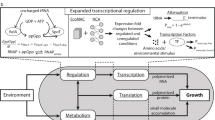
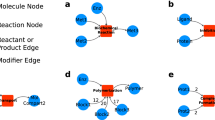
Abstract
A gene-expression model for an E-CELL simulation was constructed, and the simulation was carried out. The model was integrated with a metabolism model of the self-sustaining virtual cell model which was constructed based on aMycoplasma genitalium cell. Details of the model structure and the results of the simulation are shown. AnEscherichia coli lac-operon model was also constructed by integrating and abstracting the gene-expression model. Wherever possible, experimental parameters were used to construct the model
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Tomita M, Hashimoto K, Takahashi K, et al. (1999) E-CELL: software environment for whole-cell simulation. Bioinformatics 15:72–84
Tomita M, Hashimoto K, Takahashi K, et al. (2000) The E-CELL Project: towards intergrative simulation of cellular processes. New Gener Comput 18:1–12
Tomita M (2001) Whole-cell simulation: a grand challenge of the 21 st century. Trends Biotechnol 19(6):205–210
Triendl R (2000) Computerized role models. Nature, 417(6892):7
Fraser CM, Gocayne JD, White O, et al. (1995) The minimal gene complement ofMycoplasma genitalium. Science 270:397–403
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hashimoto, K., Seno, S., Dhar, P.K. et al. Integrative modeling of gene expression and metabolism with E-CELL System. Artif Life Robotics 6, 99–107 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481322
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481322