Abstract
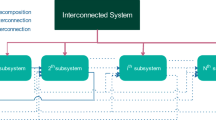
The stability analysis of interconnected large-scale systems is generally characterized by some degree of difficulty, specifically when the interconnections gather a large number of nonlinear subsystems and the couplings evolve according to nonlinear functions in time. In this paper, a novel systematic analysis procedure of fully interconnected discrete-time nonlinear systems with nonlinear interconnections is presented. First, a new arrow form representation of the interconnected system state space model is generated. The obtained generalized thin arrow state matrix is developed by combining the instantaneous subsystems characteristic polynomials, as well as a set of arbitrary and freely parameters. Then, the stability analysis is achieved using the comparison principle and vector norms by translating the stability properties of the lower-dimensional comparison system into those of the considered interconnected system. Aside the proposed systematic formulation and simplicity over existing techniques based mainly on LMIs, it is shown that through an appropriate choice of the model parameters, the developed stability conditions are opportune to locate interesting estimation of the stability domains. Lastly, two numerical examples are included to show the effectiveness of the proposed approach.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Baizid, G. Giglio, F. Pierri, M.A. Trujillo, G. Antonelli, F. Caccavale, A. Viguria, S. Chiaverini, A. Ollero, Behavioral control of unmanned aerial vehicle manipulator systems. Auton Robot (2016). doi:10.1007/s10514-016-9590-0
M. Benrejeb, Stability study of two level hierarchical nonlinear systems. Plenary session at the 12th IFAC Symposium on Large Scale Systems: Theory and Applications, pp. 30-41 (2010)
M. Benrejeb, On the use of arrow form matrices for processes stability and stabilizability studies. Plenary lecture at the IEEE International Conference on Systems and Computer Science ICSCS, pp. 1–8 (2013)
M. Benrejeb, P. Borne, On an algebraic stability criterion for non-linear processes. Interpretation in the frequency domain. in Proceedings of the Measurement and Control International Symposium MECO’78, pp. 678–682 (1978)
M. Benrejeb, P. Borne, F. Laurent, On an application of the arrow form representation in the processes analysis (in frensh). RAIRO Autom. 16(2), 133–146 (1982)
M. Benrejeb, D. Soudani, A. Sakly, P. Borne, New discrete Tanaka Sugeno Kang fuzzy systems characterization and stability domain. Int. J. Comput. Commun. 1(4), 9–19 (2006)
A. Berman, R. Plemmons, Nonnegative Matrices in the Mathematical Sciences (Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, 1994)
P. Borne, M. Dambrine, W. Perruquetti, J. Richard, Vector Lyapunov funtions: Nonlinear, time-varying, ordinary and functional differential equations, in Advances in Stability Theory at the End of the 20th Century (Stability and Control: Theory, Methods and Applications), ed. by A. Martynyuk (Taylor and Francis, London, 2003), pp. 49–73
P. Borne, J. C. Gentina, F. Laurent, Stability study of large scale non linear discrete systems by the use of vectorial norms. Proceedings of the Large Scale Systems Theory and Applications, 187–194 (1976)
P. Borne, J. Richard, N. Radhy, Stability, stabilization, regulation using vector norms, in Nonlinear Systems: Stability and Stabilization, ed. by A. Fossard, D. Normand-Cyrot (Chapman and Hall and Masson, London, 1996), pp. 45–90
D. Chatterjee, D. Liberzon, Stability analysis of deterministic and stochastic switched systems via a comparison principle and multiple Lyapunov functions. SIAM J. Control Optim. 45(1), 174–206 (2006)
X. Chen, S. Stankovic, Decomposition and decentralized control of systems with multi-overlapping structure. Automatica 41(10), 1765–1772 (2005)
