Abstract
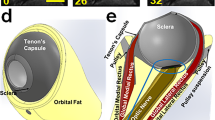
In blind subjects who still have functional retinal ganglion cells, electrical stimuli applied to the optic nerve can produce localised visual sensations. This has been demonstrated with an intracranially implanted self-sizing spiral cuff electrode, but, to avoid skull opening, intra-orbital cuff implantation is now considered. In its orbital segment, the optic nerve is surrounded by subarachnoidal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and dura mater. Dura mater is a tough fibrous tissue that can impede electrical stimulation. In the study, the issue of whether or not to remove the dura mater at the implantation site was addressed using simulation on numerical models. Several volume conductor models were built representing, respectively: the cuff implanted directly around the nerve; the cuff over the nerve after connective tissue encapsulated the implant; and the cuff electrode placed around the dura mater. Stimulation-induced electric potential fields were computed for these configurations using a full 3D finite elements software. Responses of fibres within the nerve were computed. A large range of dural conductivities and several CSF thicknesses were considered. In all simulated conditions, the presence of dura mater around a layer of CSF increased excitation thresholds. Selectivity performance also decreased, but was found to be independent of the CSF thickness. However, simulations showed that, if the diameter of the cuff electrode is adapted to the target nerve, the injected charge associated with activation is limited within a reasonable range. Electrical stimulation of the optic nerve with a cuff electrode implanted around the dura mater should therefore be feasible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butt, A. M., andJenkins, H. G. (1994): ‘Morphological changes in oligodendrocytes in the intact mouse optic nerve following intravitreal injection of tumour necrosis factor’,J. Neuroimmunol.,51, pp. 27–33
Chintalacharuvu, R. R., Ksienski, D. A., andMortimer, J. T. (1991): ‘A numerical analysis of the electric field generated by a nerve cuff electrode’,Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 13th Ann. Conf.,13, pp. 912–913
Coburn, B., andSin, W. K. (1985): ‘A theoretical study of epidural electrical stimulation of the spinal cord-Part I: Finite element analysis of stimulus fields’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,32, pp. 971–977
Cuoco, F. A., andDurand, D. M. (2000): ‘Measurement of external pressures generated by nerve cuff electrodes’,IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng.,8, pp. 35–41
Delbeke, J., Wanet-Defalque, M.-C., Gerard, B., Troosters, M., Michaux, G., andVeraart, C. (2002): ‘The microsystems based visual prosthesis for optic nerve stimulation’,Artif. Organs,26, pp. 232–234
Delbeke, J., Oozeer M., andVeraart C. (2003): ‘Position, size and luminosity of phosphenes generated by direct optic nerve stimulation’,Vision Res.,43, pp. 1091–1102
George, A., andLiu, J. W. (1981): ‘Computer solution of large sparse positive definite systems’, (Prentice Hall, 1981)
Goodall, E., Kosterman, L., andStruijk, J. (1995): ‘Modeling study of activation and propagation delays during stimulation of peripheral nerve fibers with a tripolar cuff electrode’,IEEE Trans. Rehab. Eng.,3, pp. 272–282
Griffin, A. E., andBurke, W. (1974): ‘The distribution and nerve fibre groups in the optic tract and lateral geniculate nucleus of macaca irus’,Proc. Aust. Physiol. Pharmacol. Soc.,5, pp. 74P
Grill, W. M., andMortimer, J. T. (1994): ‘Electrical properties of implant encapsulation tissue’,Ann. Biomed. Eng.,22, pp. 23–33
Hibbert, D. B., Weitzner, K., andCarter, P. (2001): ‘Voltammetry of platinum in artificial perilymph solution’,J. Electrochem. Soc.,148, pp. E1-E7
Humayun, M. S., de Juan, E., Jr, Dagnelie, G., Greenberg, R. J., Propst, R. H., andPhillips, D. H. (1996): ‘Visual perception elicited by electrical stimulation of retina in blind humans’,Arch. Ophthalmol.,114, pp. 40–46
Jonas, J. B., Muller-Bergh, J. A., Schlotzer-Schrehardt, U. M., andNaumann, G. O. (1990): ‘Histomorphometry of the human optic nerve’,Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.,31, pp. 736–744
Killer, H. E., Laeng, H. R., Flammer, J., andGroscurth, P. (2003): ‘Architecture of arachnoid trabeculae, pillars, and septa in the subarachnoid space of the human optic nerve: anatomy and clinical considerations’,Br. J. Ophthalmol.,87, pp. 777–781
Knight, R. S., Fielder, A. R., andFirth, J. L. (1986): ‘Benign intracranial hypertension: visual loss and optic nerve sheath fenestration’,J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry,49, pp. 243–250
Magnaes, B. (1976): ‘Body position and cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Part 2: clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point’,J. Neurosurg.,44, pp. 698–705.
