Abstract
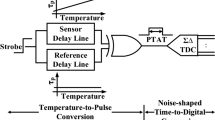
This article reports a time-domain smart temperature sensor using current starved inverters (CSIs) and switched ring oscillator-based time-to-digital converter (SRO-TDC) in a standard \({180} \hbox { nm}\) CMOS process. A novel temperature-to-time converter (TTC) is proposed using complementary delay lines, which are designed by utilising CSIs. The proportional to absolute temperature delay line offers a temperature coefficient (TC) of 615 ppm/\(^{\circ }\hbox {C}\), whereas the complementary to absolute temperature delay line possesses a TC of 300 ppm/\(^{\circ }\hbox {C}\), over 0–100 \(^{\circ }\hbox {C}\) temperature range. A novel multipath delay cell-based coupled oscillator is proposed for SRO-TDC. The proposed SRO-TDC operates as readout circuit for the sensor, which achieves 30 ns range at 12 ps resolution. The uncertainty of the sensor is limited to \(\pm \,0.63\,^{\circ }\hbox {C}\), after the 2-point calibration at \(20\,^{\circ }\hbox {C}\) and \(80\,^{\circ }\hbox {C}\), which is because of complementary delay lines in TTC and noise shaping behaviour of the SRO-TDC. The sensor achieves \(0.4\,\upmu \hbox {s}\) conversion time at \(0.04\,^{\circ }\hbox {C}\) resolution.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.E. Allen, D. Holberg, CMOS Analog Circuit Design (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2012)
R. Baird, T. Fiez, Linearity enhancement of multibit $\Delta \Sigma $ A/D and D/A converters using data weighted averaging. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digit. Signal Process. 42(12), 753–762 (1995)
R.J. Baker, CMOS: Circuit Design, Layout, and Simulation (Wiley, Hoboken, 2010)
C.C. Chen, C.L. Chen, Y. Lin, S.Q. You, An all-digital time-domain smart temperature sensor with a cost-efficient curvature correction. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 27(1), 29–36 (2019)
P. Chen, C.-C. Chen, C.-C. Tsai, L. Wen-Fu, A time-to-digital-converter-based CMOS smart temperature sensor. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 40(8), 1642–1648 (2005)
R. Dastanian, E. Abiri, M. Ataiyan, A 0.5 V, 112 nW CMOS temperature sensor for RFID food monitoring application. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 41(2), 145–152 (2017)
A. Elshazly, S. Rao, B. Young, P.K. Hanumolu, A noise-shaping time-to-digital converter using switched-ring oscillators-analysis, design, and measurement techniques. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 49(5), 1184–1197 (2014)
D. Ha, K. Woo, S. Meninger, T. Xanthopoulos, E. Crain, D. Ham, Time-domain CMOS temperature sensors with dual delay-locked loops for microprocessor thermal monitoring. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 20(9), 1590–1601 (2012)
M. Heidarpour Roshan, S. Zaliasl, K. Joo, K. Souri, R. Palwai, L.W. Chen, A. Singh, S. Pamarti, N.J. Miller, J.C. Doll, C. Arft, S. Tabatabaei, C. Sechen, A. Partridge, V. Menon, A MEMS-assisted temperature sensor with 20-$\mu K$ resolution, conversion rate of 200 S/s, and FOM of 0.04 pJK$^{2}$. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 52(1), 185–197 (2017)
Q. Huang, H. Joo, J. Kim, C. Zhan, J. Burm, An energy-efficient frequency-domain CMOS temperature sensor with switched vernier time-to-digital conversion. IEEE Sens. J. 17(10), 3001–3011 (2017)
S. Hwang, J. Koo, K. Kim, H. Lee, C. Kim, A 0.008 ${\text{ mm }}^{2}$ 500 $\mu {\rm W}$ 469 kS/s frequency-to-digital converter based CMOS temperature sensor with process variation compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 60(9), 2241–2248 (2013)
K. Kim, H. Lee, S. Jung, C. Kim, A 366 kS/s 400 $\mu $W 0.0013 mm$^2$ frequency-to-digital converter based CMOS temperature sensor utilizing multiphase clock, in 2009 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (IEEE, 2009), pp. 203–206
H. Lakdawala, Y.W. Li, A. Raychowdhury, G. Taylor, K. Soumyanath, A 1.05 V 1.6 mW, 0.45 $^{\circ }$C 3$\sigma $ resolution $\Sigma \Delta $ based temperature sensor with parasitic resistance compensation in 32 nm digital CMOS process. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 44(12), 3621–3630 (2009)
M. Lee, A.A. Abidi, A 9 b, 1.25 ps resolution coarse-fine time-to-digital converter in 90 nm CMOS that amplifies a time residue. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 43(4), 769–777 (2008)
