linear programming”, Dissertation, University of California, Los Angeles (June 1973). (Available as Working Paper 200, Western Management Science Institute, UCLA).
R.D. McBride, “A spike collective dynamic factorization algorithm for the simplex method”,Management Science 24 (1978) 1031–1042.
J.K. Reid, “A sparsity-exploiting variant of the Bartels—Golub decomposition for linear programming bases”, Report CSS 20, Computer Science and Systems Division, A.E.R.E., Harwell, England (1975).
J.K. Reid, “FORTRAN subroutines for handling linear programming basis”, Report AERE-R 8269, Computer Science and Systems Division, A.E.R.E., Harwell, England (1976).
M.A. Saunders, “A fast, stable implementation of the simplex method using Bartels—Golub updating”, in: J.R. Bunch and D.J. Rose, eds.,Sparse matrix computations (Academic Press, New York, 1976) pp. 213–226.
J.H. Wilkinson,Rounding errors in algebraic processes (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported in part by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, Air Force System Command, USAF, under AFOSR Contract/Grant Number AFOSR-74-2715.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McBride, R.D. A bump triangular dynamic factorization algorithm for the simplex method. Mathematical Programming 18, 49–61 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01588296
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01588296