Abstract
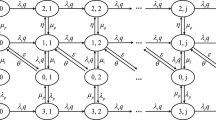
In this paper, out-of-slot random access protocols for voice services that operate in microcellular environment are studied and simulated. The bearer service is assumed to be structured as time division multiple access/frequency division multiple access/frequency division duplex (TDMA/ FDMA/FDD). According to a stratification of information flow ascall, talkspurt, andpacket, the protocols are implemented at the talkspurt level. During a call, talkspurts generate a stream of packets. Each talkspurt has to reserve a voice time slot with a special control packet sent in a dedicate control slot (out of slot signaling). After a successful access, a voice slot is assigned for the duration of the talkspurt. This work concentrates on the out of slot random access method. When a transition from the idle state to the active state occurs, a voice terminal starts generating a talkspurt. Access for a voice slotV is then initiated via a dedicated control slotC. The time spent in gaining aV slot depends on the kind of random access protocol used in theC slots. Once the access reservation phase is successful, the talkspurt starts the second phase of information transmission in a freeV slot. If allV slots are occupied by other talkspurts, the new talkspurt is queued until aV slot becomes free. If the sum of the access and queueing times exceeds a thresh-old, a portion of the talkspurt is clipped. In our work we define an analytical model to evaluate the percentage of clipped voice packets. Simulations validate the analytical model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Filipiak,Real Time Network Management, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1991.
S. R. Sach, Alternative local area network access protocols,IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 26, No. 3, pp. 25–45, 1988.
V. O. K. Li and T-Y. Yan, An integrated voice and data multiplexing access scheme for land mobile satellite system,IEEE Proceedings, Vol. 27, No. 11, pp. 1611–1619, 1984.
D. Rachaudury and K. Joseph, Channel access protocols for Kuband VSAT networks: a comparative evolution,IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 26, No. 5, pp. 34–44, 1988.
D. J. Goodman, Cellular packet communications,IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 38, No. 8, pp. 1272–1280, 1990.
N. M. Mitrou, Th. D. Orinos, and E. N. Protonotarios, A reservation multiple access protocol for micro cellular mobile-communication systems,IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, Vol. 39, No. 4, pp. 340–351. 1990.
S. Jangi and L. Merakos, Performance analysis of reservation random access protocols for cellular packet communications, Proc. GLOBECOM'91, pp. 895–900, 1991.
C. J. Weinstein, Fractional speech loss and talker activity model for TASI and for packet-switched speech,IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. COM-26, No. 8, pp. 1253–1257, 1978.
V. Casares and J. Paradells, Variable voice service rate in wireless access packet networks, Proceedings of Wireless 93, pp. 609–623, Calgary, 1993.
V. Casares and J. Alcober, Voice and data integration in wireless networks, Proceedings of Wireless 94, pp. 1–11, Calgary, 1994.
R. B. Cooper,Introduction to Queueing Theory, Macmillan, New York, 1972.
S. Jangi and L. Merakos, Performance analysis of reservation random access protocols for wireless access networks,IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 42, No. 2/3/4, pp. 1223–1234, 1994.
R. L. Rivest, Network control by Bayesian broadcast,IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, Vol. IT-33, No. 3, pp. 323–327, 1987.
M. Paterakis and P. Papantoni-Kazakos, A simple window random access algorithm with advantageous properties,IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, Vol. 35, No. 5, pp. 1124–1130, 1989.
G. A. Cunningham III, Delay versus throughput comparisons for stablilized ALOHA,IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 38, No. 11, pp. 1932–1934, 1990.
A. M. Law and W. D. Kelton,Simulation Modeling and Analysis, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1982.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The second version of this work was rewritten while the author was a visiting scholar at WINLAB
The IS-54 standard itself has the TDMA/FDMA structure. The ETDMA “enhancement” appears to be very much like what is described in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giner, V.C. An approximate analysis of TDMA out-of-slot random access protocols for microcellular mobile communications. Int J Wireless Inf Networks 3, 41–53 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02106661
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02106661