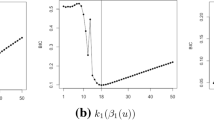
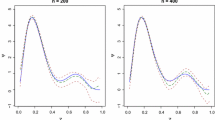
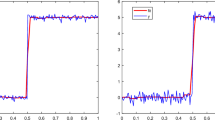
Summary
In some regression settings one would like to combine the flexibility of nonparametric smoothing with some prior knowledge about the regression curve. Such prior knowledge may come from a physical or economic theory, leading to shape constraints such as the underlying regression curve being positive, monotone, convex or concave. We propose a new method for calculating smoothing splines that fulfill these kinds of constraints. Our approach leads to a quadratic programming problem and the infinite number of constraints are replaced by a finite number of constraints that are chosen adaptively. We show that the resulting problem can be solved using the algorithm of Goldfarb and Idnani (1982, 1983) and illustrate our method on several real data sets.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowman, A.W. and Azzalini, A. (1997).Applied Smoothing Techniques for Data Analysis: The Kernel Approach with S-Plus Elustrations, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Bowman, A.W., Jones, M.C. and Gijbels, I. (1998). Testing monotonicity of regression,Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 7(4): 489–500.
DASL (1992). The Data and Story Library, accessible electronically at StatLib (CMU). URL:http://www.stat. emu.edu/DASL/
DeBoor, C. (1978).A Practical Guide, to Splines, Vol. 27 ofApplied Mathematical Sciences, Springer-Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg.
Delecroix, M. and Thomas-Agnan, C. (2000). Spline and kernel regression under shape restrictions,in Schimek (2000), pp. 109–133.
Delecroix, M., Simioni, M. and Thomas-Agnan, C. (1995). A shape constrained smoother: Simulation study,Computational Statistics 10(2): 155–175.
Delecroix, M., Simioni, M. and Thomas-Agnan, C. (1996). Functional estimation under shape constraints,Journal of Nonparametric Statistics 6(1): 69–89.
Dent, W. (1973). A note on least squares fitting of functions constrained to be either nonnegative, nondecreasing or convex,Management Science 20(1): 130–132.
Dierckx, P. (1980). An algorithm for cubic spline fitting with convexity constraints,Computing 24: 349–371.
Dole, D. (1999). CoSmo: A constrained scatterplot smoother for estimating convex, monotonie tranformations,Journal of Business and Economic Statistics 17(4): 444–455.
Eilers, P.H.C. and Marx, B.D. (1996). Flexible smoothing with B-splines and penalties (with discussion),Statistical Science 11(2): 89–121.
Elfving, T. and Andersson, L.E. (1988). An algorithm for computing constrained smoothing spline functions,Numerische Mathematik 52: 583–595.
Eubank, R.L. (1999).Smoothing Splines and Nonparametric Regression, 2 edn, Marcel Dekker, New York and Basel.
Fan, J. and Gijbels, I. (1996).Local Polynomial Modelling and Its Application, Vol. 66 ofMonographs on Statistics and Applied Probability, Chapman and Hall, New York.
Fisher, N.I., Hall, P., Turlach, B.A. and Watson, G.S. (1997). On the estimation of a convex set from noisy data on its support function,Journal of the American Statistical Association 92(437): 84–91.
Fraser, D.A.S. and Massam, H. (1989). A mixed primal-dual bases algorithm for regression under inequality constraints. Application to convex regression,Scandinavian Journal of Statistics 16: 65–74.
Friedman, J.H. and Tibshirani, R. (1984). The monotone smoothing of scatterplots,Technometrics 26(3): 243–250.
Fritsch, F.N. (1990). Monotone piecewise cubic data fitting,in J.C. Mason and M.G. Cox (eds),Algorithms for Approximation II, Chapman and Hall, London, pp. 99–106.
Gaylord, C.K. and Ramirez, D.E. (1991). Monotone regression splines for smoothed bootstrapping,Computational Statistics Quarterly 6(2): 85–97.
Goldfarb, D. and Idnani, A. (1982). Dual and Primal-Dual Methods for Solving Strictly Convex Quadratic Programs,in J.P. Hennart (ed.),Numerical Analysis, Proceedings, Cocoyoc, Mexico 1981, Vol. 909 ofLecture Notes in Mathematics, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 226–239.
Goldfarb, D. and Idnani, A. (1983). A numerically stable dual method for solving strictly convex quadratic programs,Mathematical Programming 27: 1–33.
Green, P.J. and Silverman, B.W. (1994).Nonparametric Regression and Generalized Linear Models, Vol. 58 ofMonographs on Statistics and Applied Probability, Chapman and Hall, London.
Hardle, W. (1990).Applied Non-parametric Regression, Vol. 19 ofEconometric Society Monographs, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Hawkins, D.M. (1994). Fitting monotonic polynomials to data,Computational Statistics 9(3): 233–247.
He, X. and Ng, P. (1999). COBS: Qualitatively constrained smoothing via linear programming,Computational Statistics 14(3): 315–337.
He, X. and Shi, P. (1998). Monotone B-spline smoothing,Journal of the American Statistical Association 93(442): 643–650.
Hildreth, C. (1954). Point estimates of ordinates of concave functions,Journal of the American Statistical Association 49: 598–619.
