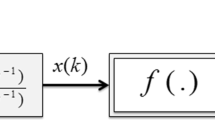
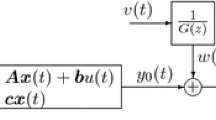
Abstract
Many control algorithms are based on the mathematical models of dynamic systems. System identification is used to determine the structures and parameters of dynamic systems. Some identification algorithms (e.g., the least squares algorithm) can be applied to estimate the parameters of linear regressive systems or linear-parameter systems with white noise disturbances. This paper derives two recursive extended least squares parameter estimation algorithms for Wiener nonlinear systems with moving average noises based on over-parameterization models. The simulation results indicate that the proposed algorithms are effective.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Dehghan, M. Hajarian, Two algorithms for finding the Hermitian reflexive and skew-Hermitian solutions of Sylvester matrix equations. Appl. Math. Lett. 24(4), 444–449 (2011)
M. Dehghan, M. Hajarian, Analysis of an iterative algorithm to solve the generalized coupled Sylvester matrix equations. Appl. Math. Model. 35(7), 3285–3300 (2011)
M. Dehghan, M. Hajarian, SSHI methods for solving general linear matrix equations. Eng. Comput. 28(8), 1028–1043 (2011)
M. Dehghan, M. Hajarian, Fourth-order variants of Newton’s method without second derivatives for solving non-linear equations. Eng. Comput. 29(4), 356–365 (2012)
M. Dehghan, M. Hajarian, Iterative algorithms for the generalized centro-symmetric and central anti-symmetric solutions of general coupled matrix equations. Eng. Comput. 29(5), 528–560 (2012)
F. Ding, System Identification—New Theory and Methods (Science Press, Beijing, 2013)
F. Ding, Decomposition based fast least squares algorithm for output error systems. Signal Process. 93(5), 1235–1242 (2013)
F. Ding, Hierarchical multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for Hammerstein nonlinear system modeling. Appl. Math. Model. 37(4), 1694–1704 (2013)
F. Ding, Two-stage least squares based iterative estimation algorithm for CARARMA system modeling. Appl. Math. Model. 37(7), 4798–4808 (2013)
F. Ding, Coupled-least-squares identification for multivariable systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 7(1), 68–79 (2013)
F. Ding, T. Chen, Identification of Hammerstein nonlinear ARMAX systems. Automatica 41(9), 1479–1489 (2005)
J. Ding, F. Ding, Bias compensation based parameter estimation for output error moving average systems. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 25(12), 1100–1111 (2011)
F. Ding, Y. Gu, Performance analysis of the auxiliary model based least squares identification algorithm for one-step state delay systems. Int. J. Comput. Math. 89(15), 2019–2028 (2012)
F. Ding, Y. Gu, Performance analysis of the auxiliary model-based stochastic gradient parameter estimation algorithm for state space systems with one-step state delay. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(2), 585–599 (2013)
J. Ding, Y. Shi et al., A modified stochastic gradient based parameter estimation algorithm for dual-rate sampled-data systems. Digit. Signal Process. 20(4), 1238–1249 (2010)
J. Ding, F. Ding et al., Hierarchical least squares identification for linear SISO systems with dual-rate sampled-data. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 56(11), 2677–2683 (2011)
F. Ding, X.P. Liu, G. Liu, Identification methods for Hammerstein nonlinear systems. Digit. Signal Process. 21(2), 215–238 (2011)
F. Ding, Y.J. Liu, B. Bao, Gradient based and least squares based iterative estimation algorithms for multi-input multi-output systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part I, J. Syst. Control Eng. 226(1), 43–55 (2012)
F. Ding, X.G. Liu, J. Chu, Gradient-based and least-squares-based iterative algorithms for Hammerstein systems using the hierarchical identification principle. IET Control Theory Appl. 7(2), 176–184 (2013)
F. Ding, J.X. Ma, Y.S. Xiao, Newton iterative identification for a class of output nonlinear systems with moving average noises. Nonlinear Dyn. 74(1–2), 21–30 (2013)
W. Fan, Identification of a class of Wiener nonlinear systems (I). Master’s Degree Thesis, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China, 2008
Y. Gu, X.L. Lu, R.F. Ding, Parameter and state estimation algorithm for a state space model with a one-unit state delay. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(5), 2267–2280 (2013)
H.Q. Han, L. Xie et al., Hierarchical least squares based iterative identification for multivariable systems with moving average noises. Math. Comput. Model. 51(9–10), 1213–1220 (2010)
Y.B. Hu, Iterative and recursive least squares estimation algorithms for moving average systems. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 34, 12–19 (2013)
J.H. Li, Parameter estimation for Hammerstein CARARMA systems based on the Newton iteration. Appl. Math. Lett. 26(1), 91–96 (2013)
J.H. Li, F. Ding, Maximum likelihood stochastic gradient estimation for Hammerstein systems with colored noise based on the key term separation technique. Comput. Math. Appl. 62(11), 4170–4177 (2011)
H. Li, Y. Shi, Robust H-infty filtering for nonlinear stochastic systems with uncertainties and random delays modeled by Markov chains. Automatica 48(1), 159–166 (2012)
J.H. Li, R.F. Ding, Y. Yang, Iterative parameter identification methods for nonlinear functions. Appl. Math. Model. 36(6), 2739–2750 (2012)
