Abstract
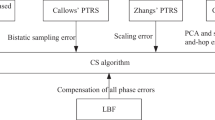
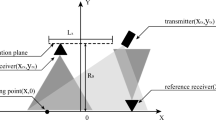
Using Legendre polynomials and the derivation method of the implicit function, this paper proposes a range-Doppler algorithm for multireceiver synthetic aperture sonar. Based on Legendre polynomials, the two-way slant range is first expanded into a power series with respect to the slow time. Then, the derivation method of the implicit function is exploited to deduce the point of stationary phase and point target reference spectrum (PTRS). Based on this PTRS, the paper presents an imaging algorithm, which uses the range-dependent sub-block processing method to cancel the space-variant coupling between the range and azimuth dimensions. Simulation results and real data processing are presented to validate the proposed method.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Abramowitz, I.A. Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables (National Bureau of Standards, New York, 1972)
J. Akhtar, Removal of range ambiguities with orthogonal block coding techniques. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 29(2), 311–330 (2010)
M.R. Azimi-Sadjadi, M. Klausner, J. Kopacz, Detection of underwater targets using a subspace-based method with learning. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 42(4), 869–879 (2017)
A.B. Bellettini, M.A. Pinto, Theoretical accuracy of synthetic aperture sonar micronavigation using a displaced phase-center antenna. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 27(4), 780–789 (2002)
D. Bi, Y. Xie, Y.R. Zheng, Synthetic aperture radar imaging using basis selection compressed sensing. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 34(8), 2561–2576 (2015)
W.W. Bonifant, M.A. Richards, J.H. McClellan, Interferometric height estimation of the seafloor via synthetic aperture sonar in the presence of motion errors. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 147(6), 322–330 (2000)
S. Chen, H. Wang, F. Xu, Y. Jin, Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 54(8), 4806–4817 (2016)
I.G. Cumming, F.H. Wong, Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar: Algorithms and Implementation (Artech House, Norwood, 2005)
A. Gaibel, A. Boag, Back-projection SAR imaging using FFT, in European Radar Conference (London, UK, 2016), pp. 69–72
P.T. Gough, M.P. Hayes, D.R. Wilkinson, An efficient image reconstruction algorithm for a multiple hydrophone array synthetic aperture sonar, in European Conference on Underwater Acoustics (Lyon, France, 2000), pp. 395–400
P.E. Hagen, R.E. Hansen, Area coverage rate of synthetic aperture sonars, in MTS/IEEE Oceans Conference (Aberdeen, UK, 2007), pp. 1–5
A.J. Hunter, S. Dugelay, W.L.J. Fox, Repeat-pass synthetic aperture sonar micronavigation using redundant phase center arrays. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 41(4), 820–830 (2016)
P. Imperatore, A. Pepe, R. Lanari, Spaceborne synthetic aperture radar data focusing on multicore-based architectures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 54(8), 4712–4731 (2016)
X. K. Jiang, C. Sun, J. Feng, A novel image reconstruction algorithm for synthetic aperture sonar with single transmitter and multiple receiver configuration, in MTS/IEEE Oceans Conference (Kobe, Japan, 2004), pp. 1940–1944
K.A. Johnson, M.P. Hayes, P.T. Gough, A method for estimating the sub-wavelength sway of a sonar towfish. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 20(4), 258–267 (1995)
G. Krieger, N. Gebert, A. Moreira, Unambiguous SAR signal reconstruction from nonuniform displaced phase center sampling. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 1(4), 260–264 (2004)
J. Mckay, V. Monga, R.G. Raj, Robust sonar ATR through Bayesian pose-corrected sparse classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 55(10), 5563–5576 (2017)
T.G. Michael, B. Marchand, J.D. Tucker, T.M. Marston, D.D. Sternlicht, M.R. Azimi-Sadjadi, Williams, Image-based automated change detection for synthetic aperture sonar by multistage coregistration and canonical correlation analysis. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 41(3), 592–612 (2016)
Y.L. Neo, F. Wong, I.G. Cumming, Processing of azimuth-invariant bistatic SAR data using the range Doppler algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 46(1), 14–21 (2008)
Y. Pailhas, Y. Petillot, K. Brown, B. Mulgrew, Spatially distributed MIMO sonar systems: principles and capabilities. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 42(3), 738–751 (2017)
A. Papoulis, Generalized sampling expansion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. CAS-24(11), 652–654 (1977)
K.D. Rolt, H. Schmidt, Azimuthal ambiguities in synthetic aperture sonar and synthetic aperture radar imagery. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 17(1), 73–79 (1992)
S.A.V. Synnes, A.J. Hunter, R.E. Hansen, T.O. Sæbø, H.J. Callow, R.V. Vossen, A. Austeng, Wideband synthetic aperture sonar backprojection with maximization of wave number domain support. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 42(4), 880–891 (2017)
F. Wang, X. Li, A new method of deriving spectrum for bistatic SAR processing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 7(3), 483–486 (2010)
V.T. Wang, M.P. Hayes, Synthetic aperture sonar track registration using SIFT image correspondences. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 42(4), 901–903 (2017)
W. Wang, R. Wang, Y. Deng, W. Xu, L. Hou, Improved digital beam-forming approach with scaling function for range multi-channel synthetic aperture radar system. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 10(2), 379–385 (2016)
T. Xiong, M.D. Xing, Y. Wang, R. Guo, J.L. Sheng, Z. Bao, Using derivatives of an implicit function to obtain the stationary phase of the two- dimensional spectrum for bistatic SAR imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 8(6), 1165–1169 (2011)
H. Yang, J. Tang, Q. Li, X. Liu, Processing of non-uniform azimuth sampling in multiple-receiver synthetic aperture sonar image, in MTS/IEEE Oceans Conference (Aberdeen, UK, 2007), pp. 1–4
H. Zhang, Y. Deng, R. Wang, N. Li, S. Zhao, F. Hong, L. Wu, O. Loffeld, Spaceborne/stationary bistatic SAR imaging with TerraSAR-X as an illuminator in staring-spotlight mode. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 54(9), 5203–5216 (2016)
X. Zhang, X. Chen, W. Qu, Influence of the stop-and-hop assumption on synthetic aperture sonar imagery, in IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology (Chengdu, China, 2017), pp. 1601–1607
X. Zhang, J. Tang, F. Wang, S. Bai, D. Liu, Accurate back projection imaging algorithm for multireceiver SAS in engineering application. J. Nav. Univ. Eng. 26(2), 20–24 (2014)
X. Zhang, J. Tang, H. Zhong, Multireceiver correction for the chirp scaling algorithm in synthetic aperture sonar. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 39(3), 472–481 (2014)
H. Zhu, C. Li, L. Zhang, J. Shen, River channel extraction from SAR images by combing gray and morphological features. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 34(7), 2271–2286 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61601473) and the National Key Laboratory Foundation of China (9140C290401150C29132). The authors thank LetPub (www.LetPub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Yang, P. & Dai, X. Focusing Multireceiver SAS Data Based on the Fourth-Order Legendre Expansion. Circuits Syst Signal Process 38, 2607–2629 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0982-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0982-6