Abstract
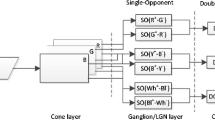
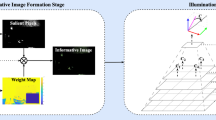
Both physiological and psychological evidences suggest that the human visual system analyze images in neural subsystems tuned to different attributes of the stimulus. Color module and lightness module are such subsystems. Under this general result, a new physical model of trichromatic system has been developed to deal with the color constancy of computer vision. A normal color image is split into two images: the gray scale image and the equal lightness color image for the two modules. Relatively, a two-dimensional descriptor is applied to describe the property of surface reflectance in the equal lightness color image. This description of surface spectral reflectance has the property of color constancy. Image segmentation experiments based on color property of object show that the presented model is effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Brainard D H. Color constancy in the nearly natural image. II. Achromatic loci.J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1998, A15: 307–325.
Brainard D H, Freeman W T. Bayesian color constancy.J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1997, A14: 1393–1411.
Zeki S. A Vision of the Brain. Blackwell Scientific Publications, London, 1993.
Mullen K T. Contrast sensitivity of human color vision to red-green and blue-yellow chromatic gratings.J. Physiol. London, 1985, 359: 381–400.
R L De Valois, Morhan H, Snodderly D M. Psychophysical studies of monkey vision III. Spatial luminance contrast sensitivity tests of macaque and human observers.Vision Research, 1974, 14: 75–81.
Parraga C A, Brelstaff Get al. Color and luminance information in nature scenes.J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1998, A15: 563–569.
Foley J D, A van Dam. Fundamentals of Interactive Computer Graphics. Addison-Wesley, Reading MA., 1982
Gonzalez R C, Woods R E. Digital Image Processing. Third edition, Addison-Wesley, Reading MA., 1992.
Levkowitz H. Color Theory and Modeling for Computer Graphics, Visualization, and Multimedia Applications. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1997.
Judd D B, MacAdam D L, Wyszecki G W. Spectral distribution of typical daylight as a function of correlated color temperature.J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1964, 54: 1031–1040.
Marimont D H, Wandell B A. Linear models of surface and illuminant spectra.J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1992, A9: 1905–1913.
Cohen J. Dependency of the spectral reflectance curves of the Munsell color chips.Psychonomic Sci., 1964, 1: 369.
Dannemiller J L. Spectral reflectance of natural objects: How many basis functions are necessary.J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1992, A9: 507–515.
Barlow H B. What causes trichromacy? A theoretical analysis using comb-filtered spectra.Vision Res., 1982, 22: 635–643.
Stiles W S, Wyszecki G W, Ohta N. Counting metameric object-color stimuli using frequency-limited spectral reflectance functions.J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1977, 67: 779.
Maloney L, Wandell B. Color constancy: A method for recovering surface spectral reflectance.J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1986, A3: 29–33.
D’Zmura M, Lennie P. Mechanisms of color constancy.J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1986, A3: 1662–1672.
D’Zmura M, Iverson G. Color constancy I. Basic theory of two-stage linear recovery of spectral descriptions for lights and surfaces.J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1993, A10: 2148–2165.
Shafer S A. Using color to separate reflection components.Color Res. App., 1985, 10(4): 210–218.
Tao L M, Yao G Z, Wang Y J. A computational theory of human color vision.Acta Psychologia Sinica, 1993, 25: 233–240.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work is supported by the National ‘863’ High-Tech Programme of China (No. 863-306-03-01-1).
TAO Linmi is the project manager of the EC Project ARROV (Argument Reality for Remotely Operated Vehicles) in University of Verona, Italy. He received his Ph.D. degree in application of computer from Tsinghua University in 2001, his M.S. degree in visual perception from Institute of Biophysics, The Chinese Academy of Sciences in 1991, and his B.S. in biological science from Hangzhou University in 1986. In addition, he visited International Institute for Advanced Scientific Studies, Italy as a Postdoctoral Fellow in 1994. His research interests span a broad spectrum of the fields of visual perception and computer vision, especially of human color perception and machine color vision.
XU Guangyou is the Chair Professor of Institute of Human Computer Interaction and Media Integration, Dept. of Computer Science and Technology, Tsinghua University. He graduated from the Department of Automatic Control Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China in 1963. His research interests covers computer vision, human computer interaction and multimedia computing.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, L., Xu, G. A new color constancy model for machine vision. J. Comput. Sci. & Technol. 16, 567–573 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02943241
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02943241