Abstract
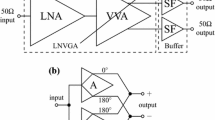
This paper presents a low-power compact variable-gain low-noise amplifier that operates over the frequency band of 17–24 GHz. A design methodology is proposed to determine the optimal size of transistors to achieve the maximum possible gain for current-steering variable-gain amplifiers (VGAs). Moreover, the effect of gain switching on the input and output return losses of current-steering VGAs is analytically studied. Also, various structures of metal-oxide-metal capacitors are examined to find the optimal structure for high-frequency applications. A proof-of-concept VGA is fabricated in a 65-nm bulk CMOS process, and it is employed in a receiver chain. The designed VGA features about 13.3 dB maximum power gain with 5-bit resolution and an average noise figure of 3 dB. The achieved root-mean-square gain error is about 0.45 dB after the fabrication process. The output 1-dB compression point of the VGA is about − 1 dBm at the center of the frequency band. The VGA consumes about 4.2 mW from a 1-V supply, and excluding the pads, it occupies a silicon area of 0.23 mm2.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Aparicio, A. Hajimiri, Capacity limits and matching properties of integrated capacitors. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 37(3), 384–393 (2002)
F.D. Baumgratz, H. Li, F. Tavernier, S. Bampi, C.E. Saavedra, A 0.4–3.3 GHz low-noise variable gain amplifier with 35 dB tuning range, 4.9 dB NF, and 40 dBm IIP2. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 94(1), 9–17 (2018)
N.-C. Chen, P.-Y. Chou, H. Graeb, M.P.-H. Lin, High-density MOM capacitor array with novel mortise-tenon structure for low-power SAR ADC, in IEEE Design Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Lausanne (2017), pp. 1757–1762
M.L. Edwards, J.H. Sinsky, A new criterion for linear 2-port stability using a single geometrically derived parameter. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 40(12), 2303–2311 (1992)
M. Elkholy, S. Shakib, J. Dunworth, V. Aparin, K. Entesari, A wideband variable gain LNA with high OIP3 for 5G using 40-nm bulk CMOS. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 28(1), 64–66 (2018)
C.-Y. Hsieh, J.-C. Kao, J.-J. Kuo, K.-Y. Lin, A 57–64 GHz low-phase-variation variable-gain amplifier, in IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Montreal (2012), pp. 1–3
S. Lee, J. Park, S. Hong, A Ka-band phase-compensated variable-gain CMOS low-noise amplifier. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 29(2), 131–133 (2019)
J. Li, Y.-Z. Xiong, Y. Li, W. Wu, Analysis and optimization of cascode structure in power amplifier for X-band phase array radar application. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 34(1), 1–20 (2015)
W.-T. Li, Y.-C. Chiang, J.-H. Tsai, H.-Y. Yang, J.-H. Cheng, T.-W. Huang, 60-GHz 5-bit phase shifter with integrated VGA phase-error compensation. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 61(3), 1224–1235 (2013)
Z. Li, X. Liu, Y. Zhuang, A 12–27 GHz SiGe BiCMOS VGA with phase shift variation compensation. Microelectron. J. 70(12), 97–106 (2017)
A. Niknejad, H. Hashemi, mm-Wave Silicon Technology: 60 GHz and Beyond (Springer, New York, 2008)
B. Razavi, RF Microelectronics, 2nd edn. (Prentice Hall, NJ, 2011), pp. 305–312
J. Shi, A. Sidelnicov, K.W.J. Chew, M.S. Chin, C. Schippel, J.M.M. dos Santos, F. Schlaphof, L. Meinshausen, J.R. Long, D.L. Harame, Evolution and optimization of BEOL MOM capacitors across advanced CMOS nodes, in IEEE European Solid-State Device Research Conference (ESSDERC), (2018), pp. 190–193
D.-S. Siao, J.-C. Kao, H. Wang, A 60 GHz low phase variation variable gain amplifier in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 24(7), 457–459 (2014)
J.-H. Tsai, J.-W. Wang, C.-H. Wu, A V-band variable gain amplifier with low phase variation using 90-nm CMOS technology. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 56(8), 1946–1949 (2014)
Y. Wang, C.-N Chen, Y.-C. Wu, H. Wang, An E-band variable gain low noise amplifier in 90-nm CMOS process using body-floating and noise reduction techniques, in 13th European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference (EuMIC), (2018), pp. 277–280
M. Yaghoobi, M. Yavari, M. Haghi Kashani, H. Ghafoorifard, S. Mirabbasi, A 55-to-64 GHz low-power small-area LNA in 65-nm CMOS with 3.8 dB average NF and ~ 12.8 dB power gain. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 29(2), 128–130 (2019)
H.-C. Yeh, S. Aloui, C.-C. Chiong, H. Wang, A wide gain control range V-band CMOS variable-gain amplifier with built-in linearizer. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 61(2), 902–913 (2013)
Y. Yi, D. Zhao, X. You, A Ka-band CMOS digital-controlled phase-invariant variable gain amplifier with 4-bit tuning range and 0.5-dB resolution, in IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), (2018), pp. 152–155
C.-H. Yu, P.-H. Lo, J.-Y. Lyu, H.-C. Kuo, H.-R. Chuang, Integrated 60-GHz CMOS variable-gain low-noise amplifier and full 360° phase shifter for phased-array RF receiving system, in IEEE 14th Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic Integrated Circuits in RF Systems, Newport Beach (2014), pp. 59–61
Acknowledgements
This work has been financially supported in part by Iran National Science Foundation (INSF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yaghoobi, M., Yavari, M. & Ghafoorifard, H. A 17-to-24 GHz Low-Power Variable-Gain Low-Noise Amplifier in 65-nm CMOS for Phased-Array Receivers. Circuits Syst Signal Process 38, 5448–5466 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01169-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01169-z