Abstract
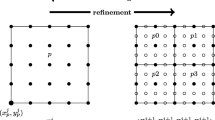
A modal wavelet transform, which overcomes the intrinsic data number limitation of power of two to conventional wavelet transform, has been applied to analysis of axial and eddy pseudo velocity fields, standard PIV velocity field and experimental PIV measurement. The modal wavelet transform is compared with the discrete wavelet transform in order to select the optimum basis function among Neumann, Dirichlet and Green function types basis functions. Consequently, it is verified that Neumann type function is the best basis because the correlation of Neumann type basis function is higher and the root mean square is lower than the other basis functions. Also, the decomposition vector patterns by Neumann type are similar to that by conventional Daubechies basis function of 4th order.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camussi, R., Coherent structure identification from wavelet analysis of particle image velocimetry data, Experiments in Fluids, 32-1 (2002), 76–86.
Christensen, K. T. and Wu, Y., Visualization and Characterization of Small-Scale Spanwise Vortices in Turbulent Channel Flow, Journal of Visualization, 8-2 (2005), 177–186.
Endo, H., Marinova, I., Hayano, S., Saito, Y. and Horii, K., Modal-wavelets and their applications, Proceeding of the 2nd Japan, Australia, New Zealand Joint Seminar on Applications of Electromagnetic Phenomena in Electrical and Mechanical Systems, (2002), 24–25.
Farge, M., Wavelet transforms and their applications to turbulence, Ann Rev Fluid Mech., 24 (1992), 395–457.
Hernandes, E., Weiss, L. G., A First Course on Wavelets, (1996), CRC Press.
Kim, W., Sung, J., Yoo, J. Y. and Lee, M. H., High-definition PIV Analysis on Vortex Shedding in the Cylinder Wake, Journal of Visualization, 7-1 (2004), 17–24.
Li, H., Hu, H., Kobayashi, K., Saga, T. and Taniguchi, N., Wavelet Multiresolution Analysis of Stereoscopic Particle-Image —Velocimetry in Lobed Jet, A.I.A.A. J., 40-6 (2002), 1037–1046.
Li, H., Takei, M., Ochi, M., Saito, Y. and Horii, K., Application of Two-dimensional Orthogonal Wavelets to Multiresolution Image Analysis of a Turbulent Jet, Transactions of the Japan Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, 42-137 (1999), 120–127.
Okamoto, K., Nishio, S., Kobayashi, T. and Saga, T., Standard images for particle imaging velocimetry, Proc. PIV-Fukui 97, (1997), 229–236.
Özsoy, E., Rambaud, P. E., Stitou, A. and Riethmuller, L. M., Vortex characteristics in laminar cavity flow at very low mach number, Experiments in Fluids, 38-2 (2005), 133–145.
Saito, Y., Smart visualized information processing (3) -Image Processing-, The Japan Society of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics, 10 (2002), 170–177 (in Japanese).
Schram, C., Rambaud, P. and Riethmuller, L. M., Wavelet based eddy structure education from a backward facing step flow investigated using particle image velocimetry, Experiments in Fluids, 36-2 (2004), 233–245.
Weng, G. W., Fan, C. W., Liao, X. G. and Qin, J., Wavelet-based image denoising in (digital) particle image velocimetry, Signal Processing, 81, (2001), 1503–1512.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Kenji Tanaka: He received his Bachelor degree in Mechanical Engineering in 1986 from Nihon University, Tokyo Japan. He also received his M.Sc.(Eng.) degree in Mechanical Engineering in 1995 from Nihon University. He has worked for Okamoto Industries, INC. since 1986. His current position is a manager of cooperate administration. His research interests are Pneumatic conveying and PIV.
Masahiro Takei: He received his M.Sc.(Eng) in Resource Engineering in 1991 from Waseda University, Tokyo Japan. He also received his Ph.D. in Resource Engineering in 1995 from Waseda University. He has worked in Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nihon University, Tokyo Japan as an associate professor since 1995. His research interests are Computed tomography, Multiphase flow, Image processing and PIV.
Yoshifuru Saito: He received his Master of engineering degree in Mechanical Engineering in 1975 from Hosei University. He is currently a Professor at Faculty of Engineering, Houei University. His current research interests are quantitative Computational Electromagnetics, Computational Inverse Analysis, Smart Visualized Information Processing, Power Electronics Power Magnetics, Micro Machines and Computational Literature.
Deog Hee Doh: He received B.A. at Korea Maritime University (KMU) (1985). He finished his M.Sc. degree at the graduate school of KMU(1988). He received his PhD. degree at the Department of Mechanical Engineering of the University of Tokyo, Japan in 1995. His graduate works is on the development of 3D-PTV and simultaneous measurement techniques on temperature and velocity fields for thermal flows. He worked as an invited researcher for the Advanced Fluid Engineering Research Center (AFERC) in 1995. He has been working for Korea Maritime University since 1995 at the Division of Mechanical and Information Engineering. His research interests are to develop spatial measurement techniques such as 3D-PIVs, 3D-PTVs, micro-/nano-4D-PTVs for nano-/bio- thermal flows.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, K., Takei, M., Saito, Y. et al. Application of modal wavelets to PIV measurements by selecting basis function. J Vis 9, 445–455 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03181784
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03181784