J. Maneatis, M. Horowitz, Precise delay generation using coupled oscillators. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 28(12), 1273–1282 (1993)
J. Marin, E. Sacco, J. Vergauwen, G. Gielen, A single-temperature-calibration 0.18-$\mu $m CMOS time-based resistive sensor interface with low drift over a -40 $^{\circ }$C to 175 $^{\circ }$C temperature range, in ESSCIRC 2018—IEEE 44th European Solid State Circuits Conference (ESSCIRC) (IEEE, 2018), pp. 330–333
S. Pan, K.A.A. Makinwa, A 0.25 mm$^2$-resistor-based temperature sensor with an inaccuracy of 0.12 $^{\circ }$C (3$\sigma $) from $-55~^{\circ }$C to 125 $^{\circ }$C. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 53(12), 3347–3355 (2018)
S. Pan, K.A.A. Makinwa, Energy-efficient high-resolution resistor-based temperature sensors, in Hybrid ADCs, Smart Sensors for the IoT, and Sub-1V & Advanced Node Analog Circuit Design: Advances in Analog Circuit Design 2017, ed. by P. Harpe, K.A.A. Makinwa, A. Baschirotto (Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2018), pp. 183–200
J.H. Park, D.H. Jung, S.O. Jung, GRO-TDC with gate-switch-based delay cell halving resolution limit. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 45(12), 2211–2225 (2017)
S. Pavan, R. Schreier, G.C. Temes, Understanding Delta-Sigma Data Converters (Wiley, New York, 2017)
T. Someya, A.K.M.M. Islam, T. Sakurai, M. Takamiya, An 11-nW CMOS temperature-to-digital converter utilizing sub-threshold current at sub-thermal drain voltage. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 54(3), 613–622 (2019)
W. Song, J. Lee, N. Cho, J. Burm, An ultralow power time-domain temperature sensor with time-domain delta-sigma TDC. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 64(10), 1117–1121 (2017)
U. Sonmez, F. Sebastiano, K.A.A. Makinwa, Compact thermal-diffusivity-based temperature sensors in 40-nm CMOS for SoC thermal monitoring. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 52(3), 834–843 (2017)
K. Souri, Y. Chae, K.A.A. Makinwa, A CMOS temperature sensor with a voltage-calibrated inaccuracy of $\pm $0.15$^{\circ }$C (3$\sigma $) from $-55^{\circ }$C to 125$^{\circ }$C. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 48(1), 292–301 (2013)
K. Souri, K.A.A. Makinwa, A 0.12 mm$^{2}$ 7.4 $\mu $W micropower temperature sensor with an inaccuracy of $\pm $0.2$^{\circ }$C (3$\sigma $) from $-30^{\circ }$C to 125$^{\circ }$C. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 46(7), 1693–1700 (2011)
Z. Tang, Y. Fang, X.P. Yu, Z. Shi, N. Tan, A CMOS temperature sensor with versatile readout scheme and high accuracy for multi-sensor systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 65(11), 3821–3829 (2018)
Y. Tsividis, C. McAndrew, Operation and Modeling of the MOS Transistor (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2011)
H. Xin, M. Andraud, P. Baltus, E. Cantatore, P. Harpe, A 174 pW–488.3 nW 1 S/s–100 kS/s all-dynamic resistive temperature sensor with speed/resolution/resistance adaptability. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Lett. 1(3), 70–73 (2018)
F. Yuan, CMOS Time-Mode Circuits and Systems (CRC Press, Cambridge, 2015)
D. Zhu, L. Siek, A 0.058 mm$^{2}$ 24 $\mu $W temperature sensor in 40-nm CMOS process with $\pm $0.5 $^{\circ }$C inaccuracy from $-55~^{\circ }$C to 175 $^{\circ }$C. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37(6), 2278–2298 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by Visvesvaraya PhD Scheme for Electronics & IT, MeitY, Govt. of India, Grant No. PhDMLA/4(29)/2015-16/01 and Special Manpower Development Programme for Chips-to-System Design, MeitY, Govt. of India, Grant No. 9(1)/2014-MDD (Vol III). Semi-Conductor Laboratory, Department of Space, Government of India, is acknowledged for valuable support. Amrita Dikshit is also acknowledged for her contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishna, R.S.S.M.R., Mal, A.K. & Mahapatra, R. Time-Domain Smart Temperature Sensor Using Current Starved Inverters and Switched Ring Oscillator-Based Time-to-Digital Converter. Circuits Syst Signal Process 39, 1751–1769 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01233-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01233-8