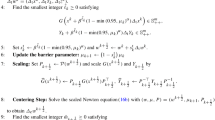Abstract.
Global and local convergence properties of a primal-dual interior-point pure potential-reduction algorithm for linear programming problems is analyzed. This algorithm is a primal-dual variant of the Iri-Imai method and uses modified Newton search directions to minimize the Tanabe-Todd-Ye (TTY) potential function. A polynomial time complexity for the method is demonstrated. Furthermore, this method is shown to have a unique accumulation point even for degenerate problems and to have Q-quadratic convergence to this point by an appropriate choice of the step-sizes. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first superlinear convergence result on degenerate linear programs for primal-dual interior-point algorithms that do not follow the central path.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: February 12, 1998 / Accepted: March 3, 2000¶Published online January 17, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tütüncü, R. Quadratic convergence of potential-reduction methods for degenerate problems. Math. Program. 90, 169–203 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00011418
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00011418