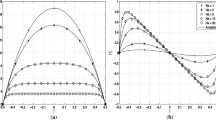
Summary
The magnetohydrodynamic model system is integrated numerically as an initial-value problem. The system is integrated using two-different numerical methods. The first uses a special finite difference scheme introduced byBellman. The second makes use of the classical method of converting a partial differential equation into an infinite system of ordinary differential equations. The formulation for each computational scheme is discussed and numerical example presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Burgers, J. M.: Advances in Applied Mechanics. Vol. 1, p. 171. New York: Academic Press, Inc. 1948.
Thomas, J. H.: Numerical Experiments on a Model System for Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence. Phys. Fluids11, 1245 (1968).
Bellman, R. E., R. E. Klaba, andB. Kotkin: On a New Approach to the Computational Solution of Partial Differential Equations. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U. S.48, 1325 (1962).
Bellman, R. E., I. Cherry, andC. M. Wing: A Note on the Numerical Integration of a Class of Nonlinear Hyperbolic Equations. Quart. Appl. Math.16, 181 (1958).
Bellman, R. E., S. P. Azen, andJ. M. Richardson: On New and Direct Computational Approaches to Some Mathematical Models of Turbulence. Quart. Appl. Math.23, 55 (1965).
Bellman, R. E.: On the Existence and Boundedness of Solution of Nonlinear Partial Differential Equation of Parabolic Type. Trans. Am. Math. Soc.64, 21 (1948).
Ralson, A., andH. S. Wilf: Mathematical Method of Digital Computer, p. 95. New York: Wiley. 1960.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 10 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeng, DT. Direct computational approaches to a magnetohydrodynamic model system. Computing 7, 1–12 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02279936
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02279936