Holm, S. and Frisén, M. (1985). Nonparametric regression with simple curve characteristics,Research Report 4, Statistiska Institutionen, Göteborgs Universitet, Viktoriagatan 13, S 41–125 Göteborg, Sweden.
Irvine, L.D., Marin, S.P. and Smith, P.W. (1986). Constrained interpolation and smoothing,Constructive Approximation 2(2); 129–151.
Kelly, C. and Rice, J. (1990). Monotone smoothing with application to doseresponse curves and the assessment of synergism,Biometrics 46: 1071–1085.
Knafl, G., Sacks, J., Spiegelman, C. and Ylvisaker, D. (1984). Nonparametric calibration,Technometrics 26(3): 233–241.
Kooperberg, C. and Stone, C.J. (1991). A study of logspline density estimation,Computational Statistics & Data Analysis 12(3): 327–347.
Loader, C. (1999).Local Regression and Likelihood, Statistics and Computing, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Mammen, E. and Thomas-Agnan, C. (1999). Smoothing splines and shape restrictions,Scandinavian Journal of Statististics 26: 239–252.
Mammen, E., Marron, J.S., Turlach, B.A. and Wand, M.P. (2001). A general projection framework for constrained smoothing,Statistical Science 16(3): 232–248.
Marron, J.S., Turlach, B.A. and Wand, M.P. (1997). Local polynomial smoothing under qualitative constraints, in L. Billard and N.I. Fisher (eds),Graph-Image-Vision, Vol. 28 ofComputing Science and Statistics, Interface Foundation of North America, Inc., Fairfax Station, VA 22039-7460, pp. 647–652. URL:https://doi.org/www.maths.uwa.edu.au/~berwin/psfiles/interface96.ps.gz
Matzkin, R.L. (1991). Semiparametric estimation of monotone and concave utility functions for polychotomous choice models,Econometrica 59(5): 1315–1327.
Matzkin, R.L. (1994). Restrictions of economic theory in nonparametric methods, in R.F. Engle and D.L. McFadden (eds),Handbook of Econometrics, Vol. 4, North Holland, Amsterdam, chapter 42, pp. 2523–2558.
Micchelli, C.A., Smith, P.W., Swetitis, J. and Ward, J.D. (1985). Constrained Lp approximation,Constructive Approximation 1(1): 93–102.
Müller, H.G. (1988).Nonparametric Regression Analysis of Longitudinal Data, Vol. 46 ofLecture Notes in Statistics, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Ramsay, J.O. (1988). Monotone regression splines in action (with discussion),Statistical Science 3(4): 425–461.
Ramsay, J.O. (1998). Estimating smooth monotone functions,Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B 60(2): 365–375.
Reinsch, C.R. (1967). Smoothing by spline functions,Numerische Mathematik 10: 177–183.
Reinsch, C.R. (1971). Smoothing by spline functions. II,Numerische Mathematik 16: 451–454.
Schimek, M.G. (ed.) (2000).Smoothing and Regression. Approaches, Computation and Application, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Schmidt, J.W. (1987). An unconstrained dual program for computing convex C1-spline approximants,Computing 39: 133–140.
Schmidt, J.W. and Scholz, I. (1990). A dual algorithm for convex-concave data smoothing by cubic C2-splines,Numerische Mathematik 57: 333–350.
Schwetlick, H. and Kunert, V. (1993). Spline smoothing under constraints on derivatives,BIT 33: 512–528.
Scott, D.W. (1992).Multivariate Density Estimation: Theory, Practice, and Visualization, John Wiley & Sons, New York, Chichester.
Simonoff, J.S. (1996).Smoothing Methods in Statistics, Springer Series in Statistics, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Tantiyaswasdikul, C. and Woodroofe, M.B. (1994). Isotonic smoothing splines under sequential designs,Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference 38: 75–88.
Terrell, G.R. (1993). Spline density estimators,Proceedings of the Statistical Computing Section, American Statistical Association, 1429 Duke Street, Alexandria, VA 22314, pp. 255–260.
Thompson, J.R. and Tapia, R.A. (1990).Nonparametric Function Estimation, Modeling, and Simulation, SIAM, Philadelphia.
Utreras, F.I. (1985). Smoothing noisy data under monotonicity constraints: Existence, characterization and convergence rates,Numerische Mathematik 47: 611–625.
Villalobos, M. and Wahba, G. (1987). Inequality-constrained multivariate smoothing splines with application to the estimation of posterior probabilities,Journal of the American Statistical Association 82(397): 239–248.
Wahba, G. (1990).Spline Functions for Observational Data, Vol. 59 ofCBMS-NSF Regional Conference series, SIAM, Philadelphia.
Wand, M.P. and Jones, M.C. (1995).Kernel smoothing, Vol. 60 ofMonographs on Statistics and Applied Probability, Chapman and Hall, London.
Acknowledgements
I am grateful to Ming-Yen Cheng and Nader Tajvidi for helpful discussions. This work was partly carried out within the Cooperative Research Centre for Advanced Computational Systems established under the Australian Government’s Cooperative Research Centres Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turlach, B.A. Shape constrained smoothing using smoothing splines. Computational Statistics 20, 81–104 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02736124
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02736124