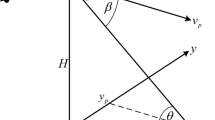
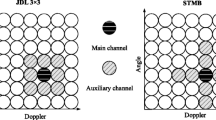
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a sparsity-based direct data domain space-time adaptive processing (D3-STAP) algorithm for airborne radar that considers the intrinsic clutter motion (ICM). The proposed D3-STAP scheme models the received returns in the presence of ICM as a sparse measurement model. Then, we derive the principle of the sparsity-based D3-STAP that uses the focal underdetermined system solution (FOCUSS) method. The proposed D3-STAP algorithm estimates the clutter covariance matrix by a Hadamard product of the covariance matrix taper (CMT) and the clutter covariance matrix estimate with the FOCUSS technique. In addition, we develop a CMT adaptation approach for the proposed D3-STAP algorithm to automatically select the best CMT. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms the existing D3-STAP using the least-squares technique and the sparsity-based D3-STAP algorithm without CMT.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Note that the above equation makes use of the fact that \(\left( \mathbf{A} \odot \mathbf{B}\right) \left( \mathbf{C} \odot \mathbf{D}\right) ^H = \left( \mathbf{A} \mathbf{C}^H\right) \odot \left( \mathbf{B} \mathbf{D}^H\right) ,\) where \(\mathbf{A}, \mathbf{B}\) are \(g \times h\) and \(\mathbf{C}, \mathbf{D}\) are \(e \times h\) matrices [7].
This assumption is also seen in CMT methods developed by Guerci in [8].
This is where we exploit both the orthogonality of \(\mathbf{Q}\) and the white Gaussianity of the thermal noise.
Significant elements are defined by those whose powers are higher than the thermal noise level.
Regarding the FOCUSS algorithm, the MATLAB code can be downloaded at http://dsp.ucsd.edu/~zhilin/MFCOUSS.m.
References
E. Aboutanios, B. Mulgrew, A STAP algorithm for radar target detection in heterogeneous environments, in IEEE Workshop Statist. Signal Process.(2005), pp. 966–971
E. Aboutanios, B. Mulgrew, Hybrid detection approach for STAP in heterogeneous clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 46, 1021–1033 (2010)
S.F. Cotter, B.D. Rao, K. Engan, K. Kreutz-Delgado, Sparse solutions to linear inverse problems with multiple measurement vectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53, 2477–2488 (2005)
J.-F. Degurse, L. Savy, S. Marcos, Reduced-rank STAP for target detection in heterogeneous environments. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 50, 1153–1162 (2014)
J.-F. Degurse, L. Savy, S. Marcos, J.-P. Molini, Deterministic aided STAP for target detection in heterogeneous situations. Int. J. Antennas Propagat. (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/826935
M. Elad, Why simple shrinkage is still relevant for redundant representations? IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52, 5559–5569 (2006)
J.R. Guerci, Space-Time Adaptive Processing for Radar (Artech House, London, 2003)
J.R. Guerci, Theory and application of covariance matrix tapers for robust adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 47, 977–985 (1999)
J.R. Guerci, E.J. Baranoski, Knowledge-aided adaptive radar at DARPA: an overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 23, 41–50 (2006)
J.R. Guerci, J.S. Bergin, Principal components, covariance matrix tapers, and the subspace leakage problem. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 38, 152–162 (2002)
J.S. Goldstein, I.S. Reed, Theory of partially adaptive radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 33, 1309–1325 (1997)
I.F. Gorodnitsky, B.D. Rao, Sparse signal reconstruction from limited data using FOCUSS: a re-weighted minimum norm algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45, 600–616 (1997)
R.A. Horn, C.R. Johnson, Matrix Analysis (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1985)
R. Klemm, Principles of Space-Time Adaptive Processing (Institute of Electrical Engineering, London, UK, 2006)
J. Li, X. Zhu, P. Stoica, M. Rangaswamy, High resolution angle-Doppler imaging for MTI radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 46, 1544–1556 (2010)