J.H. Li, F. Ding, G.W. Yang, Maximum likelihood least squares identification method for input nonlinear finite impulse response moving average systems. Math. Comput. Model. 55(3–4), 442–450 (2012)
Y.J. Liu, Y.S. Xiao, X.L. Zhao, Multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for multiple-input single-output systems using the auxiliary model. Appl. Math. Comput. 215(4), 1477–1483 (2009)
Y.J. Liu, J. Sheng, R.F. Ding, Convergence of stochastic gradient algorithm for multivariable ARX-like systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 59(8), 2615–2627 (2010)
Y.J. Liu, F. Ding, Y. Shi, Least squares estimation for a class of non-uniformly sampled systems based on the hierarchical identification principle. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(6), 1985–2000 (2012)
M.M. Liu, Y.S. Xiao, R.F. Ding, Iterative identification algorithm for Wiener nonlinear systems using the Newton method. Appl. Math. Model. 37(9), 6584–6591 (2013)
J.X. Ma, F. Ding, Recursive relations of the cost functions for the least squares algorithms for multivariable systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(1), 83–101 (2013)
B. Shen, Z.D. Wang et al., H-infinity filtering for uncertain time-varying systems with multiple randomly occurred nonlinearities and successive packet dropouts. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 21(14), 1693–1709 (2011)
B. Shen, Z.D. Wang et al., Sampled-data H-infinity filtering for stochastic genetic regulatory networks. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 21(15), 1759–1777 (2011)
Y. Shi, T. Chen, Optimal design of multi-channel transmultiplexers with stopband energy and passband magnitude constraints. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II, Analog Digit. Signal Process. 50(9), 659–662 (2003)
Y. Shi, H. Fang, Kalman filter based identification for systems with randomly missing measurements in a network environment. Int. J. Control 83(3), 538–551 (2010)
Y. Shi, B. Yu, Output feedback stabilization of networked control systems with random delays modeled by Markov chains. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 54(7), 1668–1674 (2009)
Y. Shi, B. Yu, Robust mixed H-2/H-infinity control of networked control systems with random time delays in both forward and backward communication links. Automatica 47(4), 754–760 (2011)
R.M. Udrea, D.N. Vizireanu, S. Ciochina, An improved spectral subtraction method for speech enhancement using a perceptual weighting filter. Digit. Signal Process. 18(4), 581–587 (2008)
R.M. Udrea, D.N. Vizireanu, S. Ciochina, S. Halunga, Nonlinear spectral subtraction method for colored noise reduction using multi-band Bark scale. Signal Process. 88(5), 1299–1303 (2008)
D.N. Vizireanu, S.V. Halunga, Simple, fast and accurate eight points amplitude estimation method of sinusoidal signals for DSP based instrumentation. J. Instrum. 7(4), P04001 (2012)
D.Q. Wang, Least squares-based recursive and iterative estimation for output error moving average systems using data filtering. IET Control Theory Appl. 5(14), 1648–1657 (2011)
D.Q. Wang, F. Ding, Extended stochastic gradient identification algorithms for Hammerstein-Wiener ARMAX systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 56(12), 3157–3164 (2008)
D.Q. Wang, F. Ding, Least squares based and gradient based iterative identification for Wiener nonlinear systems. Signal Process. 91(5), 1182–1189 (2011)
D.Q. Wang, F. Ding, Hierarchical least squares estimation algorithm for Hammerstein-Wiener systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19(12), 825–828 (2012)
D.Q. Wang, R. Ding, X.Z. Dong, Iterative parameter estimation for a class of multivariable systems based on the hierarchical identification principle and the gradient search. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(6), 2167–2177 (2012)
W.L. Xiong, J.X. Ma, R.F. Ding, An iterative numerical algorithm for modeling a class of Wiener nonlinear systems. Appl. Math. Lett. 26(4), 487–493 (2013)
Y. Zhang, Unbiased identification of a class of multi-input single-output systems with correlated disturbances using bias compensation methods. Math. Comput. Model. 53(9–10), 1810–1819 (2011)
Y. Zhang, G.M. Cui, Bias compensation methods for stochastic systems with colored noise. Appl. Math. Model. 35(4), 1709–1716 (2011)
J.B. Zhang, F. Ding, Y. Shi, Self-tuning control based on multi-innovation stochastic gradient parameter estimation. Syst. Control Lett. 58(1), 69–75 (2009)
Z.N. Zhang, F. Ding, X.G. Liu, Hierarchical gradient based iterative parameter estimation algorithm for multivariable output error moving average systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 61(3), 672–682 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51204149), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2-9-2012-45), and the Open Project Fund of the Key Laboratory on Deep GeoDrilling Technology of the Ministry of Land and Resources (No. NLSD201213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Liu, B., Zhou, Q. et al. Recursive Extended Least Squares Parameter Estimation for Wiener Nonlinear Systems with Moving Average Noises. Circuits Syst Signal Process 33, 655–664 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-013-9652-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-013-9652-x