Abstract
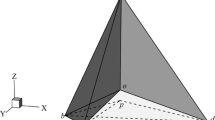
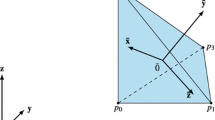
In this paper, a simulated three-dimensional virtual environment is created with a virtual 3D track ball for virtual object control. We propose a new technique called HV Partition to detect accurate collision in the assembly of two polyhedral solids in virtual simulation. This is a solid interference detection methodology achieved by automatically partitioning the object into smaller solid boxes. An important advantage of this methodology compared with other approaches is that it can deal with non-convex objects. This means that mechanical components, represented by non-convex polyhedra, traversing any degree of freedom, can be used in this virtual environment. Using this HV Partition method, the precise interference between two polyhedral solid objects can be found. The HV Partition methodology is applied following initial approximate collision detection using traditional bounding box and bounding sphere methods. The smaller the number of smaller boxes, the quicker is the performance of the collision algorithm. An optimal partition method is also given to reduce the number of smaller boxes in an object.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Cohen, J.D., Lin, M.C., Manocha, D., (1994).Exact Collision Detection for Interactive Environments. Proceeding of the Tenth Annual Symposium on Computer Geometry. (New York, ACM Press).
Fa, M., Fernando, T., Dew, P.M. and Munlin, M., (1994).Constraint-based 3D Manipulation Techniques within Virtual environments. International State of the Art Conference on Virtual Reality Applications, Leeds.
Fairchild, K.M., Poston, T. and Brichen, W., (1994).Efficient Virtual Collision Detection for Multiple users in Large Virtual Spaces. Virtual Reality Software and Technology.
Figueiredo, M., Teixeira, J.C., Bohm, K., (1994).Direct Interactions in Virtual Environments. CG topics.
Ganter, M.A. and Isarankura, B.P., (1990).Dynamic Collision Detection Using Space Partitioning. Advances in Design Automation1, 175–181.
Kovesi, P.K., (1985).Collision Avoidance. ICAR, 51–58.
Rogers, D.F. and Adams, J.A., (1976).Mathematical Elements for Computer Graphics. (McGraw-Hill Book Company).
Tornero, J., Hamlin, J. and Kelley, R.B., (1991).Spherical-Object Representation and Fast Distance Computation for Robotic Applications. Proceedings of the 1991 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation3, 1602–1608.
Uchiki, T., Ohashi, T. and Tokoro, M., (1983).Collision Detection in Motion Simulation. Computer and Graphics7(3–4), 285–293.
Yuen, M.M.F., (1988).A Technique for Collision Detection and Obstacles Avoidance in Solid Modelling Based Mechanism Design. 4th International Conference on Computer-Aided Production Engineering4, 391–400.
Zyda, M.J., Osborne, W.D., Monahan, J.G., Pratt, D.R., (1993).NPSNET: Real-time Collision Detection and Response. The Journal of Visualization and Computer Animation4(1):13–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, J.J., Clark, D.E.R. & Simmons, J.E.L. Collision detection methodologies for rigid body assembly in a virtual environment. Virtual Reality 1, 41–48 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02009712
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02009712