Abstract
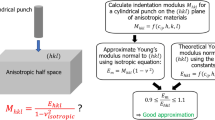
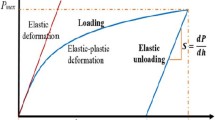
Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio of a tissue can be simultaneously obtained using two indentation tests with two different sized indentors in two indentations. Owing to the assumption of infinitesimal deformation of the indentation, the finite deformation effect of indentation on the calculated material parameters was not fully understood in the double indentation approach. However, indentation tests with infinitesimal deformation are not practical for the measurement of real tissues. Accordingly, finite element models were developed to simulate the indentation with different indentor diameters and different deformation ratios to investigate the finite deformation effect of indentation. The results indicated that Young's modulus E increased with the increase in the indentation deformation w, if the finite deformation effect of indentation was not considered. This phenomenon became obvious when Poisson's ratio v approached 0.5 and/or the ratio of indentor radius and tissue thickness a/h increased. The calculated Young's modulus could be different by 23% at 10% deformation in comparison with its real value. The results also demonstrated that the finite deformation effect to indentation on the calculation of Poisson's ratio v was much smaller. After the finite deformation effect of indentation was considered, the error of the calculated Young's modulus could be controlled within 5% (a/h=1) and 2% (a/h=2) for deformation up to 10%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athanasiou, K. A., Agarwal, A., andDzida, F. J. (1994): ‘Comparative study if the intrinsic mechanical properties of the human acetabular and femoral head cartilage’,J. Orthop. Res.,12, pp. 340–349
Barker, M. K., andSeedhom, B. B. (1997): ‘Articular cartilage deformation under physiological cyclic loading—apparatus and measurement technique’,J. Biomech.,30, pp. 377–381
Hayes, W. C., Keer, L. M., Herrmann, G., andMockros, L. F. (1972): ‘A mathematical analysis for indentation tests of articular cartilage’,J. Biomech.,5, pp. 541–551
Jin, H., andLewis, J. L. (2004): ‘Determination of Poisson's ratio of articular cartilage by indentation using different-sized indenters’,J. Biomech. Eng.,126, pp. 138–145
Jurvelin, J. S., Buschmann, M. D., andHunziker, E. B. (1997): ‘Optical and mechanical determination of Poisson's ratio of adult bovine humeral articular cartilage’,J. Biomech.,30, pp. 235–241
Kempson, G. E., Freeman, M. A. R., andSwanson, S. A. V. (1971): ‘The determination of a creep modulus for articular cartilage from indentation tests on the human femoral head’,J. Biomech.,4, pp. 239–250
Klaesner, J. W., Commean, P. K., Hastings, M. K., Zou, D. Q., andMueller, M. J. (2001): ‘Accuracy and reliability testing of a portable soft tissue indentor’,IEEE. Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng.,9, pp. 232–240
Mak, A. F. T., Liu, G. H. W., andLee, S. Y. (1994): ‘Biomechanical assessment of below-knee residual limb tissue’,J. Rehabil. Res. Dev.,31, pp. 188–198
Mow, V. C., Gibbs, M. C., Lai, W. M., Zhu, W. B., andAthanasiou, K. A. (1989): ‘Biphasic indentation of articular cartilage. Part II: a numerical algorithm and an experimental study’,J. Biomech.,22, pp. 853–861
Pierard, G. E. (1984): ‘Evaluation of mechanical properties of skin by indentation and compression methods’,Dermatology,168, pp. 61–66
Spilker, R. L., Suh, J. K., andMow, V. C. (1992): ‘A finite element analysis of the indentation stress-relaxation response of linear biphasic articular cartilage’,J. Biomech. Eng.,114, pp. 191–201
Suh, J. K. F., Youn, I., andFu, F. H. (2001): ‘Anin situ calibration of an ultrasound transducer: a potential application for an ultrasonic indentation test of articular cartilage’,J. Biomech.,34, pp. 1347–1353
Toyras, J., Lyyra, L. T., Niinimaki, M., Lindgren, R., Nieminen, M. T., Kiviranta, I., andJurvelin, J. S. (2001): ‘Estimation of the Young's modulus of articular cartilage using an arthroscopic indentation instrument and ultrasonic measurement of tissue thickness’,J. Biomech.,34, pp. 251–256
Zhang, M., Zheng, Y. P., andMak, A. F. T. (1997): ‘Estimating the effective Young's modulus of soft tissues from indentation tests-nonlinear finite element analysis of effects of frication and large deformation’,Med. Eng. Phys.,19, pp. 512–517
Zheng, Y. P., andMak, A. F. T. (1996): ‘An ultrasound indentation system for biomechanical properties assessment of soft tissuein-vivo’,IEEE. Trans. Biomed. Eng.,43, pp. 912–918
Zheng, Y. P., Mak, A. F. T., andLue, B. (1999): ‘Objective assessment of limb tissue elasticity: Development of a manual indentation procedure’,J. Rehabil. Res. Dev.,36, pp. 71–85
Zheng, Y. P., Choi, Y. K. C., Wong, K., Chan, S., andMak, A. F. T. (2000): ‘Biomechanical assessment of plantar foot tissue in diabetic patients using an ultrasound indentation system’,Ultrasound Med. Biol.,26, pp. 451–456
Zheng, Y. P., Mak, A. F. T., andLeung, A. K. L. (2001): ‘State of the art methods for geometric and biomechanical assessments of residual limbs: A review’,J. Rehabil. Res. Dev.,38, pp. 487–504
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, A.P.C., Zheng, Y.P. Estimation of Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio of soft tissue from indentation using two different-sized indentors: Finite element analysis of the finite deformation effect. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 43, 258–264 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345964
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345964