Abstract.
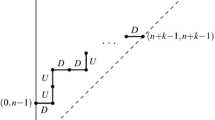
Priority trees (p-trees ) are a certain variety of binary trees of size n constructed from permutations of the numbers 1, . . ,n . In this paper we analyze several parameters depending on n (the size) and j (a number between 1 and n ), such as the length of the left path (connecting the root and the leftmost leaf), the height of node j (the distance from the root), the number of left edges on the path from the root to node j , the number of descendants of node j , the number of key comparisons when inserting an element between j and j+1 , the number of key comparisons when cutting the p-trees into two p-trees , the number of nodes with 0 , 1 , or 2 children. Methodologically, recursions are set up according to a fundamental decomposition of the family \( \cal A \) of p-trees (using auxiliary quantities \( \cal B \) and \( \cal C\) ); using generating functions, they lead to systems of differential equations that can be solved explicitly with some efforts. The quantities of interest can then be identified as coefficients in the explicit forms of the generating functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received December 19, 1997; revised March 1, 1998.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panholzer, A., Prodinger, H. Average-Case Analysis of Priority Trees: A Structure for Priority Queue Administration . Algorithmica 22, 600–630 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009243
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009243