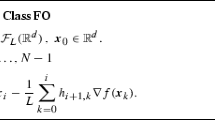Abstract
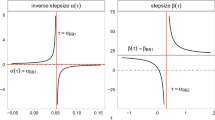
The computation of step-sizes which guarantee convergence in unconstrained minimization by descent methods is considered. The use of a “control” or “range” function is highly attractive for this purpose because of its simplicity. Since the Armijo-Goldstein test may fail prematurely due to numerical instability near the minimizer, we consider a range function based on gradient values alone as has been done forg convex in [8]. Numerical algorithms are given for the computation of step-sizes whose behaviour under roundoff is shown to be benign in the sense of F. L. Bauer [5].
Zusammenfassung
Es wird die Berechnung konvergenzerzeugender Schrittweiten bei Abstiegsverfahren zur unrestringierten Minimierung betrachtet. Die Verwendung einer „Kontroll-” oder „Bereichs”-Funktion ist in diesem Zusammenhang wegen ihrer Einfachheit besonders attraktiv. Da der Test nach Armijo und Goldstein in der Nähe eines Minimums aufgrund numerischer Instabilität vorzeitig versagen kann, betrachten wir eine Bereichsfunktion, in die nur Gradientenwerte eingehen, wie dies in [8] für den konvexen Fall geschehen ist. Es werden numerische Algorithmen zur Schrittweitenberechnung angegeben, deren Verhalten unter Rundungsfehlereinfluß gutartig ist im Sinne von F. L. Bauer [5].
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, J. P.: Factors affecting the stability of methods of the Davidon-Fletcher-Powell type. Unpublished paper referenced in: Numerical methods for unconstrained optimization (Murray, W., ed.), p. 103. New York-London: Academic Press 1972.
Altman, M.: Generalized gradient methods of minimizing a functional. Bull. Acad. Polon. Sci.14, 313–318 (1966).
Armijo, L.: Minimization of functions having Lipschitz-continuous first partial derivatives. Pacif. J. Math.16, 1–3 (1966).
Barth, W.: Nullstellenbestimmung mit der Intervallrechnung. Computing8, 320–328 (1971).
Bauer, F. L.: Numerische Abschätzung und Berechnung von Eigenwerten nichtsymmetrischer Matrizen. Aplikace Matematiky10, 178–189 (1965).
Brent, R. P.: Algorithms for minimization without derivatives. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall 1973.
Daniel, J. W.: Convergent step sizes for gradient like feasible direction algorithms for constrained optimization, pp. 245–274, in: Nonlinear Programming (Rosen, Mangasarian, Ritter, eds.). New York-London: Academic Press 1970.
Dietze, S., Schwetlick, H.: Über die Schrittweitenwahl bei Abstiegsverfahren zur Minimierung konvexer Funktionen. ZAMM51, 451–454 (1971).
Goldstein, A. A.: Constructive real analysis. New York: Harper & Row 1967.
Lenard, M.: Practical convergence conditions for the Davidon-Fletcher-Powell method. Math. Prog.9, 69–86 (1975).
Ortega, J. M., Rheinboldt, W. C.: Iterative solution of nonlinear equations in several variables. New York-London: Academic Press 1970.
Wolfe, P.: Convergence conditions for ascent methods. SIAM Review11, 226–235 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spellucci, P. Numerically stable computation of step-sizes for descent methods. The nonconvex case. Computing 18, 149–160 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02243624
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02243624