N.Y. Chiang, V.M. Zavala, Large-scale optimal control of interconnected natural gas and electrical transmission systems. Appl. Energy 168, 226–235 (2016)
S. Dashkovskiy, B. Rüffer, F. Wirth, Small gain theorems for large scale systems and construction of ISS Lyapunov functions. SIAM J. Control Optim. 48(6), 4089–4118 (2010)
Y. Ebihara, D. Peaucelle, D. Arzelier, Analysis and Synthesis of Interconnected Positive Systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control (2016). doi:10.1109/TAC.2016.2558287
S. Elmadssia, K. Saadaoui, M. Benrejeb, New stability conditions for nonlinear time varying delay systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 47(9), 2009–2021 (2016)
R.L. Filali, M. Benrejeb, P. Borne, On observer-based secure communication design using discrete-time hyperchaotic systems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 19(5), 1424–1432 (2014)
R. Geiselhart, M. Lazar, F. Wirth, A relaxed small-gain theorems for interconnected discrete-time systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 3(60), 812–817 (2015)
R. Geiselhart, F.R. Wirth, Relaxed ISS small-gain gain theorems for discrete-time systems. SIAM J. Control Optim. 54(2), 423–449 (2016)
J. Gentina, P. Borne, C. Burgat, J. Bernussou, L. Grujic, On the stability of large scale systems. Vector norms (in french). RAIRO Autom. 13(1), 57–75 (1979)
V. Ghanbari, P. Wu, P. J. Antsaklis, Large-Scale Dissipative and Passive Control Systems and the Role of Star and Cyclic Symmetries, IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. doi:10.1109/TAC.2016.2528824
W. Haddad, D. Bernstein, Explicit construction of quadratic Lyapunov functions for the small gain, positivity, circle, and Popov theorems and their application to robust stability. part II: Discrete-time theory. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 4(2), 249–265 (1994)
W. Haddad, S. Nersesov, Stability and Control of Large-Scale Dynamical Systems: A Vector Dissipative Systems Approach (Princeton University Press, Princeton, 2011)
T. Ishizaki, K. Kashima, J.I. Imura, K. Aihara, Model reduction and clusterization of large-scale bidirectional networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 59(1), 48–63 (2014)
Z. Jiang, Y. Wang, Input-to-state stability for discrete-time nonlinear systems. Automatica 6(37), 857–869 (2001)
E. Jury, B. Lee, On the stability of a certain class of nonlinear sampled data systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 9(1), 51–61 (1964)
I. Karafyllis, Z. Jiang, A vector small-gain theorem for general non-linear control systems. IMA J. Math. Control Inf. 28(3), 309–344 (2011)
R. Kozlov, O. Kozlova, Investigation of stability of nonlinear continuous-discrete models of economic dynamics using vector Lyapunov function. I. J. Comput. Sys. Sc. Int.+ 48(2), 262–271 (2009)
H. Li, Y. Shi, W. Yan, Distributed receding horizon control of constrained nonlinear vehicle formations with guaranteed \(\gamma \)-gain stability. Automatica 68, 148–154 (2016)
B. Liu, C. Xu, D. Liu, Input-to-state-stability-type comparison principles and input-to-state stability for discrete-time dynamical networks with time delays. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 23(4), 450–472 (2013)
A. Lur’e, V. Postnikov, On the theory of stability of control systems. Appl. Math. Mech. 8(3), 246–248 (1944)
A. Michel, L. Hou, D. Liu, Stability of Dynamical Systems: Continuous, Discontinuous, and Discrete Systems (Birkhäuser Basel, Boston, 2008)
H. Nijmeijer, A. Van Der Schaft, Nonlinear Dynamical Control Systems (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1990)
N. Rouche, P. Habets, M. Laloy, Stability Theory by Liapunov’s Direct Method (Springer, New York, 1977)
B.S. Rueffer, Small-gain conditions and the comparison principle. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 55(7), 1732–1736 (2010)
T. Sarkar, M. Roozbehani, M. A. Dahleh, Robustness scaling in large networks. in Proceedings of The 2016 American Control Conference ACC 2016, pp. 197-202 (2016)
