Abstract
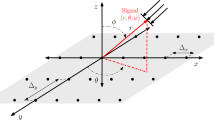
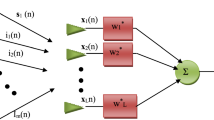
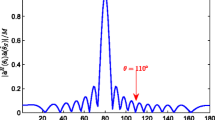
The closed-form solution of linearly constrained minimum variance (CF-LCMV) suffers heavy computational burden from two-matrix inversion when computing the optimal vector. CF-LCMV is not an adaptive beamformer and performs poorly with low signal-to-interference-plus-noise-ratio (SINR) and small number of snapshots. In this study, we derive a low-complexity iterative adaptive LCMV (IA-LCMV) algorithm based on conjugate gradient (CG) technique with threefold advantages: first, IA-LCMV can remarkably alleviate the complexity of CF-LCMV; second, IA-LCMV can adjust output adaptively with comparable convergence speed. Finally, it shows robust performance against low SINR and small number of snapshots. Simulation results demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed algorithms.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Breed, J. Strauss, A short proof of the equivalence of LCMV and GSC beamforming. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 9(6), 168–169 (2002)
C. El Kassis, J. Picheral, G. Fleury, C. Mokbel, Direction of arrival estimation using EM-ESPRIT with nonuniform arrays. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(5), 1787–1807 (2012)
O. Frost III., An algorithm for linearly constrained adaptive array processing. Proc. IEEE 60(8), 926–935 (1972)
G. Glentis, A. Jakobsson, Superfast approximative implementation of the IAA spectral estimate. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(1), 472–478 (2012)
S. Haykin, L. Li, Nonlinear adaptive prediction of nonstationary signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 43(2), 526–535 (1995)
M. Honig, J. Goldstein, Adaptive reduced-rank interference suppression based on the multistage Wiener filter. IEEE Trans. Commun. 50(6), 986–994 (2002)
H. Leung, S. Haykin, Stability of recursive QRD-LS algorithms using finite-precision systolic array implementation. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 37(5), 760–763 (1989)
Y. Liu, R. Ranganathan, M.T. Hunter, W.B. Mikhael, Complex adaptive LMS algorithm employing the conjugate gradient principle for channel estimation and equalization. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(3), 1067–1087 (2012)
L. Resende, J. Romano, M. Bellanger, A fast least-squares algorithm for linearly constrained adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 44(5), 1168–1174 (1996)
L. Scott, B. Mulgrew, Sparse LCMV beamformer design for suppression of ground clutter in airborne radar. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 43(12), 2843–2851 (1995)
M.G. Shmlik, G. Sharon, C. Israel, Low-complexity addition or removal of sensors/constraints in LCMV beamformers. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(3), 1205–1214 (2012)
R.M. Udrea, N.D. Vizireanu, S. Ciochina, An improved spectral subtraction method for speech enhancement using a perceptual weighting filter. Digit. Signal Process. 18(4), 581–587 (2008)
R.M. Udrea, N. Vizireanu, S. Ciochina, S. Halunga, Nonlinear spectral subtraction method for colored noise reduction using multi-band bark scale. Signal Process. 88(5), 1299–1303 (2008)
H.L. Van Trees, Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory, Optimum Array Processing (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 2004)
L. Wang, R. de Lamare, Constrained adaptive filtering algorithms based on conjugate gradient techniques for beamforming. IET Signal Process. 4(6), 686–697 (2010)
S. Werner, J. Apolinário Jr., M. de Campos, P. Diniz, Low-complexity constrained affine-projection algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(12), 4545–4555 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant (61201277), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2012M510168), Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province of China, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. ZYGX2010J018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Xu, B., Rao, Z. et al. Low-Complexity Iterative Adaptive Linearly Constrained Minimum Variance Beamformer. Circuits Syst Signal Process 33, 987–997 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-013-9668-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-013-9668-2