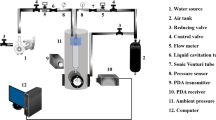
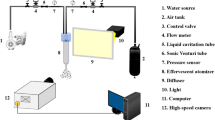
Abstract
Effervescent atomization is one of the twin-fluid atomization methods while it has better performance in terms of smaller drop sizes and/or lower injection pressures. In order to investigate the effects of the internal flow patterns on droplet characteristics, a new kind of effervescent atomizer was designed and manufactured. The bubble forming process was visualized with a high-speed camera, while the droplet size was characterized with a LDV/PDA system. The experimental results show that there are three regimes of the two-phase flows inside the discharge orifice, one is bubbly flow, another is annular flow while the other is the intermittent flow. The flow patterns transfered from bubbly flow to intermittent flow and then to annular flow with decreasing of the water flow rate. In addition, with increasing of the working pressure or decreasing of the water flow rate, the SMD (Sauter mean diameter) of the droplets decreased and the axial mean velocity increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
cross-sectional area of the mixing tube, m2
- d :
-
inside diameter of the mixing tube, m
- GLR:
-
gas to liquid mass flow-rate ratio, dimensionless
- j :
-
superficial velocity (the volumetric flow rate of fluid moving through a pipe
- M :
-
flow rate, kg/s
- P :
-
pressure, Pa
- SMD:
-
Sauter mean diameter, m
- t :
-
bubble development time, s
- t * :
-
normalized bubble development time, dimensionless
- v :
-
velocity, m/s
- v * :
-
normalized velocity, dimensionless
- ρ:
-
density, kg/m3
- τ:
-
periodicity, s
- τ* :
-
normalized periodicity, dimensionless
- B :
-
bubble
- g :
-
gas
- l :
-
liquid
References
Alpert, R. L., Incentive for Use of Misting Sprays as a Fire Suppression Flooding Agent, Proceedings of Water Mist Fire Suppression Workshop, NISTIR 5207, (l993), 31–36.
Arosio, S. and Guilizzoni, M., Structure Visualization for a Gas-Liquid Flow: Quantitative Flow Structure Fields, J. of Visualization, l.9(2006), 275–282.
Fujisawa, N., Verhoeckx, M., Dabiri, D., Gharib, M. and Hertzberg, J., Recent Progress in Flow Visualization Techniques toward the Generation of Fluid Art, J. of Visualization, 10-2 (2007), 163–170.
Jones, A. and NoIan, P. F., Discussions on the Use of Fine Water Sprays or Mists for Fire Suppression, J. Loss Prevention Process industries, 8 (1995), 17–22.
Lin, K. C., Kennedy, P. J. and Jackson, T. A., Structures of internal flow and the corresponding spray for aerated-liquid injectors, 37th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, AIAA 2001-3569, (2001).
Ninomiya, N. and Yasuda, K., Visualization and PIV Measurement of the Flow around and inside of a Falling Droplet, J. of Visualization, 9-3 (2006), 257–264.
Roesler, T. C., An Experimental Study of Aerated-liquid Atomization, (1988), PhD thesis, Purdue University.
Roesler, T. C. and Lefebvre, A. H., Studies on Aerated-liquid Atomization, Int. J. Turbo Jet Engines, 6 (1989), 221–230.
Roesler, T. C. and Lefebvre, A. H., Photographic Studies on Aerated-liquid Atomization, Combustion Fundamentals and Applications, Proceedings of the Meeting of the Central States Section of the Combustion Institute (Indianapolis, Indiana), Paper 3, (1988).
Sovani, S. D., Sojka, P. E. and Lefebvre, A. H., Effervescent atomization, Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 27 (2001), 483–521.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was partially presented on the 9th Asian Symposium on Visualization, Hong Kong, 4–8 June, 2007.
Huang Xin: He received his PhD. in 2007 from State Key Lab. of Fire Science, University of Science & Technology of China. He is currently an assistant professor of the Tianjin Fire Research Institute, the Ministry of Public Security of China. His research interests are modeling and experimental study on water mist fire suppression.
Wang Xishi: He received his M.Sc. degree in 1997 from Anhui Institute of Optic & Fine Mechanics of Chinese Academia Sinica and his PhD. in 2002 from University of Science & Technology of China. At the end of 2002, he worked at the Department of Chemical System Engineering of the University of Tokyo for 3 months as a visiting scientist. During 2003 to 2005, he worked as a postdoctor at the Department of
Mechanical Engineering of the Hong Kong University of Science & Technology. He is currently an associate professor of the State Key Lab. of Fire Science, University of Science & Technology of China. His current research focus on two/multi phase flows, laser based diagnostic techniques, fire suppression mechanisms and technologies.
Liao Guangxuan: He is currently a professor and executive director of the State Key Lab. of Fire Science, University of Science & Technology of China. His research interests include fire safety science and technology, simulation of fire process, fire suppression and extinction mechanisms by water mist, diagnostics of combustion flow field.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Wang, X. & Liao, G. Visualization of two phase flow inside an effervescent atomizer. J Vis 11, 299–308 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182198
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182198