McCreery, D. B., andAgnew, W. F. (1990): ‘Mechanisms of stimulation-induced neural damage and their relation to guidelines for safe stimulation’in Agnew, W. F., andMcCreery, D. B. (Eds):’ Neural prostheses: Fundamental studies (Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, 1990)
McCreery, D. B., Agnew, W. F., Yuen, T. G. H., andBullara, L. A. (1990): ‘Charge density and charge per phase as cofactors in neural injury induced by electrical stimulation’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,37, pp. 996–1001
McCreery, D. B., Agnew, W. F., Yuen, T. G. H., andBullara, L. A. (1995): ‘Relationship between stimulus amplitude, stimulus frequency and neural damage during electrical stimulation of sciatic nerve of cat’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,33, pp. 426–429
McNeal, D. (1976): ‘Analysis of a model for excitation of myelinated nerve’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,23, pp. 329–337
Mokri, B., Hunter, S. F., Atkinson, J. L. andPiepgras, D. G. (1998): ‘Orthostatic headaches caused by CSF leak but with normal CSF pressures’,J. Neurol.,51, pp. 786–790
Morgan, W. H., Yu, D. Y., Cooper, R. L., Alder, V. A., Cringle, S. J., andConstable, I. J. (1995): ‘The influence of cerebrospinal fluid pressure on the lamina cribosa tissue pressure gradient’,Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.,36, pp. 1163–1172
Naito, J. (1996): ‘Morphological and quantitative analysis of the fascicular pattern of monkey optic nerve’,Cell Tissue Res.,283, pp. 255–261
Naples, G. G., Mortimer, J. T., Scheiner, A., andSweeney, J. D. (1988): ‘A spiral nerve cuff electrode for peripheral nerve stimulation’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,35, pp. 905–916
Ogden, T. E. (1983): ‘Nerve fiber layer of the macaque retina: retinotopic organization’,Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.,24, pp. 85–98
Oozeer, M., Andrien, A., Delbeke, J., Legat, V., andVeraart, C. (2001): ‘A modeling study of optic nerve stimulation by surface eyelid electrode’,Proc. IFESS 6th Ann. Conf.,6, pp. 102–104
Oozeer, M., Veraart, C., andDelbeke, J. (2003): ‘A modelling approach of the intra-orbital optic nerve stimulation’,Proc. 4th MATHMOD Vienna,4, p. 294
Parrini, S., Romero, E., Delbeke, J., Legat, V., andVeraart, C. (1999): ‘A hybrid finite elements—spectral method for computation of the electric potential generated by a nerve cuff electrode’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,37, pp. 733–736
Parrini, S., Delbeke, J., Legat, V., andVeraart, C. (2000): ‘A modelling analysis of human optic nerve fibre excitation based on experimental data’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,38, pp. 454–464
Rattay, F. (1990): ‘Electrical nerve stimulation: theory, experiments and applications’ (Springer-Verlag, New-York, 1990)
Robblee, L. S., Lefko, J. L., andBrummer, S. B. (1983): ‘Activated iridium: An electrode suitable for reversible charge injection in saline solution’,J. Electrochem. Soc.,130, pp. 731–733
Rose, T. L., andRobblee, L. S. (1990): ‘Electrical stimulation with Pt electrodes. VIII. Electrochemically safe charge injection limits with 0.2 ms pulses’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,37, pp. 1118–1120
Schwarz, J., Reid, G., andBostock, H. (1995): ‘Action potentials and membrane currents in the human node of Ranvier’,Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol.,430, pp. 283–292
Stone, J. L. (1983): ‘Parallel processing in the visual system’ (Plenum Press, New York, 1983)
Stone, J. L., Barlow, W. E., Humayun, M. S., de Juan, E., Jr, andMilam, A. H. (1992): ‘Morphometric analysis of macular photoreceptors and ganglion cells in retinas with retinitis pigmentosa’Arch. Ophthalmol.,110, pp. 1634–1639
Struijk, J. J., Holsheimer, J., Barolat, G., He, J., andBoom, B. K. (1993): ‘Paresthesia thresholds in spinal cord stimulation: a comparison of theoretical results with clinical data’,IEEE Trans. Rehab. Eng.,1, pp. 101–108
Thoma, H., Gerner, H., Holle, J., Kluger, P., Mayr, W., Meister, B., Schwanda, G., andStohr, H. (1987): ‘The phrenic pacemaker: substitution of paralyzed functions in tetraplegia’,Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs. Trans.,10, pp. 472–479
Veltink, P. H., van Veen, B. K., Struijk, J. J., andBoom, H. B. (1989): ‘A modeling study of nerve fascicle stimulation’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,36, pp. 683–692
Veraart, C., Raftopoulos, C., Mortimer, J. T., Delbeke, J., Pins, D., Michaux, G., Vanlierde, A., Parrini S., andWanet-Defalque, M.-C. (1998): ‘Visual sensations produced by optic nerve stimulation using an implanted self-sizing spiral cuff electrode’,Brain Res.,813, pp. 181–186
Veraart, C., Duret, F., Brelen, M., Oozeer, M., andDelbeke, J. (2004): ‘Vision rehabilitation in the case of blindness’,Expert Rev. Med. Devices,1, pp. 139–153
Villain, M., Sandillon, F., Muller, A., Candon, E., Alonso, G., Arnaud, B., andPrivat, A. (2002): ‘Macroglial alterations after isolated optic nerve sheath fenestration in rabbit’,Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.,43, pp. 120–128
Weerasuriya, A., Spangler, R. A., Rapoport, S. I., andTaylor, R. E. (1984): ‘AC impedance of the perineurium of the frog sciatic nerve’,Biophys. J.,46, pp. 167–174
Wesselink, W. A., Holsheimer, J., andBoom, H. B. (1998): ‘Analysis of current density and related parameters in spinal cord stimulation’,IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng.,6, pp. 200–207
Wesselink, W., Holsheimer, J., andBoom, H. (1999): ‘A model of the electrical behaviour of myelinated sensory nerve fibres based on human data’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,37, pp. 228–235
Zrenner, E., Miliczek, K. D., Gabel, V. P., Graf, H. G., Guenther, E., Haemmerle, H., Hoefflinger, B., Kohler, K., Nisch, W., Schubert, M., Stett, A., andWeiss, S. (1997): ‘The development of subretinal microphotodiodes for replacement of degenerated photoreceptors’,Ophthalm. Res.,29, pp. 269–280
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oozeer, M., Veraart, C., Legat, V. et al. Simulation of intra-orbital optic nerve electrical stimulation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 43, 608–617 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02351034
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02351034