Abstract
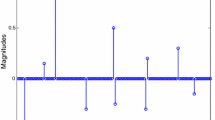
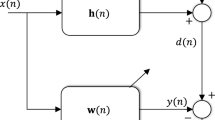
The well-known reweighted zero-attracting least mean square algorithm (RZA-LMS) has been effective for the estimation of sparse system channels. However, the RZA-LMS algorithm utilizes a fixed step size to balance the steady-state mean square error and the convergence speed, resulting in a reduction in its performance. Thus, a trade-off between the convergence rate and the steady-state mean square error must be made. In this paper, utilizing the nonlinear relationship between the step size and the power of the noise-free prior error, a variable step-size strategy based on an error function is proposed. The simulation results indicate that the proposed variable step-size algorithm shows a better performance than the conventional RZA-LMS for both the sparse and the non-sparse systems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Aboulnasr, K. Mayyas, A robust variable step-size LMS-type algorithm: analysis and simulation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45(3), 631–639 (1997)
J. Benesty, S.L. Gay, An improved PNLMS algorithm, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, & Signal Processing (2002), pp. II-1881–II-1884
M.Z.A. Bhotto, A. Antoniou, A family of shrinkage adaptive filtering algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(7), 1689–1697 (2013)
Y. Chen, Y. Gu, A.O. Hero, Sparse LMS for system identification, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech & Signal Processing (2009), pp. 3125–3128
D.L. Duttweiler, Proportionate normalized least-mean-squares adaptation in echo cancellers. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 8(5), 508–518 (2000)
H. Deng, M. Doroslovacki, Improving convergence of the PNLMS algorithm for sparse impulse response identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 12(3), 181–184 (2005)
H. Deng, M. Doroslovacki, Proportionate adaptive algorithms for network echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(5), 1794–1803 (2006)
B. Farhang-Boroujeny, Adaptive Filters: Theory and Applications, 2nd edn. (Wiley, Chichester, 2013)
S.L. Gay, An efficient, fast converging adaptive filter for network echo cancellation, in Conference Record of the Thirty-Second Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers (1998), pp. 394–398
Y. Gao, S. Xie, A variable step-size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm and its analysis. Acta Electron. Sin. 29(8), 1094–1097 (2001)
H.C. Huang, J. Lee, A new variable step-size NLMS algorithm and its performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(4), 2055–2060 (2012)
M.A. Iqbal, S.L. Grant, Novel variable step size nlms algorithms for echo cancellation, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (2008), pp. 241–244
C. Paleologu, J. Benesty, S. Ciochina, Sparse Adaptive Filters for Echo Cancellation (Morgan & Claypool, San Rafael, 2010)
J. Qin, J. Ouyang, A novel variable step-size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm based on sigmoid function. J. Data Acquis. Process. 12(3), 171–174 (1997)
V. Stojanovic, N. Nedic, Robust Kalman filtering for nonlinear multivariable stochastic systems in the presence of non-Gaussian noise. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 26(3), 445–460 (2015)
V. Stojanovic, N. Nedic, Robust identification of OE model with constrained output using optimal input design. J. Frankl. Inst. 353(2), 576–593 (2015)
Z. Yang, Y.R. Zheng, S.L. Grant, Proportionate affine projection sign algorithms for network echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(8), 2273–2284 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Program for ChangJiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT1299), and the special fund of Chongqing Key Laboratory (CSTC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, T., Lin, Y. A Variable Step-Size Strategy Based on Error Function for Sparse System Identification. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 1301–1310 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0344-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0344-1