Abstract
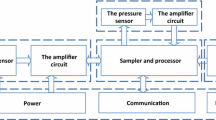
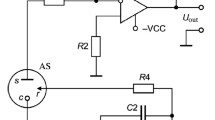
The study presents the results of the development of an analyser to measure sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) gas in breathing circuits, for application is studies of lung function. The analyser consists of an in-line breathing circuit measurement transducer and a compact unit for signal treatment. The detector unit of the analyser consists of a near-infrared light source, a bandpass filter and a pyro-electrical detector. When incremental steps of SF6 gas between 0 and 2% were presented to the analyser, the maximum deviation from the theoretical calibration curve was calculated to be 0.01% SF6. The step response of the analyser (10–90%) was 250 ms. The sensitivity of the analyser to ambient temperature was 0.01% SF6 °C−1 in the range between 0 and 2% SF6. It is concluded that the analyser presented is accurate, and has a sufficient response speed to be used in clinical measurement settings. Furthermore, the analyser is resistant to changes in temperature, gas flow, orientation and movement, which are likely to occur in clinical measurement settings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beydon, L., Svantesson, C., Brauer, K., Lemaire, F., andJonson, B. (1996): ‘Respiratory mechanics in patients ventilated for critical lung disease’,Eur. Respir. J.,9, pp. 262–273
East, T. D., Andriano, K. P., andPace, N. L. (1987): ‘Automated measurement of functional residual capacity by sulfur hexafluoride washout’,J. Clin. Monit.,3, pp. 14–21
East, T. D., Int Veen, J. C., Jonker, T. A., Pace, N. L., andMcJames, S. (1988): ‘Computer-controlled positive end-expiratory pressure titration for effective oxygenation without frequent blood gases’,Crit. Care Med.,16, pp. 252–257
East, T. D., Wortelboer, P. J., Van Ark, E., Bloem, F. H., Peng, L., Pace, N. L., Crapo, R. O., Drews, D., andClemmer, T. P. (1990). ‘Automated sulfur hexafluoride washout functional residual capacity measurement system for any mode of mechanical ventilation as well as spontaneous respiration’,Crit. Care Med.,18, pp. 84–91
Engel, L. A., Paiva, M., Siegler, D. I., andFukuchi, Y. (1979): ‘Dual tracer single breath studies of gas transport in the lung’,Respir. Physiol.,36, pp. 103–119
Gauger, P. G., Overbeck, M. C., Chambers, S. D., Weber, E. D., andHirschl, R. B. (1996): ‘Measuring functional residual capacity in normal and oleic acid-injured lungs’,J. Surg. Res.,63, pp. 204–208
Hedenstierna, G. (1993): ‘The recording of FRC — is it of importance and can it be made simple? [editorial; comment]’,Intens. Care Med.,19, pp. 365–366
Huygen, P. E., Feenstra, B. W., Hoorn, E., Jansen, J. R., andZwart, A. (1991): ‘PDPS: a pulmonary data processing system for assessment of gas exchange properties by multiple gas washout’,Comput Methods Progr. Biomed.,36, pp. 223–235
Huygen, P. E., Gultuna, I., Ince, C., Zwart, A., Bogaard, J. M., Feenstra, B. W., andBruining, H. A. (1993): ‘A new ventilation inhomogeneity index from multiple breath indicator gas washout tests in mechanically ventilated patients’,Crit. Care Med.,21, pp. 1149–1158
Jonmarker, C., Castor, R., Drefeldt, B., andWerner, O. (1985a): ‘An analyzer for in-line measurement of expiratory sulfur hexafluoride concentration’,Anesthesiology,63, pp. 84–88
Jonmarker, C., Jansson, L., Jonson, B., Larsson, A., andWerner, O. (1985b): ‘Measurement of functional residual capacity by sulfur hexafluoride washout’,Anesthesiology,63, pp. 89–95
Kanhai, J. K., Caspers, P. J., Reinders, E. G., Pompe, J. C., Bruining, H. A., andPuppels, G. J. (2003): ‘A fast, digitally controlled flow proportional gas injection system for studies in lung function’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,50, pp. 1268–1275
Kelly, S., Cohen, C., Powell, E., Paiva, M., andEngel, L. A. (1982): ‘Gas mixing in the lungs of dogs and pigs’,Respir. Physiol.,47, pp. 341–349
Kinsella, S. M. (1985): ‘Assessment of the Hewlett-Packard HP47210A capnometer’,Br. J. Anaesth.,57, pp. 919–923
Larsson, A., Linnarsson, D., Jonmarker, C., Jonson, B., Larsson, H., andWerner, O. (1987): ‘Measurement of lung volume by sulfur hexafluoride washout during spontaneous and controlled ventilation: further development of a method’,Anesthesiology,67, pp. 543–550
Meyers, J. R., Lembeck, L., O'kane, H., andBaue, A. E. (1975): ‘Changes in functional residual capacity of the lung after operation’,Arch. Surg.,110, pp. 576–583
Numa, A. H., Hammer, J., andNewth, C. J. (1997): ‘Effect of prone and supine positions on functional residual capacity, oxygenation, and respiratory mechanics in ventilated infants and children’,Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.,156, pp. 1185–1189
Olsson, S. G., Fletcher, R., Jonson, B., Nordstöm, L., andPrakash, O. (1980): ‘Clinical studies of gas exchange during ventilatory support—a method using the Siemens-Elema CO2 analyzer’,Br. J. Anaesth.,52, pp. 491–499
Rimensberger, P. C., andBryan, A. C. (1999): ‘Measurement of functional residual capacity in the critically ill. Relevance for the assessment of respiratory mechanics during mechanical ventilation’,Intens. Care Med.,25, pp. 540–542
Schulze, A., Schaller, P., Topfer, A., andKirpalani, H. (1994): ‘Measurement of functional residual capacity by sulfur hexafluoride in small-volume lungs during spontaneous breathing and mechanical ventilation’,Pediatr. Res.,35, pp. 494–499
Solomon, R. J. (1981): ‘A reliable, accurate CO2 analyser for medical use’,Hewlett-Packard J., pp. 3–20
Vilstrup, C. T., Bjorklund, L. J., Larsson, A., Lachmann, B., andWerner, O. (1992): ‘Functional residual capacity and ventilation homogeneity in mechanically ventilated small neonates’,J. Appl. Physiol.,73, pp. 276–783
Wauer, H. J., Lorenz, B. A., andKox, W. J. (1998): (FRC measurement in intensive care patients. A definition of standards)
FRC-Messung bei beatmeten Intensivpatienten. Eine Standortbestimmung,Anaesthesist,47, pp. 844–855
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanhai, J.K.K., Eijskoot, F., Reinders, E.G.J. et al. Design and validation of an analyser to measure sulphur hexafluoride gas during respiration. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 43, 686–692 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02351044
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02351044