M.E. Sezer, D.D. Siljak, Robust stability of discrete systems. Int. J. Control 48(5), 2055–2063 (1988)
B. Sfaihi, M. Benrejeb, On Order Reduction and Stability Analysis of Singularly Perturbed T-S Fuzzy Models. in Proceedings of The IEEE International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies CoDIT’13, pp. 106-111 (2013)
B. Sfaihi, M. Benrejeb, On stability analysis of nonlinear discrete singularly perturbed T-S fuzzy models. Int. J. Dyn. Control 1(1), 20–31 (2013)
B. Sfaihi, M. Benrejeb, On stability conditions of singularly perturbed nonlinear Lur’e discrete-time systems. Nonlinear Dyn. Syst. Theory 13(2), 203–216 (2013)
J. Shi, J. Zhang, X. Xu, X. Yu, Stability analysis of stochastic interconnected systems by vector Lyapunov function method. Asian J Control 17(5), 1789–1797 (2015)
D. Siljak, Decentralized Control of Complex Systems (Academic Press, Boston, 1991)
E. Sontag, Smooth stabilization implies coprime factorization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 34(4), 435–443 (1989)
D. Swaroop, J.K. Hedrick, String stability of interconnected systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 41(3), 349–357 (1996)
H. Tanner, S. Loizou, K. Kyriakopoulo, Nonholonomic navigation and control of multiple mobile manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 19, 53–64 (2003)
Y. Tsypkin, The absolute stability of large-scale nonlinear sampled-data systems. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR+ 145(10), 52–55 (1962)
M.H. Wu, S. Ogawa, A. Konno, Symmetry position/force hybrid control for cooperative object transportation using multiple humanoid robots. Adv. Robot. 30(2), 131–149 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendices
1.1 Appendix A1
The nonlinear system (1) can be described, in state space, as
with \(x_k^i = {\left[ {x_{1,k}^i, \ldots ,x_{{n_i} - 1,k}^i,x_{{n_i},k}^i} \right] ^T} \in {\mathfrak {R}^{{n_i}}}\) the system \({S_i}\) state vector, \({A_{ii}}\left( . \right) \in {\mathfrak {R}^{{n_i} \times {n_i}}}\) and \({B_{ii}}\left( . \right) \in {\mathfrak {R}^{{n_i}}}\). A change of variables defined by \(z_k^i = {P_i}x_k^i\)
with \(z_k^i \in {\mathfrak {R}^{{n_i}}}\), \({P_i} \in {\mathfrak {R}^{{n_i} \times {n_i}}}\) an invertible transformation and \({\alpha _{i,j}}\) , \(j = 1,2, \cdots ,{n_i} - 1\) distinct constant arbitrary parameters, leads to the system dynamics
with for \(\forall j=1,2,\ldots ,{{n}_{i}}-1\),
Polynomials \({{P}_{{{A}_{ii}}}}(\,.\,,{{\lambda }_{{}}})\) and \({{R}_{ii}}(\,.\,,{{\lambda }_{{}}})\) are defined by
and
where \({P_{{A_{ii}}}}(\,.\,,{\lambda _{}})\) denotes the instantaneous characteristic polynomial of the system \({S_i}\) described by (1), (48) or (51).
1.2 Appendix A2
Consider the discrete nonlinear Lur’e system described by means of the following block-oriented model of Fig. 8 where \(f\left( . \right) :\mathfrak {R}\rightarrow \mathfrak {R}\) represents a nonlinear function, \({{B}_{0}}\left( s \right) ={{s}^{-1}}\left( 1-{{e}^{-Ts}} \right) \) a zero-order holder and \({{T}_{{}}}=0.2s\) the sampling time. \(D\left( s\right) =s\left( 1+{{\tau }_{1}}s \right) \left( 1+{{\tau }_{2}}s \right) \) and \(N\left( s\right) ={{\lambda }_{2}}{{s}^{2}}+{{\lambda }_{1}}s+{{\lambda }_{0}}\) are polynomials with constant parameters \({{\tau }_{1}}=0.1s\), \({{\tau }_{2}}=0.005s\), \({{\lambda }_{0}}=0.98\), \({{\lambda }_{1}}=0.098\) and \({{\lambda }_{2}}=4.7\,\,{{10}^{-4}}\).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sfaihi, B., Fekih, S. & Benrejeb, M. New Approach for Stability Analysis of Interconnected Nonlinear Discrete-Time Systems Based on Vector Norms. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 3983–4005 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0511-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0511-z