Abstract
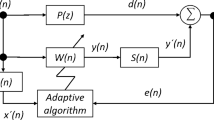
A conventional single-channel feedforward active noise control (ANC) system encounters noise from multiple sources. In many cases, there is a reference signal that is independently available which is correlated with the ambient noise. However, in some situations, a portion of the noise generated is uncorrelated with the reference signal. In this paper, a new hybrid ANC (HANC) system is proposed using a convex combination of time and frequency domain Filtered-X LMS (FXLMS) algorithms. The feedforward part uses a time domain FXLMS (TDFXLMS) algorithm to control disturbances that are correlated with the reference noise and the feedback part uses a multiresolution analysis-based frequency domain wavelet packet FXLMS (WPFXLMS) algorithm to control the uncorrelated disturbances encountered during the operation of an ANC system. An extra adaptive filter is used to smoothen the error signal in the HANC system. An effort is made to exploit the benefits of the structural design and time–frequency domain signal processing techniques for active control of disturbances that are both correlated and uncorrelated with the reference noise. As a result of the convex combination of the TDFXLMS and WPFXLMS algorithms in a HANC system, the proposed method is successful in canceling the disturbances encountered by the ANC system from multiple noise sources.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.T. Akhtar, W. Mitsuhashi, Improving performance of hybrid active noise control systems for uncorrelated narrowband disturbances. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(7), 2058–2066 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2011.2112349
M. Bouchard, S. Quednau, Multichannel recursive-least-square algorithms and fast-transversal-filter algorithms for active noise control and sound reproduction systems. IEEE Speech Audio Process. 8(5), 606–618 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/89.861382
S. Elliott, Signal Processing for Active Control (Academic Press, London, 2001)
E. Hansler, G. Schmidt, Acoustic Echo and Noise Control: A Practical Approach (Wiley, Hoboken, 2005)
S.S. Haykin, Adaptive Filter Theory (Pearson Education, Kannur, 2008)
C.E. Heil, D.F. Walnut, Continuous and discrete wavelet transforms. SIAM Rev. 31(4), 628–666 (1989)
S. Hosur, A.H. Tewfik, Wavelet transform domain adaptive FIR filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45(3), 617–630 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1109/78.558477
T. Kosaka, S.J. Elliott, C.C. Boucher, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP-97 A novel frequency domain filtered-x LMS algorithm for active noise reduction, vol. 1 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.1997.599658
S.M. Kuo, D. Morgan, Active noise control systems: algorithms and DSP implementations (Wiley, New York, 1995)
S.M. Kuo, D.R. Morgan, Active noise control: a tutorial review. Proc. IEEE 87(6), 943–973 (1999)
S.M. Kuo, R.K. Yenduri, A. Gupta, Frequency-domain delayless active sound quality control algorithm. J. Sound Vib. 318(4), 715–724 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2008.04.029
B. Liang, S. Iwnicki, A. Ball, A.E. Young, Adaptive noise cancelling and time–frequency techniques for rail surface defect detection. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 54, 41–51 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2014.06.012
P. Lueg, Process of silencing sound oscillations, U.S. Patent No. 2,043,416, 9 Jun 1936
L. Luo, J. Sun, B. Huang, A novel feedback active noise control for broadband chaotic noise and random noise. Appl. Acoust. 116, 229–237 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.09.029
S. Mallat, A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing (Academic Press, London, 1999)
L. Mokhtarpour, H. Hassanpour, A self-tuning hybrid active noise control system. J. Frankl. Inst. 349(5), 1904–1914 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2012.02.016
T. Padhi, M. Chandra, A. Kar, Performance evaluation of hybrid active noise control system with online secondary path modeling. Appl. Acoust. 133, 215–226 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2017.12.029
T. Padhi, M. Chandra, A. Kar, M.N.S. Swamy, Design and analysis of an improved hybrid active noise control system. Appl. Acoust. 127, 260–269 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2017.06.014
Z. Qiu, C.M. Lee, Z.H. Xu, L.N. Sui, A multi-resolution filtered-x LMS algorithm based on discrete wavelet transform for active noise control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 66, 458–469 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.05.024
D.C. Swanson, S.M. Hirsch, K.M. Reichard, J. Tichy, Development of a frequency-domain filtered-x intensity ANC algorithm. Appl. Acoust. 57(1), 39–49 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-682X(98)00046-2
X.L. Tang, C.M. Lee, Time–frequency-domain filtered-x LMS algorithm for active noise control. J. Sound Vib. 331(23), 5002–5011 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2012.07.009
L. Wu, X. Qiu, I.S. Burnett, Y. Guo, Decoupling feedforward and feedback structures in hybrid active noise control systems for uncorrelated narrowband disturbances. J. Sound Vib. 350, 1–10 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2015.04.018
M. Wu, X. Qiu, G. Chen, An overlap-save frequency-domain implementation of the delayless subband ANC algorithm. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 16(8), 1706–1710 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2008.2005030
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padhi, T., Chandra, M., Kar, A. et al. A New Hybrid Active Noise Control System with Convex Combination of Time and Frequency Domain Filtered-X LMS Algorithms. Circuits Syst Signal Process 37, 3275–3294 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0784-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0784-x