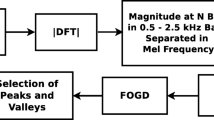
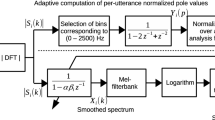
Abstract
Spotting of keywords in continuous speech signal with the aid of the computer is called a keyword spotting (KWS) system. A variety of strategies have been suggested in the literature to detect keywords from the adult’s speech effectively. However, only a limited number of studies have been reported for KWS in children’s speech. Due to the difference in physiological properties, the pitch and speaking rate of children’s differ from the adult’s. Consequently, KWS system model parameters trained on the speech data from adult’s signal yield poor performance for children speech. In this paper, we have developed a KWS system for spotting keywords from children’s speech using models trained on adults’ speech. The proposed approach uses spectral moment time–frequency distribution augmented by low-order cepstral (SMAC) as the front-end feature. The mismatches due to differences in pitch and speaking rate of children and adult speakers are further mitigated by data-augmented training using explicit pitch and speaking rate modifications. The experimental findings presented in this paper show that the SMAC feature offers significantly better output for both clean and noisy test conditions than the conventional Mel frequency cepstral coefficients.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The speech data that support the findings of this study are available online at WSJCAM0 Cambridge Read News and the PF-STAR British English Children’s Speech Corpus.
References
A. Batliner, M. Blomberg, S. D’Arcy, D. Elenius, D. Giuliani, M. Gerosa, C. Hacker, M. Russell, S. Steidl, M. Wong, The PF_STAR children’s speech corpus, in INTERSPEECH, pp. 2761–2764 (2005)
A. Becerra, J.I. de la Rosa, E. González, Speech recognition in a dialog system: from conventional to deep processing. Multimed. Tools Appl. 77(12), 15875–15911 (2018)
H. Benisty, I. Katz, K. Crammer, D. Malah, Discriminative keyword spotting for limited-data applications. Speech Commun. 99, 1–11 (2018)
D. Can, M. Saraclar, Lattice indexing for spoken term detection. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(8), 2338–2347 (2011)
G. Chen, C. Parada, G. Heigold, Small-footprint keyword spotting using deep neural networks, in Proceedings IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 4087–4091 (2014)
I.F. Chen, C. Ni, B.P. Lim, N.F. Chen, C.H. Lee, A keyword-aware language modelling approach to spoken keyword search. J. Signal Process. Syst. 82(2), 197–206 (2016)
W.M. Fisher, Ther DARPA speech recognition research database: specifications and status, in Proceedings DARPA Workshop on Speech Recognition, Feb. 1986, pp. 93–99 (1986)
M. Gerosa, D. Giuliani, S. Narayanan, A. Potamianos, A review of ASR technologies for children’s speech, in Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Child, Computer and Interaction, pp. 7:1–7:8 (2009)
D.R.H. Miller, M. Kleber, C.L. Kao, O. Kimball, T. Colthurst, S.A. Lowe, R.M. Schwartz, H. Gish, Rapid and accurate spoken term detection, in Proceedings INTERSPEECH (2007)
K.S.R. Murthy, B. Yegnanarayana, Epoch extraction from speech signals. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 16, 1602–1613 (2008)
B. Pattanayak, J.K. Rout, G. Pradhan, Adaptive spectral smoothening for development of robust keyword spotting system. IET Signal Proc. 13(5), 544–550 (2019)
D. Povey, A. Ghoshal, G. Boulianne, L. Burget, O. Glembek, N. Goel, M. Hannemann, P. Motlicek, Y. Qian, P. Schwarz et al., The Kaldi speech recognition toolkit, in Proceedings Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding (2011)
K.S. Rao, B. Yegnanarayana, Prosody modification using instants of significant excitation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 14(3), 972–980 (2006)
S.P. Rath, D. Povey, K. Veselỳ, J. Cernockỳ, Improved feature processing for deep neural networks, in Proceedings INTERSPEECH, pp. 109–113 (2013)
T. Robinson, J. Fransen, D. Pye, J. Foote, S. Renals, WSJCAMO: a British English speech corpus for large vocabulary continuous speech recognition, in 1995 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. vol. 1, pp. 81–84. IEEE (1995)
M. Russell, S. D’Arcy, Challenges for computer recognition of children’s speech, in Speech and Language Technology in Education (SLaTE2007), pp. 108–111 (2007)
M. Shah, S. Arunachalam, J. Wang, D. Blaauw, D. Sylvester, H.S. Kim, J.S. Seo, C. Chakrabarti, A fixed-point neural network architecture for speech applications on resource-constrained hardware. J. Signal Process. Syst. 90(5), 727–741 (2018)
S. Shahnawazuddin, A. Dey, R. Sinha, Pitch-adaptive front-end features for robust children’s ASR, in Proceedings INTERSPEECH, pp. 3459–3463 (2016)
S. Shahnawazuddin, N. Adiga, H.K. Kathania, Effect of prosody modification on children’s ASR. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 24(11), 1749–1753 (2017)
S. Shahnawazuddin, R. Sinha, G. Pradhan, Pitch-normalized acoustic features for robust children’s speech recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 24(8), 1128–1132 (2017)
S. Shahnawazuddin, K. Maity, G. Pradhan, Improving the performance of keyword spotting system for children’s speech through prosody modification. Digit. Signal Proc. 86, 11–18 (2019)
H. Sundar, J.F. Lehman, R. Singh, Keyword spotting in multi-player voice-driven games for children, in Proceedings Sixteenth Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, pp. 1660–1664 (2015)
P. Tsiakoulis, A. Potamianos, D. Dimitriadis, Spectral moment features augmented by low order cepstral coefficients for robust ASR. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(6), 551–554 (2010)
A. Varga, H.J. Steeneken, Assessment for automatic speech recognition: II. Noisex-92: a database and an experiment to study the effect of additive noise on speech recognition systems. Speech Commun. 12(3), 247–251 (1993)
S. Wegmann, A. Faria, A. Janin, K. Riedhammer, N. Morgan, The TAO of ATWV: probing the mysteries of keyword search performance, in 2013 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, pp. 192–197. IEEE (2013)
M. Wöllmer, B. Schuller, A. Batliner, S. Steidl, D. Seppi, Tandem decoding of children’s speech for keyword detection in a child-robot interaction scenario. ACM Trans. Speech Lang. Process. (TSLP) 7(4), 1–22 (2011)
Y.D. Wu, B.L. Liu, Keyword spotting method based on speech feature space trace matching, in Proceedings of the 2003 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics. vol. 5, pp. 3188–3192. IEEE (2003)
I.C. Yadav, S. Shahnawazuddin, G. Pradhan, Addressing noise and pitch sensitivity of speech recognition system through variational mode decomposition based spectral smoothing. Digit. Signal Proc. 86, 55–64 (2019)
N. Zhao, H. Yang, Realizing speech to gesture conversion by keyword spotting. In: Proceedings Chinese Spoken Language Processing (ISCSLP), pp. 1–5 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maity, K., Pradhan, G. & Singh, J.P. A Pitch and Noise Robust Keyword Spotting System Using SMAC Features with Prosody Modification. Circuits Syst Signal Process 40, 1892–1904 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01565-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01565-w