S. Maria, J. J. Fuchs, Application of the global matched filter to STAP data an efficient algorithmic approach, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (2006), pp.14–19
W.L. Mevin, G.A. Showman, An approach to knowledge-aided covariance estimation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 42, 1021–1042 (2006)
J.T. Parker, L.C. Potter, A Bayesian perspective on sparse regularization for STAP post-processing, in IEEE Radar Conference (2010), pp. 1471–1475
B.D. Rao, K. Engan, S.F. Cotter, J. Palmer, K. Kreutz-Delgado, Subset selection in noise based on diversity measure minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 51, 760–770 (2003)
J.R. Roman, M. Rangaswamy, D.W. Davis, Q. Zhang, B. Himed, J.H. Michels, Parametric adaptive matched filter for airborne radar applications. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 36, 677–692 (2000)
S. Sen, OFDM radar space-time adaptive processing by exploiting spatio-temporal sparsity. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61, 118–130 (2013)
K. Sun, H. Meng, Y. Wang, X. Wang, Direct data domain STAP using sparse representation of clutter spectrum. Signal Process. 91, 2222–2236 (2011)
I.W. Selesnick, S.U. Pillai, K.Y. Li, B. Himed, Angle-Doppler processing using sparse regularization, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (2010), pp. 2750–2753
T.K. Sarkar, H. Wang, S. Park, R. Adve, J. Koh, K. Kim, Y. Zhang, M.C. Wicks, R.D. Brown, A deterministic least-squares approach to space-time adaptive processing (STAP). IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 49, 91–103 (2001)
K. Sun, H. Zhang, G. Li, H. Meng, X. Wang, A novel STAP algorithm using sparse recovery technique, in IGARSS (2009), pp. 336–339
J. Ward, Space-Time Adaptive Processing for Airborne Radar. Technical Report (MIT Lincoln laboratory, Lexington, MA, 1994). 1015
M.C. Wicks, M. Rangaswamy, R. Adve, T.B. Hale, Space-time adaptive processing: a knowledge-based perspective for airborne radar. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 23, 51–65 (2006)
Y. Wu, J. Tang, Y. Peng, On the essence of knowledge-aided clutter covariance estimate and its convergence. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 47, 569–585 (2011)
T. Xia, Y. Zheng, Q. Wan, X. Wang, Adaptive regularized FOCUSS algorithm, in IEEE Radar Conference (2007), pp. 282–284
E. Yang, R. Adve, J. Chun, J. Chun, Hybrid direct data domain sigma-delta space-time adaptive processing algorithm in non-homogeneous clutter. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 4, 611–625 (2010)
Z. Yang, X. Li, H. Wang, Performance analysis of STAP algorithms based on fast sparse recovery techniques. Progr. Electromagn. Res. B 41, 251–268 (2012)
Z. Yang, X. Li, H. Wang, W. Jiang, Adaptive clutter suppression based on iterative adaptive approach for airborne radar. Signal Process. 93, 3567–3577 (2013)
Z. Yang, X. Li, H. Wang, W. Jiang, On clutter sparsity analysis in space-time adaptive processing airborne radar. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens. Lett. 10, 1214–1218 (2013)
Z. Yang, X. Li, H. Wang, L. Nie, Sparsity-based space-time adaptive processing using complex-valued homotopy technique for airborne radar. IET Signal Process. 8, 552–564 (2014)
Z. Yang, R.C. de Lamare, X. Li, \(L_1\)-regularized STAP algorithms with a generalized sidelobe canceler architecture for airborne radar. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60, 674–686 (2012)
Z. Yang, R.C. de Lamare, X. Li, Sparsity-aware space-time adaptive processing algorithms with \(L_1\)-norm regularization for airborne radar. IET Signal Process. 6, 413–423 (2012)
M. Zatman, Comments on Theory and application of covariance matrix tapers for robust adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 48, 1796–1800 (2000)
Acknowledgments
This work was funded in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61401478.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Qin, Y., de Lamare, R.C. et al. Sparsity-Based Direct Data Domain Space-Time Adaptive Processing with Intrinsic Clutter Motion. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 219–246 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0301-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0301-z