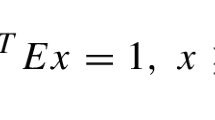Abstract
In this work non-convex programs are analyzed via Legendre transform. The first part includes definitions and the classification of programs that can be handled by the transformation. It is shown that differentiable functions that are represented as a sum of strictly concave and convex functions belong to this class. Conditions under which a function may have such representation are given. Pseudo duality is defined and the pseudo duality theorem for non linear programs with equality constraints is proved.
The techniques described are constructive ones, and they enable tocalculate explicitly a pseudo dual once the primal program is given. Several examples are included. In the convex case these techniques enable the explicit calculation of the dual even in cases where direct calculation was not possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.T. Rockafellar,Convex analysis (Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ. 1970).
W. Fenchel, “On conjugate convex functions”,Canadian Journal of Mathematics 1 (1949) 73–77.
R.J. Duffin, E.L. Peterson and C. Zener,Geometric programming, (John Wiley, New York, 1967).
S. Yutav, “Pseudo duality in mathematical programming”, Ph.D. Dissertation, Faculty of Industrial and Management Engineering, Technion (Haifa, 1978).
I. Ekeland, “Legendre duality in nonconvex optimization and calculus of variations”,SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization 15 (1977) 905–934.
U. Passy and S. Yutav, “Pseudo duality in mathematical programming part A: unconstrained and equality constraints”, Operation Research, Statistics and Economics Mimeograph Series No. 208, Faculty of Indust. Engrg. and Management, Technion, Haifa, Israel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Passy, U., Yutav, S. Pseudo duality in mathematical programming: Unconstrained problems and problems with equality constraints. Mathematical Programming 18, 248–273 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01588322
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01588322