Abstract
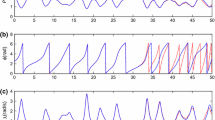
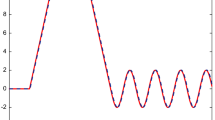
In this paper, a fault estimation problem for a class of nonlinear systems subject to multiplicative faults and unknown disturbances is investigated. Multiplicative faults usually mixed with system states and inputs can cause additional complexity in the design of fault estimator due to parameter changes within process. Especially for the nonlinear system corrupted with unknown disturbances, it is not an easy work to distinguish the real fault factor from the mixed term. Under the nonlinear Lipschitz condition, the proposed robust adaptive fault estimation approach not only estimates the multiplicative faults and system states simultaneously, but also extracts the real effect of the faults. Meanwhile, the effect of disturbances is restricted to an L 2 gain performance criteria which can be formulated into the basic feasibility problem of a linear matrix inequality (LMI). In order to reduce the conservatism of the proposed method, a relaxing Lipschitz matrix is introduced. Finally, an illustrative example is applied to verify the efficiency of the proposed robust adaptive estimation scheme.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Blanke, M. Kinnaert, J. Lunze, M. Staroswiecki, Fault Diagnosis and Fault-Tolerant Control, 2nd edn. (Springer, Berlin, 2006)
J.D. Boskovic, S.E. Bergstrom, R.K. Mehra, Robust integrated flight control design under failures, damage, and state-dependent disturbances. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 28(5), 902–917 (2005)
J. Chen, R.J. Patton, Robust Model-Based Fault Diagnosis for Dynamic Systems. (Kluwer Academic, Norwell, 1999)
S.X. Ding, Model-Based Fault Diagnosis Techniques: Design Schemes, Algorithms, and Tools (Springer, Berlin, 2008)
G.R. Duan, R.J. Patton, Robust fault detection using Luenberger-type unknown input observers—a parametric approach. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 32(4), 533–540 (2001)
S.X. Ding, P.M. Frank, E.L. Ding, An approach to the detection of multiplicative faults in uncertain dynamic systems, in Proceedings of the 41st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (2003), pp. 4371–4376
P.M. Frank, Fault diagnosis in dynamic systems using analytical and knowledge-based redundancy—a survey and some new results. Automatica 26(3), 459–474 (1990)
Z. Gao, S.X. Ding, Actuator fault robust estimation and fault-tolerant control for a class of nonlinear descriptor systems. Automatica 43(5), 912–920 (2007)
M. Hou, Estimation of sinusoidal frequencies and amplitudes using adaptive identifier and observer. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 52(3), 493–499 (2007)
R. Isermann, Model-based fault-detection and diagnosis-status and applications. Annu. Rev. Control 29(1), 71–85 (2005)
R. Isermann, Fault-Diagnosis Systems (Springer, Berlin, 2006)
P.A. Ioannou, J. Sun, Robust Adaptive Control (Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1996)
B. Jiang, M. Staroswiecki, V. Cocquempot, Fault diagnosis based on adaptive observer for a class of non-linear systems with unknown parameters. Int. J. Control 77(4), 367–383 (2004)
B. Jiang, M. Staroswiecki, V. Cocquempot, Fault accommodation for nonlinear dynamic systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 51(9), 1578–1583 (2006)
C.D. Persis, A. Isidori, A geometric approach to nonlinear fault detection and isolation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 46(6), 853–865 (2001)
G. Phanomchoeng, R. Rajamani, Observer design for Lipschitz nonlinear systems using Riccati equations, in American Control Conference (2010), pp. 6060–6065
C.P. Tan, C. Edwards, Multiplicative fault reconstruction using sliding mode observers, in 5th Asian Control Conference (2004), pp. 957–962
K. Vijayaraghavan, R. Rajamani, J. Bokor, Quantitative fault estimation for a class of non-linear systems. Int. J. Control 80(1), 64–74 (2007)
A. Xu, Q. Zhang, Nonlinear system fault diagnosis based on adaptive estimation. Automatica 40(7), 1181–1193 (1994)
X.G. Yan, C. Edwards, Nonlinear robust fault reconstruction and estimation using a sliding mode observer. Automatica 43(9), 1605–1614 (2007)
Y. Zhang, J. Jiang, Bibliographical review on reconfigurable fault-tolerant control systems. Annu. Rev. Control 32(2), 229–252 (2008)
X. Zhang, M.M. Polycarpou, T. Parisini, Fault diagnosis of a class of nonlinear uncertain systems with Lipschitz nonlinearities using adaptive estimation. Automatica 46(2), 290–299 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, C., Duan, G. Robust Adaptive Fault Estimation for a Class of Nonlinear Systems Subject to Multiplicative Faults. Circuits Syst Signal Process 31, 2035–2046 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9434-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9434-x